Voivodeship

A voivodeship /ˈvɔɪˌvoʊdˌʃɪp/ is the area administered by a voivode (Governor) in several countries of central and eastern Europe. Voivodeships have existed since medieval times in Poland, Hungary, Lithuania, Latvia, Ukraine, Russia and Serbia. The administrative level of area (territory) of voivodeship resembles that of a duchy in western medieval states, much as the title of voivode was equivalent to that of a duke. Other roughly equivalent titles and areas in medieval Eastern Europe included ban (bojan, vojin or bayan) and banate.
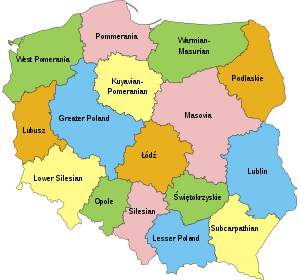
In a modern context, the word normally refers to one of the provinces (województwa) of Poland. Poland as of 2017 has 16 voivodeships.
Terminology
A voi(e)vod(e) (literally, "leader of warriors" or "war leader", equivalent to the Latin "Dux Exercituum" and the German "Herzog") was originally a military commander who stood, in a state's structure, next to the ruler. Later the word came to denote an administrative official.
Words for "voivodeship" in various languages include the Polish: województwo; the Romanian: voievodat; the Serbian: vojvodina (војводина), vojvodstvo (војводство) or vojvodovina (војводовина); the Hungarian: vajdaság; the Belarusian: ваяводства (vajаvodstva); the Lithuanian: vaivadija. Some of these words, or variants of them, may also be used in English.
Named for the word for "voivodeship" is the autonomous Serbian province of Vojvodina.
Though the word "voivodeship" (other spellings are "voievodship" and "voivodship") appears in English dictionaries such as the OED and Webster's, it is not in common general usage, and voivodeships in Poland and elsewhere are frequently referred to as "provinces".[1] Depending on context, historic voivodeships may also be referred to as "duchies", "palatinates" (the Latin word "palatinatus" was used for a voivodeship in Poland), "administrative districts" or "regions".
Current Polish Voivodeships
Since 1999, Poland has been divided into the following 16 voivodeships or provinces (for more information see Administrative divisions of Poland and Voivodeships of Poland):
- Greater Poland Voivodeship (województwo wielkopolskie)
- Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship (województwo kujawsko-pomorskie)
- Lesser Poland Voivodeship (województwo małopolskie)
- Łódź Voivodeship (województwo łódzkie)
- Lower Silesian Voivodeship (województwo dolnośląskie)
- Lublin Voivodeship (województwo lubelskie)
- Lubusz Voivodeship (województwo lubuskie)
- Masovian Voivodeship (województwo mazowieckie)
- Opole Voivodeship (województwo opolskie)
- Podlaskie Voivodeship (województwo podlaskie)
- Pomeranian Voivodeship (województwo pomorskie)
- Silesian Voivodeship (województwo śląskie)
- Subcarpathian Voivodeship (województwo podkarpackie)
- Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship (województwo świętokrzyskie)
- Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship (województwo warmińsko-mazurskie)
- West Pomeranian Voivodeship (województwo zachodniopomorskie)
Historical voivodeships
Outside Poland
.png)
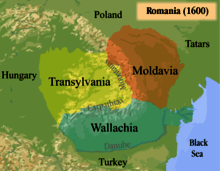
In the territory of modern Romania and Moldova, the regions of Wallachia, Moldavia and Transylvania were formerly voivodeships.
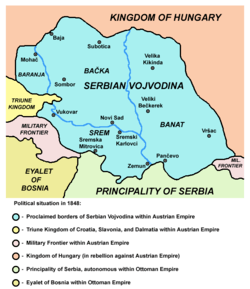
Historical voivodeships in the territory of modern Serbia include the Voivodeship of Salan (9th–10th centuries), Voivodeship of Sermon (11th century) and Voivodeship of Syrmia of Radoslav Čelnik (1527–1530). A voivodeship called Serbian Vojvodina was established in 1848–1849; this was transformed into the Voivodeship of Serbia and Temes Banat, a land within the Austro-Hungarian Empire from 1849 to 1860. This is the origin of the name of the present-day Serbian autonomous province of Vojvodina.
Historical voivodeships in the territory of modern Romania and Serbia include the Voivodeship of Glad (9th–10th centuries) and the Voivodeship of Ahtum (11th centuries).
In Poland and its territories
For more information about the divisions of Polish lands in particular periods, see Administrative divisions of Poland ("Historical").
