Vilnius Airport
| Vilnius International Airport Tarptautinis Vilniaus oro uostas | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||
| Owner | Lithuanian government | ||||||||||
| Operator | State Enterprise Tarptautinis Vilniaus oro uostas | ||||||||||
| Serves | Vilnius, Lithuania | ||||||||||
| Hub for | |||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 646 ft / 197 m | ||||||||||
| Coordinates | 54°38′13″N 025°17′16″E / 54.63694°N 25.28778°ECoordinates: 54°38′13″N 025°17′16″E / 54.63694°N 25.28778°E | ||||||||||
| Website | vilnius-airport.lt | ||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||
 VNO Location within the city | |||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Statistics (2016) | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
|
Source: Lithuanian Airports, 2016 | |||||||||||
Vilnius Airport (IATA: VNO, ICAO: EYVI) (Lithuanian: Vilniaus oro uostas) is the international airport of Vilnius, the capital of Lithuania. It is located 5.9 km (3.7 mi) south[1] of the city. It is the largest of the four commercial airports in Lithuania by passenger traffic. Today, Vilnius Airport is one of the fastest-growing airports in Europe. With one runway and an about 3.8 million passengers a year,[2] Vilnius International Airport serves as a base for Ryanair, Wizz Air and Small Planet Airlines.
The airport will be closed for 35 days from 14 July 2017 to 17 August 2017 (inclusive) for runway reconstruction work, with all flights diverted to Kaunas Airport.[3][4]
The present-day Vilnius International Airport is managed by a state owned enterprise Lithuanian Airports under the Ministry of Transport and Communications.[5]
History
Early years
The airport began operations on 17 August 1932 as Wilno–Porubanek, Porubanek was the name of the neighbouring village which today is part of the Kirtimai district of Vilnius. Before World War II it operated the then-domestic route between Vilnius and Warsaw as well as international route to Riga. Since 15 April 1939 it inaugurated a new route to Kaunas. The airport was used as a military airfield during the WWII. The airport resumed its activity as a civil airport as of 17 July 1944.[6]
Recent developments
Lithuanian Airlines (branded later as FlyLAL) was established as the Lithuanian flag carrier following independence in 1991 and inherited the Vilnius-based Aeroflot fleet of Tupolev Tu-134, Yakovlev Yak-40, Yak-42 and Antonov An-24, An-26 aircraft, but rapidly replaced these Soviet-era aircraft types with modern Boeing 737 and Boeing 757 jets and Saab 340, Saab 2000 turboprops. Operations were suspended effective 17 January 2009 as a result of growing financial difficulties. With the collapse of flyLAL, the airport lost its scheduled services to Amsterdam, Budapest, Istanbul, Madrid and Tbilisi. flyLAL used to operate to Dublin, Frankfurt, London, Milan and Paris in competition with Aer Lingus, airBaltic or Lufthansa.
AirBaltic, the national airline of Latvia and under Scandinavian Airlines part-ownership, opened up a second base at Vilnius in 2004 to complement its Riga operation and became the largest carrier at Vilnius, using Boeing 737 jets and Fokker 50 turboprops. At one point, airBaltic operated to 19 destinations from Vilnius but, in 2009, the network covered only three destinations served by two aircraft based at Vilnius.
Vilnius Airport is the main hub for Small Planet Airlines, Grand Cru Airlines, and Aviavilsa and a base for Wizz Air. It used to be a main hub for Star1 Airlines until their end of operations in September 2010 and Aurela until Aurela had lost its flight license. The airport was a secondary hub for airBaltic, Estonian Air and Skyways Express until they closed the bases in Vilnius.
On 30 June 2013 Air Lituanica also began its flights from the Vilnius Airport and established its base there serving several European cities. However, by 22 May 2015 the airline shut down all operations as well.[7]
At the platform of the airport are several Boeing 737-300 and Boeing 737-400 aircraft stored.[8][9]
Terminal
The construction of an airport building was started in 1949 and completed in 1954.[6] It features a standard 1950s Soviet airport terminal design, originally intended for an airport with up to 20 aircraft movements per day. On the outside, it is decorated with sculptures of soldiers, workers and aviators, while inside walls and ceilings feature wreaths, bay leaves and stars, and until the early 1990s, the Soviet hammer and sickle, typical decor for Soviet public buildings of early post-war years.
