Dysautonomia
| Dysautonomia | |
|---|---|
 | |
| The autonomic nervous system | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
| ICD-10 | G90 |
| ICD-9-CM | 337.9 |
| MeSH | D001342 |
Dysautonomia or autonomic dysfunction is a condition in which the autonomic nervous system (ANS) does not work properly. This may affect the functioning of the heart, bladder, intestines, sweat glands, pupils, and blood vessels; although it has many causes, not all of which classify as neuropathic.[1] A number of diseases can feature dysautonomia, such as Parkinson's disease, multiple system atrophy, autonomic failure, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS), and autonomic neuropathy.
The diagnosis is achieved through functional testing of the autonomic nervous system, focusing on the organ system affected. Investigations may be performed to identify underlying disease processes that may have led to the development of symptoms or autonomic neuropathy. Symptomatic treatment is available for many symptoms associated with dysautonomia, and some disease processes can be treated directly.[2]
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of dysautonomia are numerous and vary widely for each individual, symptoms of dysautonomia are due to inefficient or unbalanced efferent signals sent via both systems. The primary symptoms present in individuals with dysautonomia include:
- Orthostatic hypotension[3]
- Weakness[4]
- Low Blood Pressure[4]
- Bradycardia[4]
- Rapid heart rate[1]
- Anxiety[4]
- Insomnia[4]
- Chronic Fatigue[4]
- Tunnel vision[4]
- Exercise intolerance[3]
- Brain Fog[3]
- Difficulty swallowing[5]
- Bowel incontinence[3]
- Blurry or double vision[3]
- Urinary incontinence or urinary retention[3]
- Constipation[4]
- Anhydrosis[3]
- Vertigo[4]
- Dizziness[4]
- Syncope[4]
Causes
Dysautonomia may be due to inherited or degenerative neurologic diseases (primary dysautonomia)[1] or it may occur due to injury of the autonomic nervous system from an acquired disorder (secondary dysautonomia).[3][6] The most common causes of dysautonomia include:
- Toxic causes (vincristine)[4]
- Parkinson disease[5]
- Diabetes[5]
- Multiple sclerosis[5]
- Guillain Barre syndrome[5]
- HIV and AIDS[5]
- Eaton-Lambert syndrome[4]
- Autoimmune disease, such as Sjögren's syndrome or SLE (lupus)
- Amyloidosis[4]
- Alcoholism[5]
- Lyme disease [4]
- Spinal cord injury[5]
- Surgery or injury involving the nerves[5]
- Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome[7]
- Paraneoplastic syndrome[8]
In the sympathetic nervous system predominant dysautonomia is common along with fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, irritable bowel syndrome, and interstitial cystitis, raising the possibility that such dysautonomia could be their common clustering underlying pathogenesis.[9]
In addition to sometimes being a symptom of dysautonomia, anxiety can sometimes physically manifest symptoms resembling autonomic dysfunction.[10][11][12] A thorough investigation ruling out physiological causes is crucial, but in cases where relevant tests are performed and no causes are found or symptoms do not match any known disorders, a primary anxiety disorder is possible but should not be presumed.[13] For such patients, the Anxiety Sensitivity Index may have better predictivity for anxiety disorders, while the Beck Anxiety Inventory may misleadingly suggest anxiety for patients with dysautonomia.[14]
Mechanism
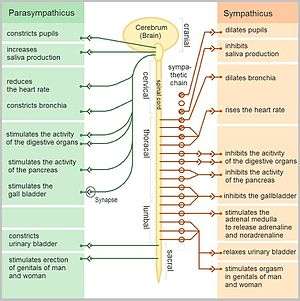
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a component of the peripheral nervous system and is made up of two branches: the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). The SNS controls the more active responses such as increasing heart rate and blood pressure. The PNS slows down the heart rate and aids in digestion, for example. Symptoms typically arise from abnormal responses of either the sympathetic or parasympathetic systems based on situation or environment.[1][15]
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of dysautonomia depends on the overall function of three autonomic functions - cardiovagal, adrenergic, and sudomotor. A diagnosis should, at a bare minimum, include measurements of blood pressure and heart rate while lying flat, and after at least 3 minutes of standing. The best way to achieve a diagnosis includes a range of testing, notably an autonomic reflex screen, tilt table test, and testing of the sudomotor response (QSART or thermoregulatory sweat test).[16] Additional tests and exams to determine a diagnosis of dysautonomia include the following:
- Cold presser[16]
- Testing for orthostatic intolerance[16]
- Hyperventilation test[16]
- Deep breathing[16]
- Valsalva maneuver[16]
- Tilt table test[16]
- Ambulatory blood pressure and EKG monitoring [4]
- Quantitative sudomotor axon reflex test (QSART)[16]
- Thermoregulatory sweat test[16]
- Nerve biopsy for small fiber neuropathy[3]
Tests to elucidate the cause of dysautonomia can include:
- Evaluation for acute (intermittent) porphyria.[3]
- Evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid via lumbar puncture[3]
Vegetative-vascular dystonia
Particularly in the Russian literature,[17] a subtype of dysautonomia which particularly affects the vascular system has been called vegetative-vascular dystonia.[18][19][20][21][22] The term vegetative reflects an older name for the autonomic nervous system: the vegetative nervous system.