Voivodeships in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (1569–1795):
- In the Polish Crown Lands:
- Poznań Voivodeship
- Kalisz Voivodeship
- Gniezno Voivodeship
- Sieradz Voivodeship
- Łęczyca Voivodeship
- Brześć Kujawski Voivodeship
- Inowrocław Voivodeship
- Chełmno Voivodeship
- Malbork Voivodeship
- Pomeranian Voivodeship
- Płock Voivodeship
- Rawa Voivodeship
- Masovian Voivodeship
- Kraków Voivodeship
- Sandomierz Voivodeship
- Lublin Voivodeship
- Podlasie Voivodeship
- Ruthenian Voivodeship
- Bełz Voivodeship
- Wolhynia Voivodeship
- Podole Voivodeship
- Bracław Voivodeship
- Kijów Voivodeship
- Czernihów Voivodeship
- In the historical Grand Duchy of Lithuania:
- In the historical Duchy of Livonia:
- Wenden Voivodeship (1598–1620)
- Dorpat Voivodeship (1598–1620)
- Parnawa Voivodeship (1598–1620)
- Inflanty Voivodeship (from the 1620s)

Voivodeships of Poland, 1921–1939:
- Silesian Voivodeship (Województwo Śląskie)
- Białystok Voivodeship (Województwo Białostockie)
- Kielce Voivodeship (Województwo Kieleckie)
- Kraków Voivodeship (Województwo Krakowskie)
- Łódź Voivodeship (Województwo Łódzkie)
- Lublin Voivodeship (Województwo Lubelskie)
- Lwów Voivodeship (Województwo Lwowskie)
- Nowogródek Voivodeship (Województwo Nowogrodzkie)
- Polesie Voivodeship (Województwo Poleskie)
- Pomeranian Voivodeship (Województwo Pomorskie)
- Poznań Voivodeship (Województwo Poznańskie)
- Stanisławów Voivodeship (Województwo Stanisławowskie)
- Tarnopol Voivodeship (Województwo Tarnopolskie)
- Warsaw Voivodeship (Województwo Warszawskie)
- Wilno Voivodeship (Województwo Wileńskie)
- Volhynian Voivodeship (Województwo Wołyńkie)
Voivodeships of Poland, 1945–1975:
- Białystok Voivodeship
- Bydgoszcz Voivodeship
- Gdańsk Voivodeship
- Katowice Voivodeship
- Kielce Voivodeship
- Koszalin Voivodeship
- Kraków Voivodeship
- Łódź Voivodeship
- Lublin Voivodeship
- Olsztyn Voivodeship
- Opole Voivodeship
- Poznań Voivodeship
- Rzeszów Voivodeship
- Szczecin Voivodeship
- Warsaw Voivodeship
- Wrocław Voivodeship
- Zielona Góra Voivodeship
Voivodeships of Poland, 1975–1998:
- Biała Podlaska Voivodeship
- Białystok Voivodeship
- Bielsko-Biała Voivodeship
- Bydgoszcz Voivodeship
- Chełm Voivodeship
- Ciechanów Voivodeship
- Częstochowa Voivodeship
- Elbląg Voivodeship
- Gdańsk Voivodeship
- Gorzów Voivodeship
- Jelenia Góra Voivodeship
- Kalisz Voivodeship
- Katowice Voivodeship
- Kielce Voivodeship
- Konin Voivodeship
- Koszalin Voivodeship
- Kraków Voivodeship
- Krosno Voivodeship
- Legnica Voivodeship
- Leszno Voivodeship
- Łódź Voivodeship
- Łomża Voivodeship
- Lublin Voivodeship
- Nowy Sacz Voivodeship
- Olsztyn Voivodeship
- Opole Voivodeship
- Ostrołęka Voivodeship
- Piotrków Voivodeship
- Piła Voivodeship
- Poznań Voivodeship
- Przemyśl Voivodeship
- Płock Voivodeship
- Radom Voivodeship
- Rzeszów Voivodeship
- Siedlce Voivodeship
- Sieradz Voivodeship
- Skierniewice Voivodeship
- Suwałki Voivodeship
- Szczecin Voivodeship
- Słupsk Voivodeship
- Tarnobrzeg Voivodeship
- Tarnów Voivodeship
- Toruń Voivodeship
- Warsaw Voivodeship
- Wałbrzych Voivodeship
- Wrocław Voivodeship
- Włocławek Voivodeship
- Zamość Voivodeship
- Zielona Góra Voivodeship
References
- ↑ "Jednostki podziału administracyjnego Polski tłumaczymy tak: województwo—province..." ("Polish administrative units are translated as follows: województwo—province..."). Arkadiusz Belczyk,"Tłumaczenie polskich nazw geograficznych na język angielski" ("Translation of Polish Geographical Names into English"), 2002-2006. For examples see New Provinces of Poland (1998); Map of Poland; English names of Polish provinces.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Flags of voivodeships of Poland. |