A new departure terminal, connected with the old building, was built in 1993.[10] Since then, the old building has been used as the arrival terminal only.[6]
In November 2007, the new 1,000 m2 (11,000 sq ft) terminal building was opened for operations which improved the capacity and facilities of the airport and complies with the requirements of the Schengen agreement. The passenger throughput of the terminal increased, passenger service quality was improved and more stringent aviation security measures were implemented. The new area of the renovated passenger terminal now reaches 3,462 m2 (37,260 sq ft). It is equipped with 6 passenger boarding bridges, modern passenger check-in equipment, new travel value and duty-free shops were opened as well as business lounge and VIP Lounge.[11]
Airlines and destinations
Passenger
Cargo
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| DHL Aviation operated by Cargoair | Leipzig/Halle, Riga |
| Transaviabaltika | Minsk |
Statistics
Passenger development

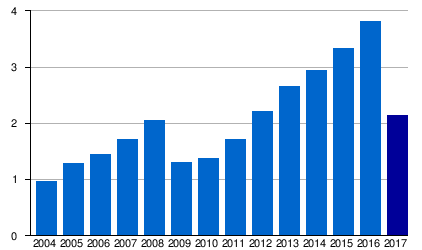 |
| Updated: 10 August 2017 |
Busiest Airports in the Baltics
| Rank | Country | Airport | 2017 (July) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Latvia | Riga International Airport | 2,746,841 (June) | 5,402,545 | 5,162,675 | 4,814,073 | 4,793,213 | 4,767,764 | 5,106,692 | 4,663,647 | 4,066,854 | 3,690,549 | 3,160,945 | 2,495,020 | 1,878,035 | 1,060,426 |
| 2. | Lithuania | Vilnius International Airport | 2,134,083 | 3,814,001 | 3,336,084 | 2,942,670 | 2,661,869 | 2,208,096 | 1,712,467 | 1,373,859 | 1,308,632 | 2,048,439 | 1,717,222 | 1,451,468 | 1,281,872 | 964,164 |
| 3. | Estonia | Tallinn Airport | 1,455,215 | 2,221,615 | 2,166,663 | 2,017,291 | 1,958,801 | 2,206,791 | 1,913,172 | 1,384,831 | 1,346,236 | 1,811,536 | 1,728,430 | 1,541,832 | 1,401,059 | 997,941 |
| 4. | Lithuania | Kaunas International Airport | 653,850 | 740,448 | 747,284 | 724,314 | 695,509 | 830,268 | 872,618 | 809,732 | 456,698 | 410,165 | 390,881 | 248,228 | 77,350 | 27,113 |
| 5. | Lithuania | Palanga International Airport | 170,844 | 232,630 | 145,441 | 132,931 | 127,890 | 128,169 | 111,133 | 102,528 | 104,600 | 101,586 | 93,379 | 110,828 | 94,000 | 76,020 |
Ground transportation
Train

Direct train services between Vilnius Airport Railway Station (referred to as "Oro uostas" in the schedules) and the central station of Vilnius were started in October 2008. Distance from the Airport to the Central Railway Station is 4.3 kilometres (2.7 mi), the journey takes 7 minutes. This is the fastest way to reach the Airport from the city center.
Bus
The direct intercity express services operate from the Airport to Klaipėda, Palanga, Minsk and Daugavpils. Also, the Latvian company Flybus.lv operates service from Vilnius airport to Riga (via Panevėžys and Bauska).[19]
Public transportation
City's buses operate from the airport. Also, the company Toks transports passengers from the bus station to Vilnius airport and back by microbuses.[19]
Incidents and accidents
- Scandinavian Airlines Flight 2748, operated with Dash-8-400 (LN-RDS) with 48 passengers and 4 crew members, took off from Copenhagen Airport on 12 September 2007. It was heading to Palanga, Lithuania, but was diverted to Vilnius Airport (better suited for an emergency landing) when landing gear problems were discovered before landing. Upon touchdown, the right landing gear collapsed. All passengers and crew were evacuated safely. The local officials at the Vilnius International Airport noted that this was the most serious incident in recent years. This accident, along with the Aalborg accident just days earlier, caused all SAS Dash 8–400 planes to be grounded until the beginning of October.
See also
References
- ↑ "EAD Basic". Ead.eurocontrol.int. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ↑ "Vilnius International Airport - Airport statistics". www.vilnius-airport.lt. Retrieved 2017-02-04.
- ↑ "Reconstruction of the runway of Vilnius Airport". Vilnius Airport.
- ↑ "Vilnius Airport to be closed for a renovation until Aug. 17". The Seattle Times. 13 July 2017.
- ↑ "Institutions and Enterprises under the Regulation of the Ministry". sumin.lrv.lt (in Lithuanian). Retrieved 2017-06-08.
- 1 2 3 "Vilnius International Airport - Istorija". www.vilnius-airport.lt. Retrieved 2017-02-04.
- ↑ "Air Lituanica ceases operations". ch-aviation. Retrieved 8 August 2015.
- ↑ "ch-aviation - Aircraft and Fleet Lists". Retrieved 14 January 2017.
- ↑ "LY-FLJ AviaAM Leasing Boeing 737-3K2 - cn 24327 / 1712". Retrieved 14 January 2017.
- ↑ iVilnius.lt. "By plane | How to arrive | Learn | iVilnius - Vilnius city guide". iVilnius - Vilnius city guide. Retrieved 2017-02-04.
- ↑ "Vilnius Airport will have a new passenger terminal". sumin.lrv.lt (in Lithuanian). Retrieved 2017-02-04.
- ↑ "Nordica offers direct flights to Tallinn from destinations all over Europe. Book now!". Retrieved 14 January 2017.
- ↑ http://corporate.ryanair.com/news/nachrichten/170208-ryanair-stellt-rekord-winterflugplan-2017-2018-fur-koln-bonn-vor/?market=de
- ↑ Liu, Jim (5 March 2017). "Ryanair W17 new routes as of 05MAR17". Routesonline. Retrieved 6 March 2017.
- ↑ "Small Planet Adds Geneva Service in Jan 2015". airlineroute.net. Retrieved 6 May 2015.
- ↑ "Small Planet Adds Lamezia Terme Operation in Sep/Oct 2015". airlineroute.net. Retrieved 6 May 2015.
- ↑ "UIA launches new flights between Lviv and Vilnius - офіційний сайт МАУ". Retrieved 14 January 2017.
- ↑ Liu, Jim (20 July 2016). "WizzAir Plans Additoinal New Routes in W16". Airlineroute, Routesonline. Retrieved 20 July 2016.
- 1 2 "Vilnius International Airport - Train / Bus". vno.lt. Retrieved 2017-02-04.
External links
![]() Media related to Vilnius International Airport at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Vilnius International Airport at Wikimedia Commons