Cefazolin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /sɪˈfæzələn/[1] |
| Trade names | Ancef, Cefacidal, other |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | intravenous, intramuscular |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | NA |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Biological half-life |
1.8 hours (given IV) 2 hours (given IM) |
| Excretion | kidney, unchanged |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.043.042 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
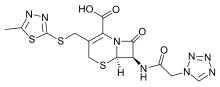
| Formula | C14H14N8O4S3 |
| Molar mass | 454.51 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Cefazolin, also known as cefazoline and cephazolin, is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. Specifically it is used to treat cellulitis, urinary tract infections, pneumonia, endocarditis, joint infection, and biliary tract infections. It is also used to prevent group B streptococcal disease around the time of delivery and before surgery. It is typically given by injection into a muscle or vein.[2]
Common side effects include diarrhea, vomiting, yeast infections, and allergic reactions.[2] It is not recommended in people who have a history of anaphylaxis to penicillin.[3] It is relatively safe for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding.[2][4] Cefazolin is in the first-generation cephalosporin class of medication and works by interfering with the bacteria's cell wall.[2]
Cefazolin was patented in 1967 and came into commercial use in 1971.[5] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system.[6] It is available as a generic medication.[2] The wholesale cost in the developing world is about 1.20 to 1.41 USD per day.[7] In the United States a course of treatment costs 25 to 50 USD.[4]
Medical uses
Cefazolin is used in a variety of infections provided that susceptible organisms are involved. It is indicated for use in the following infections:[8]
- Respiratory tract infections
- Urinary tract infections
- Skin infections
- Biliary tract infections
- Bone and joint infections
- Genital infections
- Blood infections (sepsis)
- Endocarditis
It can also be used peri-operatively to prevent infections post-surgery, and is often the preferred drug for surgical prophylaxis.[8]
There is no penetration into the central nervous system and therefore cefazolin is not effective in treating meningitis.[9]
Cefazolin has been shown to be effective in treating methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) but does not work in cases of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).[8] In many instances of staphylococcal infections, such as bacteremia, cefazolin is an alternative to penicillin in patients who are allergic to penicillin.[9] However, there is still potential for a reaction to occur with cefazolin and other cephalosporins in patients allergic to penicillin.[8] Resistance to cefazolin is seen in several species of bacteria, such as Mycoplasma and Chlamydia, in which case different generations of cephalosporins may be more effective.[10] Cefazolin does not fight against Enterococcus, anaerobic bacteria or atypical bacteria among others.[9]
Bacterial susceptibility
As a first-generation cephalosporin antibiotic, cefazolin and other first-generation antibiotics are very active against gram-positive bacteria and some gram-negative bacteria.[8] Their broad spectrum of activity can be attributed to their improved stability to many bacterial beta-lactamases compared to penicillins.[9]
Spectrum of activity
- Staphylococcus aureus (including beta-lactamase producing strains)
- Staphylococcus epidermidis
- Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pneumoniae and other strains of streptococci
Gram-Negative Aerobes:
Non susceptible
The following are not susceptible:[8][9]
- Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
- Enterococcus
- most strains of indole positive Proteus (Proteus vulgaris)
- Enterobacter spp.
- Morganella morganii
- Providencia rettgeri
- Serratia spp.
- Pseudomonas spp.
- Listeria
Special populations
Pregnancy
Cefazolin is pregnancy category B, indicating general safety for use in pregnancy. Caution should be used in breastfeeding as a small amount of cefazolin enters the breast milk.[8] Cefazolin can be used prophylactically against perinatal Group B streptococcal infection (GBS). Although penicillin and ampicillin are the standard of care for GBS prophylaxis, penicillin-allergic women with no history of anaphylaxis can be given cefazolin instead. These patients should be closely monitored as there is a small chance of an allergic reaction due to the similar structure of the antibiotics.[11]
Newborns
There has been no established safety and effectiveness for use in premature infants and neonates.[8]
Elderly
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed in clinical trials comparing elderly and younger subjects, however the trials could not eliminate the possibility that some older individuals may have a higher level of sensitivity.[8]
Additional considerations
People with kidney disease and those on hemodialysis may need the dose adjusted.[8] Cefazolin levels are not significantly affected by liver disease.
