WASP-14b
| Exoplanet | List of exoplanets | |
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Parent star | ||
| Star | WASP-14 | |
| Constellation | Boötes | |
| Right ascension | (α) | 14h 33m 06.356s[1] |
| Declination | (δ) | +21° 53′ 40.99″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude | (mV) | 9.75 |
| Distance | 520 ± 245 ly (160 ± 75 pc) | |
| Spectral type | F5V | |
| Orbital elements | ||
| Semi-major axis | (a) | 0.037+0.001 −0.002 AU |
| Periastron | (q) | 0.033 AU |
| Apastron | (Q) | 0.041 AU |
| Eccentricity | (e) | 0.095+0.004 −0.007 |
| Orbital period | (P) | 2.243756+5E-6 −1E-6 d |
| Inclination | (i) | 84.79+0.52 −0.67° |
| Argument of periastron |
(ω) | 254.9+0.92 −1.72° |
| Time of transit | (Tt) | 2454465.81963+0.00065 −0.00034 JD |
| Physical characteristics | ||
| Mass | (m) | 7.725+0.43 −0.67 MJ |
| Radius | (r) | 1.259+0.08 −0.058 RJ |
| Density | (ρ) | 5133 kg m−3 |
| Surface gravity | (g) | 126.2 m/s² (12.87 g) |
| Temperature | (T) | 2800 |
| Discovery information | ||
| Discovery date | April 1, 2008 | |
| Discoverer(s) | Cameron et al. (SuperWASP) | |
| Discovery method | Transit | |
| Discovery site | SAAO | |
| Discovery status | Published[2] | |
| Database references | ||
| Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia | data | |
| SIMBAD | data | |
| Exoplanet Archive | data | |
| Open Exoplanet Catalogue | data | |
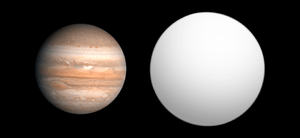
WASP-14b is an extrasolar planet discovered in 2008 by SuperWASP using the transit method. Follow-up radial velocity measurements showed that the mass of WASP-14b is almost eight times larger than that of Jupiter. The radius found by the transit observations show that it has a radius 25% larger than Jupiter. This makes WASP-14b one of the densest exoplanets known.[2] Its radius best fits the model of Jonathan Fortney.[3]
Rotation
As of August 2008, the most recent calculation of WASP-14b's Rossiter–McLaughlin effect and so spin-orbit angle was −14 ± 17 degrees.[4] It is too eccentric for its age and so is possibly pulled into its orbit by another planet.[2]
References
- 1 2 Zacharias, N.; et al. (2013). "The Fourth US Naval Observatory CCD Astrograph Catalog (UCAC4)". The Astronomical Journal. 145 (2). 44. Bibcode:2013AJ....145...44Z. arXiv:1212.6182
 . doi:10.1088/0004-6256/145/2/44.Vizier catalog entry
. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/145/2/44.Vizier catalog entry - 1 2 3 Joshi, Y. C.; et al. (2008). "WASP-14b: A 7.7 Mjup transiting exoplanet in an eccentric orbit". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 392 (4): 1532–1538. Bibcode:2009MNRAS.392.1532J. arXiv:0806.1478
 . doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.14178.x.
. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.14178.x. - ↑ Fortney; Marley, M. S.; Barnes, J. W. (2007). "Planetary Radii across Five Orders of Magnitude in Mass and Stellar Insolation: Application to Transits". The Astrophysical Journal. 659 (2): 1661–1672. Bibcode:2007ApJ...659.1661F. arXiv:astro-ph/0612671
 . doi:10.1086/512120.
. doi:10.1086/512120. - ↑ Winn, Joshua N. (2008). "Measuring accurate transit parameters". Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union. 4: 99. arXiv:0807.4929v2
 . doi:10.1017/S174392130802629X.
. doi:10.1017/S174392130802629X.
External links
![]() Media related to WASP-14b at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to WASP-14b at Wikimedia Commons
Coordinates: ![]() 14h 33m 06s, +21° 53′ 41″
14h 33m 06s, +21° 53′ 41″
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.