Management

The treatment of dysautonomia can be difficult, since it is made up of many different symptoms, a combination of drug therapies is often required to manage individual symptomatic complaints. Therefore, if an autoimmune neuropathy is the case, then treatment with immunomodulatory therapies is done, or if diabetes mellitus is the cause, control of blood glucose is important.[3] In treatment there can be: proton-pump inhibitors and H2 receptor antagonists used for digestive symptoms such as acid reflux.[23]
For the treatment of genitourinary autonomic neuropathy medications may include sildenafil (a guanine monophosphate type-5 phosphodiesterase inhibitor). For the treatment of hyperhidrosis, anticholinergic agents such as trihexyphenidyl or scopolamine can be used, also intracutaneous injection of botulinum toxin type A can be used for management in some cases.[24]
Balloon angioplasty, a procedure referred to as transvascular autonomic modulation, is specifically not approved for the treatment of autonomic dysfunction.[25]
Prognosis
The prognosis of dysautonomia depends on several factors, individuals with chronic, progressive, generalized dysautonomia in the setting of central nervous system degeneration such as Parkinson's disease or multiple system atrophy have a generally poorer long-term prognosis. Consequently, dysautonomia could be fatal due to pneumonia, acute respiratory failure, or sudden cardiopulmonary arrest.[1]
According to Vinik, et al., it was found that autonomic dysfunction symptoms such as orthostatic hypotension, gastroparesis, and gustatory sweating are more frequently identified in mortalities.[26]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Dysautonomia". NINDS. Retrieved 2012-04-03.
- ↑ Iodice, V; Sandroni, Paola; Vernino, Steven. "Efficacy of immunotherapy in seropositive and seronegative putative autoimmune autonomic ganglionopathy.". Neurology. 72: 2002–8. PMC 2837591
 . PMID 19506222. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181a92b52.
. PMID 19506222. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181a92b52. - 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 "Autonomic Neuropathy Clinical Presentation: History, Physical, Causes". emedicine.medscape.com. Retrieved 2016-02-21.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 "Autonomic Neuropathy. Information about AN. Patient | Patient". Patient. Retrieved 2016-02-21.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "Autonomic neuropathy: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". www.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2016-02-20.
- ↑ KIRK, KATHERINE A; SHOYKHET, MICHAEL; JEONG, JONG H; TYLER-KABARA, ELIZABETH C; HENDERSON, MARYANNE J; BELL, MICHAEL J; FINK, ERICKA L (2012-08-01). "Dysautonomia after pediatric brain injury". Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology. 54 (8): 759–764. ISSN 0012-1622. PMC 3393822
 . PMID 22712762. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8749.2012.04322.x.
. PMID 22712762. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8749.2012.04322.x. - ↑ De Wandele I, Rombaut L, Leybaert L, Van, de Borne P, De Backer T, Malfait F, De Paepe A, Calders P (2014). "Dysautonomia and its underlying mechanisms in the hypermobility type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome". Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 44: 93–100. PMID 24507822. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.12.006.
- ↑ "Paraneoplastic syndromes of the nervous system". Mayo Clinic. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 13 September 2016.
- ↑ Martínez-Martínez LA, Mora T, Vargas A, Fuentes-Iniestra M, Martínez-Lavín M (Apr 2014). "Sympathetic nervous system dysfunction in fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, irritable bowel syndrome, and interstitial cystitis: a review of case-control studies.". J Clin Rheumatol. 20: 146–50. PMID 24662556. doi:10.1097/RHU.0000000000000089.
- ↑ "Medscape Log In". www.medscape.com. Retrieved 2017-06-02.
- ↑ Ackerman, Kurt; DiMartini, Andrea F. (2015). Psychosomatic Medicine. Oxford University Press, Incorporated. ISBN 9780199329311.
- ↑ Carr, Alan; McNulty, Muireann (2016-03-31). The Handbook of Adult Clinical Psychology: An Evidence Based Practice Approach. Routledge. ISBN 9781317576143.
