Zamboanga Sibugay
| Zamboanga Sibugay | ||
|---|---|---|
| Province | ||
| Province of Zamboanga Sibugay | ||
| ||
 Location in the Philippines | ||
| Coordinates: 7°48′N 122°40′E / 7.8°N 122.67°ECoordinates: 7°48′N 122°40′E / 7.8°N 122.67°E | ||
| Country | Philippines | |
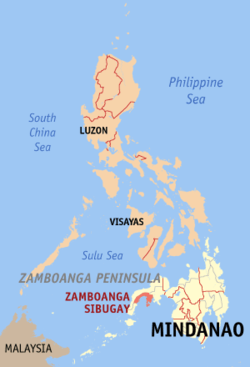
| Region | Zamboanga Peninsula (Region IX) | |
| Founded | 22 February 2001 | |
| Capital | Ipil | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlalawigan | |
| • Governor | Wilter Y. Palma (LP) | |
| • Vice Governor | Atty. Eldwin M. Alibutdan ([]) | |
| Area[1] | ||
| • Total | 3,607.75 km2 (1,392.96 sq mi) | |
| Area rank | 36th out of 81 | |
| Population (2015 census)[2] | ||
| • Total | 633,129 | |
| • Rank | 44th out of 81 | |
| • Density | 180/km2 (450/sq mi) | |
| • Density rank | 49th out of 81 | |
| Divisions | ||
| • Municipalities | ||
| • Barangays | 389 | |
| • Districts | 1st and 2nd districts of Zamboanga Sibugay | |
| Time zone | PHT (UTC+8) | |
| ZIP code | 7001–7039 | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)62 | |
| ISO 3166 code | PH | |
| Spoken languages | ||
| Website |
www | |
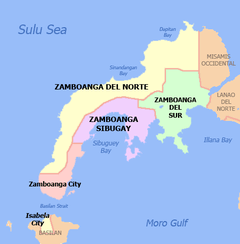
Zamboanga Sibugay (Cebuano: Lalawigan sa Zamboanga Sibugay, Chavacano: Provincia de Zamboanga Sibugay, Filipino: Lalawigan ng Zamboanga Sibugay) is a province in the Philippines located in the Zamboanga Peninsula region in Mindanao. Its capital is Ipil and it borders Zamboanga del Norte to the north, Zamboanga del Sur to the east and Zamboanga City to the southwest. To the south lies Sibuguey Bay in the Moro Gulf.
Zamboanga Sibugay is the 79th province created in the Philippines, when its territories were carved out from the third district of Zamboanga del Sur in 2001. Hence it the fourth newest province, being before now-defunct Shariff Kabunsuan (October 2006), Dinagat Islands (December 2006) and Davao Occidental (2013).
History
Zamboanga Sibugay was formerly part of Zamboanga del Sur. Attempts to divide Zamboanga del Sur into separate provinces date as far back as the 1960s. Several bills were filed in the Philippine Congress, but remained unacted. The new province was finally created by Republic Act No. 8973[3] passed on November 7, 2000 and signed into law by President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo on February 24, 2001. Zamboanga del Sur Third District Representative George Hofer was elected as its first governor in 2001.
Presently, former Diplahan Mayor Wilter Palma is the governor of the province, while the representatives of the first and second districts are Atty. Belma Cabilao and Dr. Dulce Ann K. Hofer, respectively.
Geography
Zamboanga Sibugay covers a total area of 3,607.75 square kilometres (1,392.96 sq mi)[4] occupying the south-central section of the Zamboanga Peninsula in western Mindanao, at 7°48’N 122°40’E.
To the north it intersects the common municipal boundaries of Kalawit, Tampilisan, and Godod of Zamboanga del Norte. It is bordered to the west by the municipalities of Sirawai, Siocon, and Baliguian, to the south by the Sibuguey Bay, and to the east by the municipalities of Bayog and Kumalarang of Zamboanga del Sur. It is further bordered on the southwest by Zamboanga City.
