William T. G. Morton
| William Thomas Green Morton | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born |
August 9, 1819 Charlton, Massachusetts |
| Died |
July 15, 1868 (aged 48) New York City |
| Nationality | American |
| Fields | Dentistry |
| Known for | Ether for surgical operation |
| Influences |
Charles T. Jackson Horace Wells |
| Spouse | Elizabeth Whiteman |
William Thomas Green Morton (August 9, 1819 – July 15, 1868) was an American dentist who first publicly demonstrated the use of inhaled ether as a surgical anesthetic in 1846. The promotion of his questionable claim to have been the discoverer of anesthesia became an obsession for the rest of his life.[1]
Early life
Born in Charlton, Massachusetts, William T. G. Morton was the son of James Morton, a farmer, and Rebecca (Needham) Morton. William found work as a clerk, printer, and salesman in Boston before entering Baltimore College of Dental Surgery in 1840. In 1841, he gained notoriety for developing a new process to solder false teeth onto gold plates.[2] In 1842, he left college without graduating to study in Hartford, Connecticut with dentist Horace Wells, with whom Morton shared a brief partnership. In 1843 Morton married Elizabeth Whitman of Farmington, Connecticut, the niece of former Congressman Lemuel Whitman. Her parents objected to Morton's profession and only agreed to the marriage after he promised to study medicine. In the autumn of 1844, Morton entered Harvard Medical School and attended the chemistry lectures of Dr. Charles T. Jackson, who introduced Morton to the anesthetic properties of ether. Morton then also left Harvard without graduating.[3]
Career

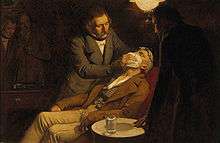
On September 30, 1846, Morton performed a painless tooth extraction after administering ether to a patient. Upon reading a favorable newspaper account of this event, Boston surgeon Henry Jacob Bigelow arranged for a now-famous demonstration of ether on October 16, 1846 at the operating theater of the Massachusetts General Hospital, or MGH. At this demonstration Dr. John Collins Warren painlessly removed a tumor from the neck of a Mr. Edward Gilbert Abbott. News of this use of ether spread rapidly around the world, and the first recorded use of ether outside the USA was in London, England, by the dentist James Robinson in a tooth extraction at the home of Dr. Francis Boote, an American doctor who had heard of Morton's and Bigelow's demonstrations.[4] The MGH theatre came to be known as the Ether Dome and has been preserved as a monument to this historic event.[5] Following the demonstration, Morton tried to hide the identity of the substance Abbott had inhaled, by referring to it as "Letheon", but it soon was found to be ether.[6]
A month after this demonstration, a patent was issued for "letheon",[7] although it was widely known by then that the inhalant was ether. The medical community at large condemned the patent as unjust and illiberal in such a humane and scientific profession.[8] Morton assured his colleagues that he would not restrict the use of ether among hospitals and charitable institutions, alleging that his motives for seeking a patent were to ensure the competent administration of ether and to prevent its misuse or abuse, as well as to recoup the expenditures of its development. Morton's pursuit of credit for and profit from the administration of ether was complicated by the furtive and sometimes deceptive tactics he employed during its development, as well as the competing claims of other doctors, most notably his former mentor, Dr. Jackson. Morton's own efforts to obtain patents overseas also undermined his assertions of philanthropic intent. Consequently, no effort was made to enforce the patent, and ether soon came into general use.
In December 1846, Morton applied to Congress for "national recompense" of $100,000, but this too was complicated by the claims of Jackson and Wells as discoverers of ether, and so Morton's application proved fruitless. He made similar applications in 1849, 1851, and 1853, and all failed. He later sought remuneration for his achievement through a futile attempt to sue the United States government. The lawyer who represented him was Richard Henry Dana, Jr.
In 1852 he received an honorary degree from the Washington University of Medicine in Baltimore, which later became the College of Physicians and Surgeons.[9]
In the spring of 1857, Amos Lawrence, a wealthy Bostonian, together with the medical professionals and influential citizens of Boston, developed a plan to raise $100,000 as a national testimonial to Morton, receiving contributions from both public and private citizens.
Morton's notoriety only increased when he served as the star defense witness in one of the most notable trials of the nineteenth century, that of John White Webster, who had been accused of the murder of Dr. George Parkman. Morton's rival, Dr. Jackson, testified for the prosecution, and the residents of Boston were anxious to witness these nemeses in courtroom combat.[10]

Morton performed public service yet again in the autumn of 1862 when he joined the Army of the Potomac as a volunteer surgeon, and applied ether to more than two thousand wounded soldiers during the battles of Fredericksburg, Chancellorsville, and the Wilderness.
