William Dean Howells
| William Dean Howells | |
|---|---|
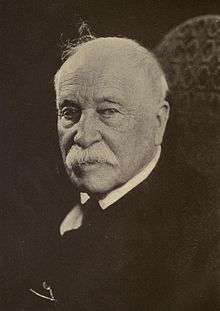 William Dean Howells, photograph by Underwood & Underwood | |
| Born |
March 1, 1837 Martins Ferry (then Martinsville), Ohio, U.S. |
| Died |
May 11, 1920 (aged 83) Manhattan, New York, U.S. |
| Spouse | Elinor Mead |
| Children |
Winifred Howells (b. 1863) John Mead Howells (b. 1868) Mildred Howells (b. 1872) |
|
| |
| Signature |
|
William Dean Howells (/ˈhaʊəlz/; March 1, 1837 – May 11, 1920) was an American realist novelist, literary critic, and playwright, nicknamed "The Dean of American Letters". He was particularly known for his tenure as editor of The Atlantic Monthly, as well as for his own prolific writings, including the Christmas story "Christmas Every Day" and the novels The Rise of Silas Lapham and A Traveler from Altruria.
Biography
Early life and family
William Dean Howells was born on March 1, 1837, in Martinsville, Ohio (now known as Martins Ferry, Ohio), to William Cooper Howells and Mary Dean Howells,[1] the second of eight children. His father was a newspaper editor and printer who moved frequently around Ohio.[2] In 1840, the family settled in Hamilton, Ohio,[3] where his father oversaw a Whig newspaper and followed Swedenborgianism.[4] Their nine years there were the longest period that they stayed in one place.[3] The family had to live frugally, although the young Howells was encouraged by his parents in his literary interests.[5] He began at an early age to help his father with typesetting and printing work, a job known at the time as a printer's devil. In 1852, his father arranged to have one of his poems published in the Ohio State Journal without telling him.
Early career
In 1856, Howells was elected as a clerk in the State House of Representatives. In 1858, he began to work at the Ohio State Journal where he wrote poetry and short stories, and also translated pieces from French, Spanish, and German. He avidly studied German and other languages and was greatly interested in Heinrich Heine. In 1860, he visited Boston and met with writers James Thomas Fields, James Russell Lowell, Oliver Wendell Holmes, Sr., Nathaniel Hawthorne, Henry David Thoreau, and Ralph Waldo Emerson. He became a personal friend to many of them, including Henry Adams, William James, Henry James, and Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr.[6]
In 1860 Howells wrote Abraham Lincoln's campaign biography Life Of Abraham Lincoln and subsequently gained a consulship in Venice. He married Elinor Mead on Christmas Eve 1862 at the American embassy in Paris. She was a sister of sculptor Larkin Goldsmith Mead and architect William Rutherford Mead of the firm McKim, Mead, and White. Among their children was architect John Mead Howells.
Editorship and other literary pursuits
The Howells returned to America in 1865 and settled in Cambridge, Massachusetts. He wrote for various magazines, including The Atlantic Monthly and Harper's Magazine. In January 1866, James Fields offered him a position as assistant editor at The Atlantic Monthly; he accepted after successfully negotiating for a higher salary, though he was frustrated by Fields' close supervision.[7]
Howells was made editor in 1871, after five years as assistant editor, and he remained in this position until 1881. In 1869, he met Mark Twain with whom he formed a longtime friendship. But his relationship with journalist Jonathan Baxter Harrison was more important for the development of his literary style and his advocacy of Realism. Harrison wrote a series of articles for The Atlantic Monthly during the 1870s on the lives of ordinary Americans.[8] Howells gave a series of twelve lectures on "Italian Poets of Our Century" for the Lowell Institute during its 1870-71 season.[9]
He published his first novel Their Wedding Journey in 1872, but his literary reputation soared with the realist novel A Modern Instance (1882), which described the decay of a marriage. His 1885 novel The Rise of Silas Lapham became his best known work, describing the rise and fall of an American entrepreneur of the paint business. His social views were also strongly represented in the novels Annie Kilburn (1888), A Hazard of New Fortunes (1890), and An Imperative Duty (1891).