- ↑ Tasman, Allan; Kay, Jerald; First, Michael B.; Lieberman, Jeffrey A.; Riba, Michelle (2015-03-30). Psychiatry, 2 Volume Set. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781118845479.
- ↑ "Psychiatric profile and attention deficits in postural tachycardia syndrome (PDF Download Available)". ResearchGate. Retrieved 2017-06-02.
- ↑ Information, National Center for Biotechnology; Pike, U. S. National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville; MD, Bethesda; Usa, 20894. "Autonomic Nervous System - National Library of Medicine". PubMed Health. Retrieved 2016-02-21.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Mustafa, Hossam I.; Fessel, Joshua P.; Barwise, John; Shannon, John R.; Raj, Satish R; Diedrich, André; Biaggioni, Italo; Robertson, David (2012-01-01). "Dysautonomia: Perioperative Implications". Anesthesiology. 116 (1): 205–215. ISSN 0003-3022. PMC 3296831
 . PMID 22143168. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e31823db712.
. PMID 22143168. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e31823db712. - ↑ Loganovsky, Konstantin (1999). "Vegetative-Vascular Dystonia and Osteoalgetic Syndrome or Chronic Fatigue Syndrome as a Characteristic After-Effect of Radioecological Disaster". Journal of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. 7 (3): 3–16. doi:10.1300/J092v07n03_02.
- ↑ Ivanova, ES; Mukharliamov, FIu; Razumov, AN; Uianaeva, AI (2008). "State-of-the-art corrective and diagnostic technologies in medical rehabilitation of patients with vegetative vascular dystonia". Voprosy kurortologii, fizioterapii, i lechebnoi fizicheskoi kultury (1): 4–7. PMID 18376477.
- ↑ Malysheva, OA; Shirinskiĭ, VS (1998). "Seasonal changes of secondary immunodeficiency in patients with vascular dystonia". Klinicheskaia meditsina. 76 (5): 34–6. PMID 9644934.
- ↑ Lobzin, VS; Poliakova, LA; Shiman, AG; Zavodnik, AI (1989). "Treatment of autonomic vascular dystonia by combined physiotherapy methods". Vrachebnoe delo (3): 22–3. PMID 2750110.
- ↑ Solov'Eva, AD; Kolosova, OA; Loseva, MM; Mindlina, GE; Ginzburg, LI (1985). "Thermography in healthy subjects and in the syndrome of vegetative-vascular dystonia". Zhurnal nevropatologii i psikhiatrii imeni S.S. Korsakova. 85 (6): 905–10. PMID 4024817.
- ↑ Isaev, DN; Efremov, KD (1983). "Psychogenic factors participating in the development of vegetovascular dystonia of the hypertensive type in children". Zhurnal nevropatologii i psikhiatrii imeni S.S. Korsakova. 83 (10): 1548–52. PMID 6659792.
- ↑ "H2 Blockers. Reducing stomach acid with H2 Blockers. | Patient". Patient. Retrieved 2016-02-21.
- ↑ http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/473205_9
- ↑ "Safety Alerts for Human Medical Products - Balloon angioplasty devices to treat autonomic dysfunction: FDA Safety Communication - FDA concern over experimental procedures". www.fda.gov. Retrieved 9 March 2017.
- ↑ Vinik, Aaron I.; Maser, Raelene E.; Mitchell, Braxton D.; Freeman, Roy (2003-05-01). "Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy". Diabetes Care. 26 (5): 1553–1579. ISSN 0149-5992. PMID 12716821. doi:10.2337/diacare.26.5.1553.
Further reading
Books
- Brading, Alison (1999). The autonomic nervous system and its effectors. Oxford: Blackwell Science. ISBN 0632026243.
- Jänig, Wilfrid (2008). Integrative action of the autonomic nervous system : neurobiology of homeostasis (Digitally printed version. ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521067545.
Journal articles
- Lara, Aline; Damasceno, Denis D.; Pires, Rita; Gros, Robert; Gomes, Enéas R.; Gavioli, Mariana; Lima, Ricardo F.; Guimarães, Diogo; Lima, Patricia (2010-04-01). "Dysautonomia Due to Reduced Cholinergic Neurotransmission Causes Cardiac Remodeling and Heart Failure". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 30 (7): 1746–1756. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 2838086
 . PMID 20123977. doi:10.1128/MCB.00996-09.
. PMID 20123977. doi:10.1128/MCB.00996-09. - Schiffer, Randolph B.; Rao, Stephen M.; Fogel, Barry S. (2003-01-01). Neuropsychiatry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 9780781726559.