Yellow 2G
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
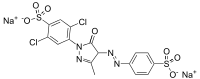
Disodium 2,5-dichloro-4-[3-methyl-5-oxo-4-(4-sulfonatophenyl)diazenyl-4H-pyrazol-1-yl]benzenesulfonate | |
| Other names
Lissamine Fast Yellow; C.I. Acid Yellow 17; C.I. 18965; Light Fast Yellow 2G; C.I. Food Yellow 5; Acid Leather Yellow 2GL; Erio Flavine SX; Fenalan Yellow G; Erio Flavine 3G; Kayacyl Yellow GG | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.026.199 |
| E number | E107 (colours) |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H10Na2N4O7S2 | |
| Molar mass | 551.29 g/mol |
| Hazards | |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S24 S25 S28A S37 S45 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Yellow 2G is a food coloring denoted by E number E107. It has the appearance of a yellow powder, and it is soluble in water. It is a synthetic yellow azo dye.
It appears to cause allergic or intolerant reactions, particularly amongst those with an aspirin intolerance and asthma sufferers. It is one of the colors that the Hyperactive Children's Support Group recommends be eliminated from the diet of children.
It is not listed by the UK's Food Standards Agency among EU approved food additives.[1] Its use is also banned in Austria, Japan, Norway, Sweden, Switzerland and the United States.
References
- ↑ Current EU approved additives and their E Numbers, Food Standards Agency, 26 November 2010
External links
![]() Media related to Yellow 2G at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Yellow 2G at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.