Zlín Z 42
| Zlin 42, 142 and 242 series | |
|---|---|
| | |
| Moravan Zlin 242L | |
| Role | Sport, personal and trainer aircraft |
| Manufacturer | Moravan Otrokovice |
| First flight | 17 October 1967 |
| Introduction | 1970 |
| Variants | Zlín Z 43 |
The Zlin Z 42 is a single-engine two-seat Czechoslovakian trainer aircraft manufactured by Moravan Otrokovice. A developed version, the Z 142, is the most popular aircraft variant in the manufacturer's aircraft line.
Design and development
The aircraft were built by Moravan Aviation, founded in 1934 by Tomáš Baťa in the Czech Republic.
As a follow-on and replacement for the successful Zlin Trener series of tandem aerobatic trainers, Moravan developed a new family of light aircraft, featuring a side-by-side seat layout, and comprising a two-seat trainer, the Zlín Z 42 and a four-seat trainer/tourer aircraft, the Zlín Z 43. The Z 42 first flew on 17 October 1967,[1] achieving airworthiness certification on 7 September 1970.[2]
The aircraft fuselage center section is of welded steel tube, covered with sheet metal and fiberglass panels. The tailcone is of monocoque construction. The empennage is of sheet metal. The two-spar wings are of all-metal construction. The tricycle landing gear is fixed, with a steerable nosewheel. Designed for aerobatics instruction, it was certified to +6.0 and -4.0 limit maneuvering load factors, and was equipped with full inverted fuel and oil systems, permitting extended inverted flight. The Z 42 is powered by a Walter inverted six-cylinder engine rated at 134 kW (180 hp).
The revised Zlín Z 42M flew in November 1972, with a revised tail taken from the Z 43, and a Constant speed propeller replacing the variable pitch propeller (where the propeller pitch is controlled by the pilot) of the original Z 42. When early Z 42s were refitted with the new propeller, they were redesignated Z 42 MU.[2]

Development continued, with the Zlin Z 142, featuring a slightly enlarged two-seat airframe based on that of the Z 42 and the more powerful (157 kW (210 hp)) Walter (now LOM) M 337 fuel-injected inverted six-cylinder, supercharged air-cooled engine of the Z 43 replacing the unsupercharged M 137 engine of the Z 42. The prototype Z-142 first flew on 29 December 1978.[3]
In the late 1980s, further development work was initiated. The inverted inline engine was replaced with a four-cylinder horizontally-opposed Lycoming IO-360 engine. This variant is designated the Z 242, and is immediately distinguishable by its relatively wide cowling which houses the flat-four engine.
Operational history
Two Z-142s were used by the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam in bombing sorties on the Sri Lankan airforce bases in Sri Lanka in 2007.[4] In October 2008 the Zlins were also used in an attack on a military base of the Sri Lanka Army, and a power station on the outskirts of the city of Colombo, Sri Lanka.[5][6]
Variants
- Zlin Z 42
- Zlin Z 42M
- Zlin Z 142

- Zlin Z 242
- 200 hp (149 kW) [7]
Operators
Civil
The aircraft is popular with flying training organizations. One of the largest fleet operators is Sault College of Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Canada, which operates eleven 242Ls.[8]
Military
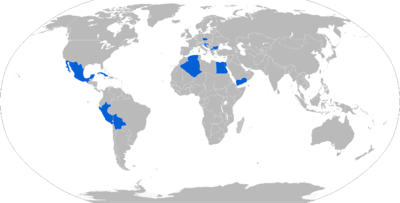
- Algerian Air Force - producing locally under Fernas-142 name [10]
- Bolivian Air Force = nine x Z242L ordered in May 2016.[11]
- Bulgarian Air Force - Z 42[12]
- Cuban Air Force - Z-142[13]
- Czech Air Force - Z-142[15]
- Macedonian Air Force - Z-242L[16]
- Mexican Navy - Z-242[17]
- Peruvian Air Force - Z-242[17]
- Yemen Air Force - Z-242.[17]
- Hungarian Air Force - Z-242L [19]
- Separatist organizations
- Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam - Air Tigers (formerly active in
 Sri Lanka)[5][6]
Sri Lanka)[5][6]
Specifications (Z42)
Data from Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1971-72 [20]
General characteristics
- Crew: one
- Capacity: one passenger or student
- Length: 7.07 m (23 ft 2 1⁄4 in)
- Wingspan: 9.11 m (29 ft 10 3⁄4 in)
- Height: 2.69 m (8 ft 10 in)
- Wing area: 13.15 m2 (141.5 sq.ft)
- Empty weight: 600 kg (1,322 lb)
- Max. takeoff weight: 920 kg (2,028 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Avia M 137A inverted 6-cylinder inline engine, 134 kW (180 hp)
Performance
- Never exceed speed: 315 km/h[21] (170 kt, 196 mph (Calibrated airspeed ))
- Maximum speed: 230 km/h (124 knots, 143 mph)
- Cruise speed: 200 km/h (108 knots, 124 mph)
- Range: 650 km (350 nm, 403 mi)
- Ferry range: 1,200 km (645 nm, 745 mi) with wingtip fuel tanks
- Service ceiling: 5,500 m (18,050 ft)
- Rate of climb: 5.0 m/s (984 ft/min)
References
- ↑ J W R Taylor 1971, p.32.