Morton was in New York City in July 1868. He was riding in a carriage with his wife when he suddenly demanded the carriage stop, and he ran into the lake in Central Park "to cool off". This peculiar behavior was because he had, in fact, suffered a major stroke (cerebrovascular accident) which proved fatal soon after. He is buried at Mount Auburn Cemetery in Watertown and Cambridge, Massachusetts. His son William J. Morton was a noted physician and authority in electrotherapeutics.
Legacy
In 1871, a committee of those involved in raising the aforementioned national testimonial published The Historical Memoranda Relative to the Discovery of Etherization to establish Morton as the inventor and revealer of anesthetic inhalation and to justify pecuniary reward to Morton's family for the "fearful moral and legal responsibility he assumed in pursuit of this discovery."[11]
Morton's life and work were later to become the subject of the 1944 Paramount Pictures film The Great Moment.
The first use of ether as an anesthetic is commemorated in the Ether Monument in the Boston Public Garden, but the designers were careful not to choose sides in the debate over who should deserve credit for the discovery. Instead, the statue depicts a doctor in medieval Moorish robes and turban.
Morton's first successful public demonstration of ether as an inhalation anesthetic was such an historic and widely publicized event that many consider him to be the "inventor and revealer" of anesthesia. However, Morton's work was preceded by that of Georgia surgeon Crawford Williamson Long, who employed ether as an anesthetic on March 30, 1842. Although Long demonstrated its use to physicians in Georgia on numerous occasions, he did not publish his findings until 1849, in The Southern Medical and Surgical Journal.[12] These pioneering uses of ether were key factors in the medical and scientific pursuit now referred to as anesthesiology, and allowed the development of modern surgery. Spread of the news of this "new" anesthetic was helped by the subsequent feud that developed between Morton and Horace Wells and Charles T. Jackson.
References
- ↑ Fenster, J. M. (2001). Ether Day: The Strange Tale of America's Greatest Medical Discovery and the Haunted Men Who Made It. New York, NY: HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0-06-019523-6.
- ↑ Packard, Francis Randolph (1901). The History of Medicine in the United States. Philadelphia and London: J. B. Lippincott Company. p. 475.
- ↑ "William Thomas Green Morton (1819-68)". Brought To Life. Science Museum: London. Retrieved 13 October 2014.
|first1=missing|last1=in Authors list (help) - ↑ Boote F. (1847). "Surgical operations performed during insensibility produced by the inhalation of sulphuric ether". Lancet. 49 (1218): 5–8. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)88271-X.
- ↑ "National Historic Landmarks Program: Ether Dome, Massachusetts General Hospital". Retrieved 2010-11-02.
- ↑ ""Letheon" Inhaler". Retrieved 2009-05-01.
- ↑ U.S. Patent No. 4848, November 12, 1846, Improvement in surgical operations.
- ↑ Smith, Stephen (1862). "The Ether Patent". Medical Times. 4 (January to July): 83–84.
- ↑ Pinsker, Sheila; Harding, Robert S. (1986). "The Morton Family Collection 1849–1911". Retrieved 2008-12-02.
- ↑ Sullivan, Robert (1971). The Disappearance of Dr. Parkman. Little, Brown, and Company.
- ↑ Committee of Citizens of Boston (1871). Historical Memoranda Relative to the Discovery of Etherization and to the Connection with it of the Late William T.G. Morton. Boston: Rand, Avery, and Frye.
- ↑ Edward J. Huth; T. J. Murray (1 January 2006). Medicine in Quotations: Views of Health and Disease Through the Ages. ACP Press. pp. 1–. ISBN 978-1-930513-67-9. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
Further reading
- Alper M. H. (1964). "The Ether Controversy Revisited (Morton WT), (Jackson CT)". Anesthesiology. 25 (4): 560–3. PMID 14192801. doi:10.1097/00000542-196407000-00017.
- Andreae H. (1969). "The discoverer of ether anesthesia, dentist Morton, born 150 years ago" [The discoverer of ether anesthesia, dentist Morton, born 150 years ago]. Zahnärztliche Praxis (in German). 20 (23): 276. PMID 5263393.