He was particularly outraged by the trials resulting from the Haymarket Riot, which led him to portray a similar riot in A Hazard of New Fortunes and to write publicly to protest the trials of the men allegedly involved in the Haymarket affair. In his public writing and in his novels, he drew attention to pressing social issues of the time. He joined the Anti-Imperialist League in 1898, in opposition to the U.S. annexation of the Philippines.
His poems were collected in 1873 and 1886, and a volume was published in 1895 under the title Stops of Various Quills. He was the initiator of the school of American realists, and he had little sympathy with any other type of fiction. However, he frequently encouraged new writers in whom he discovered new ideas or new fictional techniques, such as Stephen Crane, Frank Norris, Hamlin Garland, Harold Frederic, Abraham Cahan, Sarah Orne Jewett, and Paul Laurence Dunbar.
Later years
In 1902, Howells published The Flight of Pony Baker, a book for children partly inspired by his own childhood.[10] That same year, he bought a summer home overlooking the Piscataqua River in Kittery Point, Maine.[11] He returned there annually until Elinor's death when he left the house to his son and family and moved to a house in York Harbor. His grandson, John Noyes Mead Howells, donated the property to Harvard University as a memorial in 1979.[12] In 1904 he was one of the first seven people chosen for membership in the American Academy of Arts and Letters, of which he became president.
In February 1910, Elinor Howells began using morphine to treat her worsening neuritis.[13] She died on May 6, a few days after her birthday, and only two weeks after the death of Howells's friend Mark Twain. Henry James offered his condolences, writing, "I think of this laceration of your life with an infinite sense of all it will mean for you".[14] Howells and his daughter Mildred decided to spend part of the year in their Cambridge home on Concord Avenue; though, without Elinor, they found it "dreadful in its ghostliness and ghastliness".[15]
Howells died in his sleep shortly after midnight on May 11, 1920,[16] and was buried in Cambridge, Massachusetts.[17] Eight years later his daughter published his correspondence as a biography of his literary life.
Literary criticism
In addition to his own creative works, Howells also wrote criticism, and essays about contemporary literary figures such as Henrik Ibsen, Émile Zola, Giovanni Verga, Benito Pérez Galdós, and, especially, Leo Tolstoy, which helped establish their reputations in the United States. He also wrote critically in support of American writers Hamlin Garland, Stephen Crane, Emily Dickinson, Mary E. Wilkins Freeman, Paul Laurence Dunbar, Sarah Orne Jewett, Charles W. Chesnutt, Abraham Cahan, Madison Cawein, and Frank Norris. It is perhaps in this role that he had his greatest influence. In his "Editor's Study" column at The Atlantic Monthly and, later, at Harper's, he formulated and disseminated his theories of "realism" in literature.
Howells viewed realism as "nothing more and nothing less than the truthful treatment of material."[18]
In defense of the real, as opposed to the ideal, he wrote,
"I hope the time is coming when not only the artist, but the common, average man, who always 'has the standard of the arts in his power,' will have also the courage to apply it, and will reject the ideal grasshopper wherever he finds it, in science, in literature, in art, because it is not 'simple, natural, and honest,' because it is not like a real grasshopper. But I will own that I think the time is yet far off, and that the people who have been brought up on the ideal grasshopper, the heroic grasshopper, the impassioned grasshopper, the self-devoted, adventureful, good old romantic card-board grasshopper, must die out before the simple, honest, and natural grasshopper can have a fair field."[19]
Howells believed the future of American writing was not in poetry but in novels, a form which he saw shifting from "romance" to a serious form.[20]
Howells was a Christian socialist whose ideals were greatly influenced by Russian writer Leo Tolstoy.[21] He joined a Christian socialist group in Boston between 1889 and 1891[22] and attended several churches, including the First Spiritual Temple and the Church of the Carpenter, the latter being affiliated with the Episcopal Church and the Society of Christian Socialists.[23] These influences led him to write on issues of social justice from a moral and egalitarian point of view, being critic of the social effects of industrial capitalism.[24][25][26] He was, however, not a Marxist.[27]
Reception
Noting the "documentary" and truthful value of Howells' work, Henry James wrote: "Stroke by stroke and book by book your work was to become, for this exquisite notation of our whole democratic light and shade and give and take, in the highest degree documentary."[28] Bliss Perry considered a knowledge of his work vital for an understanding of the American provincial novel and believed that "he has never in his long career written an insincere, a slovenly, or an infelicitous page."[29]
Gallery
.jpg) William Dean Howells, c. 1870.