- 1 2 J W R Taylor 1980, p,43.
- ↑ J W R Taylor 1980, p,44.
- ↑ London, Bruce (May 2007). "Flying Tigers rule the air". The Australian. Retrieved 2008-10-29.
- 1 2 Athas, Iqbal (October 2008). "Tigers bomb army base, power station". CNN. Retrieved 2008-10-29.
- 1 2 TamilNet (October 2008). "Tigers launch airstrike in Mannaar, Colombo". Retrieved 2008-10-29.
- ↑ "Intro to Aerobatics Taught in Zlin Z-242". Flying Magazine. Vol. 126 no. 11. November 1999. p. 69.
- ↑ Transport Canada (September 2011). "Canadian Civil Aircraft Register". Archived from the original on April 9, 2010. Retrieved 12 September 2011.
- ↑ "GFS fleet". gfs.gov.hk. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
- ↑ "Des avions... made in Algeria". Aeronautique.ma. Retrieved 17 January 2016.
- ↑ "Military Aviation". Air-Britain News. Air-Britain. July 2016. p. 1145. ISSN 0950-7442.
- ↑ Hatch Flight International 29 November–5 December 1989, p. 45.
- ↑ Flight International 16–22 November 2004, p. 53.
- ↑ "Hrvatski vojni piloti na češkim avionima" [Croatian military pilots in Czech planes] (in Croatian). Nacional (weekly). 3 April 2006. Archived from the original on 7 July 2012. Retrieved 7 July 2012.
- ↑ Flight International 16–22 November 2004, p. 54.
- ↑ Flight International 16–22 November 2004, p. 73.
- 1 2 3 Jackson 2003, p. 114.
- ↑ "Zlin Z-242" Archived September 21, 2011, at the Wayback Machine.. Ministry of Defence: Slovenian Armed Forces. Retrieved 9 January 2012.
- ↑ "Hungary purchases light aircraft from Zlin". janes.com. Retrieved 17 January 2017.
- ↑ J W R Taylor 1971, pp.32-33.
- ↑ ""EASA TYPE-CERTIFICATE DATA SHEET: EASA.A.027: Z 42 Series". European Aviation Safety Agency, Issue 7, 25 April 2016. Retrieved 25 March 2017.
- Hatch, Paul. "World's Air Forces 1989". Flight International. No. 29 November–5 December 1989. pp. 37–106.
- Taylor, John W R (editor) (1971). Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1971-72. London: Sampson Low. ISBN 0 354 00094 2.
- Taylor, John W R (editor) (1980). Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1980-81. London: Jane's. ISBN 0-7106-0705-9.
- Jackson, Paul (2003). Jane's All The World's Aircraft 2003–2004. Coulsdon, UK: Jane's Information Group. ISBN 0-7106-2537-5.
- "World Air Forces 2004". Flight International. No. 16–22 November 2004. pp. 41–100.
- ^ Moravan official site. Accessed October 31, 2005.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Zlín Z-42. |