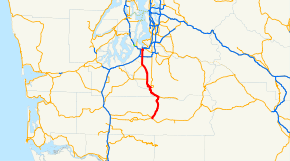
Washington State Route 7
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
SR 7 is highlighted in red. | ||||
| Route information | ||||
| Defined by RCW 47.17.030 | ||||
| Maintained by WSDOT | ||||
| Length: | 58.60 mi[1] (94.31 km) | |||
| Existed: | 1964[2] – present | |||
| Major junctions | ||||
| South end: |
| |||
|
| ||||
| North end: |
| |||
| Location | ||||
| Counties: | Lewis, Pierce | |||
| Highway system | ||||
| ||||
State Route 7 (SR 7) is a state highway in Lewis and Pierce counties, located in the U.S. state of Washington. The 58.60-mile (94.31 km) long roadway begins at U.S. Route 12 (US 12) in Morton and continues north to intersect several other state highways to Tacoma, where it ends at an interchange with Interstate 5 (I-5) and I-705. The road has several names, such as Second Street in Morton, the Mountain Highway in rural areas, Pacific Avenue in Spanaway, Parkland and Tacoma and 38th Street in Tacoma. Near the end of the highway there is a short freeway that has been proposed to be extended south parallel to an already existing railroad, owned by Tacoma Rail, which serves as the median of the short freeway.
The earliest road to use the current route of SR 7 first appeared in a 1900 map of the Tacoma area and has been part of the state highway system since 1909, when the Alder-Kosmos Road was added to the system as State Road 18. State Road 18 became part of two branches of State Road 5 in 1923 and later branches of Primary State Highway 5. During the 1964 highway renumbering, the branches became SR 7. In 2002, an auxiliary route that bypasses Tacoma, SR 704, was established and construction started in 2008 to connect I-5, Fort Lewis, McChord Air Force Base and SR 7.
Route description

State Route 7 (SR 7) begins at an intersection with U.S. Route 12 (US 12), a major east–west highway, in Morton. Traveling north as Second Street and paralleling the Morton – Tacoma (Mountain Division) route of Tacoma Rail,[1][3][4] the street intersects Main Avenue, which continues west out of the city as SR 508.[5] After leaving Morton, the highway becomes the Mountain Highway and passes through a heavily forested canyon near Mount Rainier and parallel to the Tilton River and Roundrop Creek. Bridging the Nisqually River, the highway leaves Lewis County and enters Pierce County. In Elbe, the roadway intersects SR 706, which goes east to Mount Rainier National Park. Following the Nisqually River, which has become Alder Lake, and Tacoma Rail line, SR 161 branches off towards Eatonville and SR 702 travels west from the plains to McKenna.[6][7][8][9]
Passing Elk Plain and suburban areas, the highway enters Spanaway near the Fort Lewis boundary where SR 7 intersects SR 507, which continues southwest to Chehalis. The Mountain Highway becomes Pacific Avenue and enters Parkland. Shortly after 112th Street, the roadway has a partial cloverleaf interchange with SR 512, which uses 108th Street South as two ramps.[10] Leaving Parkland and entering Tacoma, Pacific Avenue turns east as 38th Street and then has another partial cloverleaf interchange with a short freeway and the proposed route of SR 7, which is used by the roadway.[11] The freeway was the busiest segment of the highway in 2007, with an estimated daily average of 27,000 motorists.[12] The median of the freeway is the Tacoma Rail route and at the northern terminus is an interchange with Interstate 5 (I-5).[13][14] SR 7 ends at the interchange, located near the Tacoma Dome, but continues north parallel to the railroad to a single-point urban interchange with SR 509 as I-705.[6][7][8]
History
A 1900 map of the Tacoma area showed a roadway extending north from Spanaway to Tacoma that would later become SR 7.[15] In 1909, the Alder-Kosmos Road, numbered State Road 18, was added to the state highway system and ran from Kosmos north through Morton and Elbe to Alder.[16] The National Park Highway was created in 1913 and extended from the Pacific Ocean to Tacoma and south to Elbe, where it turned east into Mount Rainier National Park.[17] Both highways were replaced by two branches of State Road 5 in 1923, which traveled from Tacoma to Mount Rainier and Elbe to Chehalis.[18][19] State Road 5 became Primary State Highway 5 (PSH 5) during the creation of the Primary state highways in 1937 and the Tacoma–Mount Rainier branch remained the same, but the Elbe–Chehalis branch was shortened to Kosmos.[20][21]
The Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad started to parallel the route by 1951 between Tacoma and Morton.[22][23][24] During the 1964 highway renumbering the two branches of PSH 5 became SR 7.[2][25] Between 1968 and 2008, the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad transferred the railroad parallel to the highway to Tacoma Rail.[3][9][14] In 2002, a new auxiliary route of SR 7, SR 704 was established to provide a bypass of Tacoma to provide direct connections between Interstate 5 (I-5), Fort Lewis, McChord Air Force Base and SR 7 in Spanaway.[26] On July 30, 2008, the Washington State Department of Transportation (WSDOT) had a groundbreaking ceremony to start construction of SR 704,[27] which has been predicted to be finished after 2017.[28] The segment of the highway between SR 507 in Spanaway to SR 512 in Parkland had a very high accident rate, so WSDOT added safety improvements to the roadway in 2007.[29][30] Between Morton and Spanaway, WSDOT is currently (as of 2009) developing a route development plan to improve the roadway. The project is divided into three phases, the first phase was completed in 2006 and focused between Morton and Elbe and the second phase will be focused between Elbe and SR 702 while the third will focus between SR 702 to Spanaway.[31][32]
Major intersections
| County | Location | mi[1] | km | Destinations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lewis | Morton | 0.00 | 0.00 | Southern terminus | |
| 0.45 | 0.72 | ||||
| Pierce | Elbe | 16.82 | 27.07 | ||
| | 26.99 | 43.44 | |||
| | 36.08 | 58.07 | |||
| Spanaway | 47.38 | 76.25 | |||
| 48.33 | 77.78 | 176th Street South (East side), SR 704 (West Side) – Lakewood, Frederickson | SR 704 | ||
| Parkland | 52.55 | 84.57 | Interchange | ||
| Tacoma | 57.82 | 93.05 | South 38th Street | Interchange | |
| South end of freeway | |||||
| 58.60 | 94.31 | I-5 exit 133; northern terminus; northbound exit and southbound entrance; roadway continues beyond I-5 as I-705 | |||
| 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi | |||||
References
- 1 2 3 Washington State Department of Transportation (2008). "State Highway Log: Planning Report, SR 2 to SR 971" (PDF). Retrieved July 21, 2009.
- 1 2 Washington State Legislature (1970). "RCW 47.17.030: State route No. 7". Retrieved July 21, 2009.
- 1 2 Washington State Rail System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by United States Geological Survey. Washington State Department of Transportation. 2008. Retrieved July 21, 2009.
- ↑ TPU Rail Tracks (Map). Cartography by Tele Atlas. Tacoma Rail. 2009. Retrieved July 21, 2009.
- ↑ Washington State Department of Transportation (September 17, 2004). "SR 7; Junction SR 508" (PDF). Retrieved July 21, 2009.
- 1 2 Google (July 21, 2009). "State Route 7" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved July 21, 2009.
- 1 2 Washington State Highways, 2008–2009 (PDF) (Map) (2008–09 ed.). 1:842,000. Cartography by United States Geological Survey. Washington State Department of Transportation. 2008. § E3, F3. Retrieved July 21, 2009.
- 1 2 King, Pierce & Snohomish Counties Street Guide (Map). 1:24,000. The Thomas Guide series. Cartography by NAVTEQ. Thomas Bros., Rand McNally. 2008. pp. 803, 833, 863, 893–894, 914, 934, 954, 974–975. ISBN 0-528-86671-0.
- 1 2 Hoquiam, 1968 (Map). 1:250,000. Cartography by United States Geological Survey. University of Texas at Austin. 1968. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ Washington State Department of Transportation (January 5, 2006). "SR 512; Junction SR 7 / Pacific Avenue" (PDF). Retrieved July 21, 2009.
- ↑ Washington State Department of Transportation (September 17, 2004). "SR 7; Junction South 38th Street" (PDF). Retrieved July 21, 2009.
- ↑ Washington State Department of Transportation (2007). "2007 Annual Traffic Report" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on March 26, 2009. Retrieved July 21, 2009.
- ↑ Washington State Department of Transportation (August 27, 2008). "SR 5 – Exit 133; Junction SR 705 / SR 7" (PDF). Retrieved July 21, 2009.
- 1 2 Seattle, 1965 (Map). 1:250,000. Cartography by United States Geological Survey. University of Texas at Austin. 1965. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ Tacoma, 1900 (Map). 1:125,000. Washington 1:125,000 quadrangles. Cartography by United States Geological Survey. Washington State University. 1900. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ Washington State Legislature (March 13, 1909). "Chapter 92: Establishing Certain State Roads". Session Laws of the State of Washington. Session Laws of the State of Washington (1909 ed.). Olympia, Washington: Washington State Legislature. p. 190. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
State Road No. 18, beginning at Alder in Pierce county and running in a southerly direction by the way of Elbe to a point in State Road No. 5 near Kosmos in Lewis county.
- ↑ Washington State Legislature (March 12, 1913). "Chapter 65: Classifying Public Highways". Session Laws of the State of Washington. Session Laws of the State of Washington (1913 ed.). Olympia, Washington: Washington State Legislature. p. 222. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
g. A highway starting from the Pacific Highway in the city of Tacoma; running thence southerly by the most feasible route, to or near the town of Elbe, where it will branch, one section connecting with the government road in Rainier National Park, at or near Ashford, Pierce county, and the other by the most feasible route through Mineral, Morton, Klickitat Prairie, Forest, Chehalis, Pe Ell, South Bend, to the ocean beach at Holman in Pacific county, which shall be known as the National Park Highway.