William Dean Howells, c. 1870. Howells, by Van der Weyde, 1906.
Howells, by Van der Weyde, 1906. William Dean Howells in 1866.
William Dean Howells in 1866. Howells in 1887.
Howells in 1887. Grave of William Dean Howells, in Cambridge Cemetery.
Grave of William Dean Howells, in Cambridge Cemetery.
Works
- Venetian Life (1866)
- Italian Journeys (1867)
- Suburban Sketches (1871)[30]
- Their Wedding Journey (1872)
- A Chance Acquaintance (1873)
- The Parlor Car (1876)
- A Counterfeit Presentment (1877)
- The Lady of The Aroostook (1879)
The following were written during his residence in England and in Italy, as was The Rise of Silas Lapham in 1885.
- The Undiscovered Country (1880)
- A Fearful Responsibility (1881)
- Dr. Breen's Practice (1881)
- The Sleeping Car (1882)
- A Modern Instance (1882)
- A Woman's Reason (1883)
- Three Villages (1884)
- Tuscan Cities (1885)
- The Rise of Silas Lapham (1885)
He returned to the United States in 1886. He wrote various types of works, including fiction, poetry, and farces, of which The Sleeping Car, The Mouse-Trap, The Elevator; Christmas Every Day; and Out of the Question are characteristic.
- Indian Summer (1886)
- The Minister's Charge (1886)
- Annie Kilburn (1887/88)
- Modern Italian Poets (1887)
- April Hopes (1888)
- Mark Twain's Library of Humor (1888, in conjunction with Mark Twain)
- A Hazard of New Fortunes (1889)
- The Shadow of a Dream (1890)
- A Boy's Town (1890)
- Criticism and Fiction (1891)
- Christmas Every Day (1892)
- The Quality of Mercy (1892)
- An Imperative Duty (1892)
- The Coast of Bohemia (1893)
- My Year In a Log Cabin (1893)
- The Mouse-Trap and Other Farces (1894)
- A Traveler from Altruria (1894)
- Stops of Various Quills (1895)
- The Landlord At Lion's Head (1897)
- The Story of a Play (1898)
- Ragged Lady (1899)
- Their Silver Wedding Journey (1899)
- The Flight of Pony Baker (1902)
- The Kentons (1902)
- Questionable Shapes (1903)
- Son of Royal Langbrith (1904)
- Editha (1905)
- London Films (1905)
- Certain Delightful English Towns (1906)
- Between the Dark and the Daylight (1907)
- Through the Eye of the Needle (1907)
- Heroines of Fiction (1908)
- The Landlord At Lion's Head (1908)
- My Mark Twain: Reminiscences (1910)
- New Leaf Mills (1913)
- Seen and Unseen at Stratford-upon-Avon: A Fantasy (1914)
- The Leatherwood God (1916)
- Years of My Youth (autobiography) (1916)
See also
- William Dean Howells House, Cambridge, Massachusetts
- Redtop, his home in Belmont, Massachusetts
- American realism
Notes
- ↑ Lynn, 35
- ↑ William D.P. Bliss (ed.), The Encyclopedia of Social Reforms. Third Edition. New York: Funk and Wagnalls Co., 1897; pg. 698.
- 1 2 Lynn, 36
- ↑ Olsen, 33–34
- ↑ Olsen, 36
- ↑ See, e.g., Smith, Harriet Elinor, ed., The Autobiography of Mark Twain, Volume 1, University of California Press, 2010, p.475.
- ↑ Goodman and Dawson, 107–108
- ↑ Fryckstedt 1958
- ↑ Harriet Knight Smith, The History of the Lowell Institute, Boston: Lamson, Wolffe and Co., 1898.
- ↑ Olsen, 5
- ↑ J. Dennis Robinson. "William Dean Howells at Kittery". seacoastnh.com.
- ↑ William Dean Howells Memorial House, Kittery Point, Maine
- ↑ Goodman and Dawson, 401
- ↑ Lynn, 322
- ↑ Goodman and Dawson, 402
- ↑ Goodman and Dawson, 432
- ↑ ISITE Design. "Cambridge Cemetery - Public Works - City of Cambridge, Massachusetts". cambridgema.gov.
