Zwitterion

In chemistry, a zwitterion (/ˈtsvɪtər.aɪ.ən/ TSVIT-ər-eye-ən; from German zwitter [ˈtsvɪtɐ], meaning "hermaphrodite"), formerly called a dipolar ion, is a neutral molecule with both positive and negative electrical charges. (In some cases multiple positive and negative charges may be present.) Zwitterions are sometimes called inner salts.[1]
Unlike simple amphoteric compounds that may only form either a cationic or anionic species, a zwitterion simultaneously has both ionic states.[2]
Examples
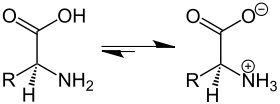
Amino acids are the best-known examples of zwitterions. These compounds contain an ammonium and a carboxylate group, and can be viewed as arising via a kind of intramolecular acid–base reaction: The amine group deprotonates the carboxylic acid.
- NH
2RCHCO
2H ⇌ NH+
3RCHCO−
2
The zwitterionic structure of glycine in the solid state has been confirmed by neutron diffraction measurements.[3] At least in some cases, the zwitterionic form of amino acids also persists in the gas phase.[4]
In addition to the amino acids, many other compounds that contain both acidic and basic centres tautomerize to the zwitterionic form. Examples, such as bicine and tricine, contain a basic secondary or tertiary amine fragment together with a carboxylic acid fragment. Neutron diffraction measurements show that solid sulfamic acid exists as a zwitterion.[5] Many alkaloids, such as LSD and psilocybin, exist as zwitterions because they contain carboxylates and ammonium centres.
Many zwitterions contain quaternary ammonium cations. Since it lacks N–H bonds, the ammonium center cannot participate in tautomerization. Zwitterions containing quaternary-ammonium centers are common in biology, a common example are the betaines, which serve as electrolytes in fish. The membrane-forming phospholipids are also commonly zwitterions. The polar head groups in these compounds are zwitterions, resulting from the presence of the anionic phosphate and cationic quaternary ammonium centres.[6]

Related compounds
Dipolar compounds and amine oxides are not classified as zwitterions;[7] zwitterionic compounds are neutral compounds having unit electrical charges on atoms.[1]
References
- 1 2 IUPAC Gold Book zwitterionic compounds/zwitterions
- ↑ "Definition of amphoteric" (2014), Chemicool. Retrieved 2016-06-14.
- ↑ Jönsson, P.-G.; Kvick, Å. (1972). "Precision neutron diffraction structure determination of protein and nucleic acid components. III. The crystal and molecular structure of the amino acid α-glycine". Acta Crystallogr. B. 28 (6): 1827–1833. doi:10.1107/S0567740872005096.
- ↑ Price, William D.; Jockusch, Rebecca A.; Williams, Evan R. (1997). "Is Arginine a Zwitterion in the Gas Phase?". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119 (49): 11988–11989. PMC 1364450
 . PMID 16479267. doi:10.1021/ja9711627. text
. PMID 16479267. doi:10.1021/ja9711627. text - ↑ R. L. Sass (April 1960). "A neutron diffraction study on the crystal structure of sulfamic acid". Acta Crystallogr. 13 (4): 320–324. doi:10.1107/S0365110X60000789.
- ↑ Nelson, D. L.; Cox, M. M. "Lehninger, Principles of Biochemistry" 3rd Ed. Worth Publishing: New York, 2000. ISBN 1-57259-153-6.
- ↑ IUPAC Gold Book dipolar compounds