As with other antibiotics, cefazolin may interact with other medications being taken. Some important drugs that may interact with cefazolin such as probenecid.[9]
Side effects
Side effects associated with use of cefazolin therapy include:[8]
- Common (1-10%): diarrhea, stomach pain or upset stomach, vomiting, and rash.
- Uncommon (<1%): dizziness, headache, fatigue, itching, transient hepatitis.[12]
Patients with penicillin allergies could experience a potential reaction to cefazolin and other cephalosporins.[8] As with other antibiotics, patients experiencing watery and/or bloody stools occurring up to three months following therapy should contact their prescriber.[8]
Like those of several other cephalosporins, the chemical structure of cefazolin contains an N-methylthiodiazole (NMTD or 1-MTD) side-chain. As the antibiotic is broken down in the body, it releases free NMTD, which can cause hypoprothrombinemia (likely due to inhibition of the enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase) and a reaction with ethanol similar to that produced by disulfiram (Antabuse), due to inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase.[13] Those with an allergy to penicillin may develop a cross sensitivity to cefazolin.[14][15]
Mechanism of action
Cefazolin inhibits cell wall biosynthesis by binding Penicillin binding proteins which stops peptidoglycan synthesis. Penicillin binding proteins are bacterial proteins that help to catalyze the last stages of peptidoglycan synthesis, which is needed to maintain the cell wall. They remove the D-alanine from the precursor of the peptidoglycan. The lack of synthesis causes the bacteria to lyse because they also continually break down their cell walls. Cefazolin is bactericidal, meaning it kills the bacteria rather than inhibiting their growth.[9]
Brand names
It was initially marketed by GlaxoSmithKline under the trade name Ancef.[16]
Other trade names include: Cefacidal, Cefamezin, Cefrina, Elzogram, Faxilen, Gramaxin, Kefzol, Kefol, Kefzolan, Kezolin, Novaporin, Reflin, Zinol, and Zolicef.
References
- ↑ "Cefazolin". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Retrieved 2016-01-21.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Cefazolin Sodium". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ↑ WHO Model Formulary 2008 (PDF). World Health Organization. 2009. p. 106. ISBN 9789241547659. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- 1 2 Hamilton, Richart (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 84. ISBN 9781284057560.
- ↑ Fischer, Janos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 493. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ↑ "WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (19th List)" (PDF). World Health Organization. April 2015. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ↑ [X "X"] Check
|url=value (help). International Drug Price Indicator Guide. Retrieved 8 December 2016. - 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 "DailyMed - CEFAZOLIN - cefazolin sodium injection, powder, for solution". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2015-11-05.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Katzung, et. al., Bertram (2015). Basic & Clinical Pharmacology. New York: McGraw Hill Education. pp. 776–778. ISBN 978-0-07-182505-4.
- ↑ "Cefazolin (Injection Route)". Mayo Clinic. 1 July 2015.
- ↑ "Prevention of Perinatal Group B Streptococcal Disease". www.cdc.gov. Retrieved 2015-11-05.
- ↑ "Cefazolin Prescribing Information" (PDF). FDA. 2004.
- ↑ Stork, CM (2006). Antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals. New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 847.
- ↑ "Pharmaceutical Sciences CSU Parenteral Antibiotic Allergy cross-sensitivity chart" (PDF). Vancouver Acute Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vancouver Hospital & Health Sciences Centre. 2016. Retrieved May 19, 2017.
- ↑ Gonzalez-Estrada, A.; Radojicic, C. (2015). "Penicillin allergy: A practical guide for clinicians". Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. 82 (5): 295–300. ISSN 0891-1150. doi:10.3949/ccjm.82a.14111.
- ↑ "Cefazolin Sodium Injection: MedlinePlus Drug Information". www.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2015-11-05.