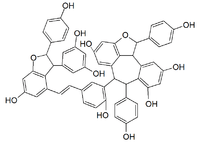
Vitisin A (stilbenoid)
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
R2-Viniferin[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C56H42O12 | |
| Molar mass | 906.92 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Vitisin A is a resveratrol tetramer found in plants of the genus Vitis. It is a complex of two resveratrol dimers, (+)-epsilon-viniferin and ampelopsin B.[2]
It shows an opposite effect to hopeaphenol on apoptosis of myocytes isolated from adult rat heart.[2][3][4]
References
- ↑ Poster at 1st International Conference of Resveratrol and Health, Jean-Claude Izard, 2010
- 1 2 Seya, K.; Kanemaru, K.; Sugimoto, C.; Suzuki, M.; Takeo, T.; Motomura, S.; Kitahara, H.; Niwa, M.; Oshima, Y.; Furukawa, K. -I. (2008). "Opposite Effects of Two Resveratrol (trans-3,5,4'-Trihydroxystilbene) Tetramers, Vitisin a and Hopeaphenol, on Apoptosis of Myocytes Isolated from Adult Rat Heart". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 328 (1): 90–98. PMID 18927354. doi:10.1124/jpet.108.143172.
- ↑ Kim, S. H.; Park, H. S.; Lee, M. S.; Cho, Y. J.; Kim, Y. S.; Hwang, J. T.; Sung, M. J.; Kim, M. S.; Kwon, D. Y. (2008). "Vitisin a inhibits adipocyte differentiation through cell cycle arrest in 3T3-L1 cells". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 372 (1): 108–113. PMID 18482581. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.04.188.
- ↑ Mi Jeong Sung, S.; Davaatseren, M.; Kim, W.; Sung Kwang, P.; Kim, S. H.; Haeng Jeon, H.; Myung Sunny, K.; Kim, Y. S.; Dae Young, K. (2009). "Vitisin a suppresses LPS-induced NO production by inhibiting ERK, p38, and NF-κB activation in RAW 264.7 cells". International Immunopharmacology. 9 (3): 319–323. PMID 19135555. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2008.12.005. INIST:21253190.
External links
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.