Varacin
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
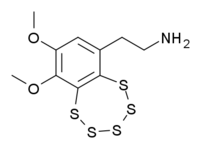
| IUPAC name
2-(6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4,5-benzopentathiepin-9-yl)ethanamine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H13NO2S5 | |
| Molar mass | 339.540 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Varacin is a bicyclic organosulfur compound originally found in marine Ascidiacea from the Polycitor genus.[1] It contains an unusual pentathiepin ring which reacts with DNA, and varacin and synthetic analogues have been investigated for their antimicrobial and antitumour properties.[2][3]
References
- ↑ Makarieva, T. N.; Stonik, V. A.; Dmitrenok, A. S.; Grebnev, B. B.; Isakov, V. V.; Rebachyk, N. M.; Rashkes, Y. W. (1995). "Varacin and three new marine antimicrobial polysulfides from the far-eastern ascidian Polycitor sp.". Journal of Natural Products. 58 (2): 254–8. PMID 7769392. doi:10.1021/np50116a015.
- ↑ Greer, A. (2001). "On the origin of cytotoxicity of the natural product varacin. A novel example of a pentathiepin reaction that provides evidence for a triatomic sulfur intermediate". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 123 (42): 10379–86. PMID 11603989. doi:10.1021/ja016495p.
- ↑ Brzostowska, E. M.; Greer, A. (2003). "The role of amine in the mechanism of pentathiepin (polysulfur) antitumor agents". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 125 (2): 396–404. PMID 12517151. doi:10.1021/ja027416s.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.