- Asbell M. B. (1970). "William Thomas Green Morton". Worcester Medical News. 35 (2): 15–8. PMID 5277344.
- Ash H. L. (1985). "Anesthesia's dental heritage (William Thomas Green Morton)". Anesthesia Progress. 32 (1): 25–9. PMC 2175398
 . PMID 3888002.
. PMID 3888002. - Deranian H. M. (1997). "The great Morton-Jackson debate". Journal of the Massachusetts Dental Society. 46 (2): 24–5. PMID 9540719.
- Figuier, Louis (1851). "Expérience d'Horace Wels à l'hôpital de Boston avec je gaz hilarant". Exposition et histoire des principales découvertes scientifiques modernes (in French). 1. Paris: Masson. p. 212. OCLC 312611474. Contains an account, in French, of the discovery of anaesthesia with ether by Morton and Jackson and of its reception in Europe.
- Heynick F (2003). "William T. G. Morton and 'The Great Moment'". Journal of the History of Dentistry. 51 (1): 27–35. PMID 12641171.
- Keys T. E. (1973). "William Thomas Green Morton (1819–1868)". Anesthesia and Analgesia. 52 (2): 166. PMID 4572338. doi:10.1213/00000539-197303000-00004.
- Leonard A. G. (1985). "Stamp recognition for William Morton". British Dental Journal. 158 (9): 345. PMID 3890908. doi:10.1038/sj.bdj.4805605.
- Morton, William T. G. (1847). Remarks on the Proper Mode of Administering Sulphuric Ether by Inhalation (PDF). Boston: Button and Wentworth. OCLC 14825070. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- Morton W. T. (1996). "SMW 100 years ago. William Thomas Green Morton and the discovery of anesthesia" [SMW 100 years ago. William Thomas Green Morton and the discovery of anesthesia]. Schweizerische Medizinische Wochenschrift (in German). 126 (47): 2040–2. PMID 8984612.
- Pavlovskiĭ L. N. (2005). "Dentist William Morton is a founder of general anesthesia" [Dentist William Morton is a founder of general anesthesia]. Likars'ka Sprava (in Russian) (1–2): 111–5. PMID 15916010.
- Rozar L. B. (1975). "Dr. William T. G. Morton D.D.S., discoverer of surgical anesthesia". CAL. 39 (1): 6–8. PMID 795512.
- Shampo M. A., Kyle R. A.; Kyle (1987). "Morton: pioneer in the use of ether". Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 62 (1): 56. PMID 3540476. doi:10.1016/s0025-6196(12)61524-9.
- Vandam L. D. (1994). "Benjamin Perley Poore and his historical materials for a biography of W.T.G. Morton, M.D". Journal of the History of Medicine and Allied Sciences. 49 (1): 5–23. PMID 8151115. doi:10.1093/jhmas/49.1.5.
- Vandam L. D. (1996). "The last days of William Thomas Green Morton". Journal of Clinical Anesthesia. 8 (6): 431–4. PMID 8872680. doi:10.1016/0952-8180(96)00125-0.
- Westhorpe R (1996). "William Morton and the first successful demonstration of anaesthesia". Anaesthesia and Intensive Care. 24 (5): 529. PMID 8909661.
- "Wimmiam McLintock Morton, T.D., L.D.S". British Dental Journal. 146 (4): 128. 1979. PMID 367405. doi:10.1038/sj.bdj.4804211.
- "Two tormented lives. Horace Wells and William Morton" [Two tormented lives. Horace Wells and William Morton]. Boletin De Información (in Spanish). 15 (117): 17–21 passim. 1971. PMID 5283677.
- "William T.G. Morton (1819–1868), demonstrator of ether anesthesia". JAMA. 194 (2): 190–1. 1965. PMID 5319582. doi:10.1001/jama.194.2.190.
- "William Thomas Green Morton". Revista Española De Anestesiología (in Spanish). 3 (4): 380–3. 1956. PMID 13389978.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to William Morton. |
| Wikisource has the text of a 1920 Encyclopedia Americana article about William T. G. Morton. |
- "William Thomas Morton". Find a Grave. Retrieved 2008-12-02.
- "Boyhood Home Sign in Charlton, Massachusetts".
- "Centennial of First Man to Employ Anaesthetic". Miami Herald Record. July 13, 1919.
- "Men Who Have Eased the World's Pain". Kansas City Star. December 29, 1913.
- "Surgery Was Agony". Worcester Daily Spy. April 23, 1893.