Wibault 3
| Wibault 3 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Single seat fighter aircraft |
| National origin | France |
| Manufacturer | Pierre Levasseur[1] |
| Designer | Michel Wibaut |
| First flight | Q1, 1923[2] |
The Wibault 3 or Wibault Wib 3 C.1 was a French parasol wing prototype fighter aircraft from the 1920s, designed for high altitude operations. Its development was abandoned after repeated materials failure in its supercharger.
Design and development
The Wib 3, or Wib 3 C.1 (the C for Chasseur or fighter, 1 indicating single seat) was Wibault's response to a call from the Service Technique de l'Aéronautique (S.T.Aé, Technical Department of Aeronautics) for a high altitude fighter. This was required to have a top speed of 240 km/h (149 mph) at 7,000 metres (23,000 ft) and a service ceiling of 8,500 metres (27,900 ft); to achieve this performance at altitude, the specification called for a turbocharged engine.[2]
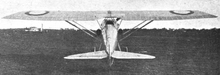
It was an all-metal aircraft in the contemporary sense, with a structure of duralumin but largely fabric covering. A parasol wing, with a cut-out in the trailing edge over the open cockpit, ensured the pilot a good all round view. The wing was straight edged with constant chord and was fitted with long span ailerons. It was braced to the lower fuselage on each side with a pair of parallel, faired struts to about half span.[1] The wing section to half span was moderately thick but thinned outboard, giving an overall maximum lift to drag ratio of almost 20.[1][2]
The Wib 3 was powered by a 224 kW (300 hp) Hispano-Suiza 8Fb upright water-cooled V-8 engine[2] with a Lamblin cylindrical radiator on each side of the fully enclosed cowling. A Rateau supercharger maintained power up to 4,600 metres (15,000 ft).[1] The fuselage was aluminium skinned from its nose to the cockpit; aft, it was fabric covered.[1] Its wire braced, almost triangular tailplane carried split elevators, the inner ends cropped to allow movement of the broad rudder. The Wib 3 had a fixed conventional undercarriage, with mainwheels on a rigid axle supported by a pair of V-struts mounted at the roots of the interplane struts. The axle was enclosed within an aerofoil shaped fairing which added 1.50 m2 (16.15 sq ft) to the wing area.[2]
On its first flight early in 1923, the Rateau turbo-supercharger was not fitted, its development having been interrupted by repeated failures caused by the difficulty of producing suitable high temperature resistant alloys. As a result, it was cancelled by the (S.T.Aé). The Wib 3 continued its flight testing until the autumn of 1923, after which the high altitude specification was withdrawn.[2]
Specifications

Data from Green & Swanborough pp.595-6[2]
General characteristics
- Crew: One
- Length: 8.20 m (26 ft 11 in)
- Wingspan: 11.72 m (38 ft 5 in)
- Height: 3.04 m (10 ft 0 in)
- Wing area: 25.00 m2 (269.1 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 994 kg (2,191 lb)
- Gross weight: 1,420 kg (3,131 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 227 kg (500 lb)[1]
- Powerplant: 1 × Hispano-Suiza 8Fb water-cooled V-8, supercharged, 220 kW (300 hp)
- Propellers: 2-bladed
Performance
- Maximum speed: 241 km/h (150 mph; 130 kn) at sea level
- Range: 853 km; 461 nmi (530 mi) at 5,044 m (16,550 ft)[1]
- Endurance: 3.0 hr
- Service ceiling: 7,000 m (23,000 ft) service
- Wing loading: 53 kg/m2 (10.8 lb/sq ft) [1]
- Power/mass: 160 W/kg (0.097 hp/lb) from Flight,[1] who give a power loading of 10.3 lb/hp
Armament
- Guns: 2×7.7 mm (0.303 in) synchronised Vickers machine guns, firing through propeller arc
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Wibault aircraft. |
Further reading
- "L'avion de Chasse Monoplan Wibault 3C1". L'Aérophile (in French): 138–141. 15 May 1923. Retrieved 30 August 2014.