- ↑ Crow, Charles L. A Companion to the Regional Literatures of America. Malden, MA: Blackwell Pub., 2003: 92. ISBN 0631226311
- ↑ Criticism and Fiction," by William Dean Howells, accessed January 6, 2010.
- ↑ Ruland, Richard and Malcolm Bradbury. From Puritanism to Postmodernism: A History of American Literature. New York: Viking, 1991: 203–204. ISBN 0-670-83592-7
- ↑ Ensign, Russell L. and Louis Patsouras. Challenging Social Injustice: Essays on Socialism and the Devaluation of the Human Spirit. Edwin Mellen Press, 1993: 19.
- ↑ Bercovitch, Sacvan and Cyrus R. K. Patell. The Cambridge History of American Literature: Volume 3, Prose Writing, 1860-1920. Cambridge University Press, 2005: 736.
- ↑ Goodman and Dawson, 308
- ↑ Davis, Cynthia J. and, Denise D. Knight. Charlotte Perkins Gilman and Her Contemporaries: Literary and Intellectual Contexts. University of Alabama Press, 2004: 21
- ↑ Link, Arthur Stanley and William A. Link. The Twentieth Century: An American History. Harlan Davidson, 1983: 17.
- ↑ Zimmerman, Jerry R. Baydo. History of the U. S. with Topics. Gregory Publishing Company, 1994: 137
- ↑ Goodman and Dawson, 120
- ↑ James, Henry, Lubbock, Percy. The letters of Henry James. New York: Scribner, 1920: 233.
- ↑ Perry, Bliss, The American Spirit in Literature, Yale University Press, 1918, Chapter X.
- ↑ "Review of Suburban Sketches by W. D. Howells". The Athenaeum (No. 2281): 75–76. 15 July 1871.
References
-
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Gilman, D. C.; Peck, H. T.; Colby, F. M., eds. (1905). "article name needed". New International Encyclopedia (1st ed.). New York: Dodd, Mead.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Gilman, D. C.; Peck, H. T.; Colby, F. M., eds. (1905). "article name needed". New International Encyclopedia (1st ed.). New York: Dodd, Mead. - Bleiler, Everett (1948). The Checklist of Fantastic Literature. Chicago: Shasta Publishers. p. 154.
- Fryckstedt, Olov W. 1958. In Quest of America: A Study of Howells' Early Development as a Novelist. Uppsala, Sweden: Thesis.
- Goodman, Susan and Carl Dawson. William Dean Howells: A Writer's Life. Berkeley: University of California Press, 2005. ISBN 0-520-23896-6
- Lynn, Kenneth S. William Dean Howells: An American Life. New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Inc., 1970. ISBN 0-15-142177-3
- Olsen, Rodney. Dancing in Chains: The Youth of William Dean Howells. New York: New York University Press, 1991. ISBN 0-8147-6172-0
Further reading
- Ulrich Halfmann and William Dean Howells, "Interviews with William Dean Howells," American Literary Realism, 1870–1910, vol. 6, no. 4 (Fall 1973), pp. 274–275, 277–279, 281–399, 401–416. In JSTOR.
- Ulrich Halfmann and Don R. Smith, "William Dean Howells: A Revised and Annotated Bibliography of Secondary Comment in Periodicals and Newspapers, 1868–1919," American Literary Realism, 1870–1910, vol. 5, no. 2 (Spring 1972), pp. 91–121. In JSTOR.
- Radavich, David. "Twain, Howells, and the Origins of Midwestern Drama." MidAmerica XXXI (2004): 25–42.
- N. S. Witschi, Traces of Gold: California's Natural Resources and the Claim to Realism in Western American Literature. Tuscaloosa, AL: University of Alabama Press, 2002.
External links
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: William Dean Howells |
| Wikisource has original works written by or about: William Dean Howells |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to William Dean Howells. |
- Works by William Dean Howells at Project Gutenberg
- Works by or about William Dean Howells at Internet Archive
- Works by William Dean Howells at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)

- Essays by William Dean Howells at Quotidiana.org
- William Dean Howells Society includes a biographical sketch of Howells, links to his works (including the "Editor's Study" columns), questions and replies, bibliographies, and pictures.
- Realism in American Literature at the Literary Movements site
- Finding aid to the Clara and Rudolf Kirk collection of William Dean Howells material at the University of Pennsylvania Libraries