Climate
The climate of the province is moderately normal (climate type III). Annual rainfall varies from 1,599 to 3,500 millimetres (63.0 to 137.8 in). Temperature is relatively warm and constant throughout the year ranging from 22 to 35 °C (72 to 95 °F). The province is situated outside the country's typhoon belt.
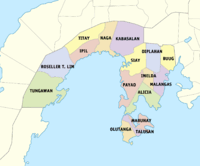
Administrative divisions
Zamboanga Sibugay comprises 16 municipalities, organized into two congressional districts and further subdivided into 389 barangays.[4]
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Demographics
| Population census of Zamboanga Sibugay | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
| 1990 | 407,038 | — |
| 1995 | 450,340 | +1.91% |
| 2000 | 497,239 | +2.15% |
| 2007 | 546,186 | +1.30% |
| 2010 | 584,685 | +2.51% |
| 2015 | 633,129 | +1.53% |
| Source: National Statistics Office[2][5][5] | ||
The population of Zamboanga Sibugay in the 2015 census was 633,129 people,[2] with a density of 180 inhabitants per square kilometre or 470 inhabitants per square mile.
The vast majority of the people of Zamboanga Sibugay speak Cebuano. Other languages such as Hiligaynon, Subanen, Zamboangueño and other ethnic tongues are also spoken, followed by English.
Religion
The province is predominantly Christian with about 45% affiliation with Roman Catholics as the predominant Christian sect. Islam is the well known minority of the province which shares about 40% of the population.
Economy
The leading industries are in the areas of semi-processed rubber,[6] rice and corn milling, ordinary food processing, wood and rattan furniture making, dried fish and squid processing, and home-made food processing. New industries include concrete products, garments, wax and candle factories, lime making, and other home and cottage industries.
Major crops produced include rice, corn, coconuts, rubber, fruit trees, vegetables, tobacco, coffee, cacao, and root crops. Livestock and poultry productions are predominantly small-scale and backyard operations. Coal mining in large and small scale and precious metal mining in small scale category are likewise present in some areas of the province.
Attractions
- Rotunda Obelisk
- Provincial Capitol
- Buluan Island
Education
Private schools include:
- Dr. Aurelio Mendoza Memorial Colleges (Dr. AMMC)
- Marcelo Spinola School (MSS)
- Marian College (MC)
- Sibugay Technical Institute, Inc. (STII)
- Universidad de Zamboanga (UZ)
- Mindanao State University Buug Campus (MSU-BC)
- Saint John College Buug (SJC)
- Medina College Ipil (MC)
- Sibugay Technical Institute, Inc. Imelda Branch (STII)
- Western Mindanao Stae University (External Studies Unit (ESU)) in the following: Alicia, Diplahan, Imelda, Ipil, Mabuhay, Naga, Olutanga, Siay, Tungawan
References
- ↑ "List of Provinces". PSGC Interactive. Makati City, Philippines: National Statistical Coordination Board. Archived from the original on January 21, 2013. Retrieved 31 July 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 Census of Population (2015). "Region IX (Zamboanga Peninsula)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ↑ "Republic Act No. 8973; An Act Creating the Province of Zamboanga Sibugay from the Province of Zamboanga del Sur and for Other Purposes". PhilippineLaw.info. Retrieved 28 September 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 "Province: Zamboanga Sibugay". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- 1 2 3 Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region IX (Zamboanga Peninsula)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ↑ Garcia, Bong (4 June 2015). "Rubber processing facility upgraded". Sun.Star Zamboanga. Sun.Star Publishing, Inc. Retrieved 19 April 2016.
THE Department of Science and Technology (Dost) has improved the rubber processing facility in Zamboanga Sibugay, as part of the agency’s effort to upgrade the rubber industry in the region.
External links
-
 Media related to Zamboanga Sibugay at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Zamboanga Sibugay at Wikimedia Commons -
 Geographic data related to Zamboanga Sibugay at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Zamboanga Sibugay at OpenStreetMap
Online news