From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 |
This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. The description on its description page there is shown below.Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help.
|
This version shows a slight Spring or Autumn axial tilt to the Earth.
Caption
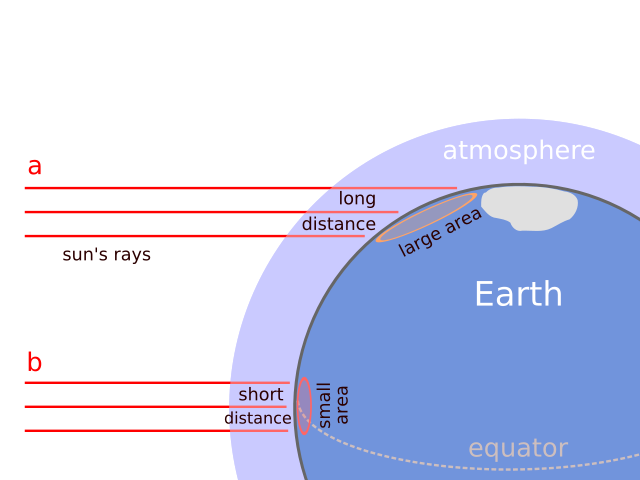
Why the polar regions are colder: Effect of the Earth's shape and atmosphere on incoming solar radiation.
Compared to equatorial regions (b), incoming solar radiation of the polar regions (a) is less intense for two reasons:
- the solar radiation arrives at an oblique angle nearer the poles, so that the energy spreads over a larger surface area, lessening its intensity.
- The radiation travels a longer distance through the atmosphere, which absorbs, scatters and reflects the solar radiation.
Tropical areas (i.e. lower latitudes, nearer the equator) receive solar which is closer to vertical.
The angle of incidence of the rays, combined with the albedo of the surface has also a strong influence on the amount of energy being absorbed (or reflected) at the surface. In the ice-covered polar zones, almost all direct energy from the sun is reflected because it is white and the angle is small. In short, the angle of incidence affects the heating of the surface in 3 different ways: length of atmospheric track, variable flux and variable reflection
For simplicity, the diagram ignores the axial tilt of the Earth, which causes each pole to slip into darkness for around 6 months of the year, and means the equator's ground is generally not perpendicular with the sun's light.
About
- Created in Inkscape (v0.45)
Based on diagrams in:
- Ecology: Theories and Applications, 4th Edition, Peter Stiling. Figure 14.2. page 231.
- Biology, third edition. Arms & Camp. Figure 49-1. page 973.
- ...and from feedback at en:Wikipedia:Picture_peer_review/Oblique_rays
Other versions
|
|
|
Northern Winter axial tilt
|
Slight Spring or Autumn tilt (my preferred version)
|
See also
Licensing
Photo credit: Peter Halasz. ( User:Pengo)
I, the copyright holder of this work, hereby publish it under the following licenses:

  |
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution ShareAlike 2.5 License. In short: you are free to share and make derivative works of the file under the conditions that you appropriately attribute it, and that you distribute it only under a license identical to this one. Official license |
You may select the license of your choice.
|
For the Creative Commons license, please give attribution to:
- Peter Halasz
- and/or, link to this image page:
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Image:Oblique_rays_04_Pengo.svg
Although not a requirement of the license, if you use this image in print or media other than the web, I would appreciate it if you let me know. Please contact me if you require alternate licensing.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
|
|
Date/Time |
Dimensions |
User |
Comment |
| current |
23:41, 29 June 2007 |
800×600 (25 KB) |
Pengo |
|
File links
The following pages on Schools Wikipedia link to this image (list may be incomplete):