- ↑ Washington State Legislature (March 19, 1909). "Chapter 185: Primary and Secondary State Highways". Session Laws of the State of Washington. Session Laws of the State of Washington (1923 ed.). Olympia, Washington: Washington State Legislature. pp. 628–629. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
SEC. 4. A primary state highway, to be known as State Road No. 5 or the National Park Highway System, is established as follows: Beginning at the City of Tacoma; thence by the most feasible route in a southeasterly direction through Elbe and Ashford to the Rainier National Park gate; also from a junction in the City of Elbe; thence in a southerly direction through Morton, Kosmos; thence in a westerly direction through Nesika, Riffe and Ethel to a junction with State Road No. 1 or the Pacific Highway at or in the vicinity of Jackson Prairie; also, from a junction at or near Kosmos in Lewis County in a northeasterly direction through Lewis in Lewis County through Sheepskull Gap; thence in a northwesterly direction through Enumclaw, Auburn, Kent to a connection with State Road No. 2 in the vicinity of Renton; also from a junction at Sheepskull Gap in a southeasterly direction to Yakima.
- ↑ Rand McNally Junior Road Map, Washington (Map). Rand McNally. 1926. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ Washington State Legislature (March 17, 1937). "Chapter 190: Establishment of Primary State Highways". Session Laws of the State of Washington. Session Laws of the State of Washington (1937 ed.). Olympia, Washington: Washington State Legislature. pp. 935–937. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
SEC. 5. A primary state highway to be known as Primary State Highway No. 5, or the National Park Highway, is hereby established according to description as follows: Beginning at Seattle, thence in a southerly direction by way of Bryn Mawr and the vicinity of Renton on Primary State Highway No. 2, thence in a southerly direction by the most feasible route to Auburn, thence in a southeasterly direction by the most feasible route by way of Enumclaw and Chinook Pass to Yakima on Primary State Highway No. 3; also beginning at a junction with Primary State Highway No. 1 in the vicinity south of Chehalis, thence in an easterly direction by the most feasible route by way of Kosmos and White Pass to a junction with Primary State Highway No. 5, as herein described, northwest of Yakima; also beginning at Tacoma on Primary State Highway No. 1, thence in a southerly direction by the most feasible route by way of Elbe, thence in an easterly direction by the most feasible route to a southwest entrance to Mount Rainier National Park; also beginning at Elbe on Primary State Highway No. 5, as herein described, thence in a southerly direction by the most feasible route to a junction with Primary State Highway No. 5, as herein described, in the vicinity of Kosmos; also beginning at Enumclaw on Primary State Highway No. 5, as herein described, thence in a southerly direction by the most feasible route to a northwest entrance to Mount Rainier National Park; also beginning at Auburn on Primary State Highway No. 5, as herein described, thence in a southerly direction by the most feasible route by way of Sumner, thence in a westerly direction by the most feasible route to Tacoma on Primary State Highway No. 1; also beginning at Auburn on Primary State Highway No. 5, as herein described, thence in a westerly direction by the most feasible route to a junction with Primary State Highway No. 1; also beginning at a junction with Primary State Highway No. 5, as herein described, in the vicinity west of Chinook Pass, thence in a southerly direction by the most feasible route to a junction with Primary State Highway No. 5, as herein described, in the vicinity west of White Pass; also beginning at Sumner on Primary State Highway No. 5, as herein described, thence in an easterly direction by the most feasible route to a junction with Primary State Highway No. 5, as herein described, in the vicinity of Buckley; also beginning at Enumclaw on Primary State Highway No. 5, as herein described, thence in a northwesterly direction by the most feasible route by way of Summit to a junction with Primary State Highway No. 2, as herein described, in the vicinity of Renton.
- ↑ Northwest, 1946 (Map). Rand McNally. 1946. p. 16. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ Hoquiam, 1951 (Map). 1:250,000. Cartography by United States Geological Survey. University of Texas at Austin. 1951. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ Hoquiam, 1958 (Map). 1:250,000. Cartography by United States Geological Survey. University of Texas at Austin. 1958. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ Seattle, 1958 (Map). 1:250,000. Cartography by United States Geological Survey. University of Texas at Austin. 1958. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ C. G. Prahl (December 1, 1965). "Identification of State Highways" (PDF). Washington State Highway Commission, Department of Highways. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ Washington State Legislature (2002). "RCW 47.17.818: State route No. 704". Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ "WSDOT Breaks Ground on First Segment of Crossbase Highway". On RAMP. August 1, 2008. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ "Cross base highway discussed". The Suburban Times. March 20, 2007. Archived from the original on September 27, 2007. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ Washington State Department of Transportation (2007). "SR 7 – SR 507 to SR 512 – Safey Improvements – Complete September 2007". Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ SR 7 Safety Improvements (Map). Washington State Department of Transportation. 2007. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ Washington State Department of Transportation (2009). "SR 7 – Corridor Improvements". Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ SR 7 – Corridor Improvements (Map). Washington State Department of Transportation. 2009. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
External links
Route map: Google
- Highways of Washington State
- US 12 (Morton) Traffic Camera
- SR 512 Interchange Traffic Camera
- I-5 / I-705 (Tacoma Dome) Traffic Camera
- Current WSDOT Projects
- Completed WSDOT Projects