Urolithin A
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
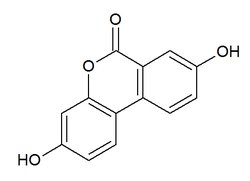
| IUPAC name
3,8-dihydroxybenzo[c]chromen-6-one | |
| Other names
Uro-A | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H8O4 | |
| Molar mass | 228.20 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Urolithin A is a urolithin, a type of microflora human metabolite of dietary ellagic acid derivatives,[1][2] such as ellagitannins.[3]
During intestinal metabolism by bacteria, ellagitannins and punicalagins are converted to urolithins, which have unknown biological activity in vivo.[4][5]
Urolithin A glucuronide is found in plasma at low concentrations.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ Larrosa, M; González-Sarrías, A; García-Conesa, MT; Tomás-Barberán, FA; Espín, JC (2006). "Urolithins, ellagic acid-derived metabolites produced by human colonic microflora, exhibit estrogenic and antiestrogenic activities". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 54 (5): 1611–1620. PMID 16506809. doi:10.1021/jf0527403.
- ↑ Vicinanza, Roberto; Zhang, Yanjun; Henning, Susanne M.; Heber, David (2013). "Pomegranate Juice Metabolites, Ellagic Acid and Urolithin A, Synergistically Inhibit Androgen-Independent Prostate Cancer Cell Growth via Distinct Effects on Cell Cycle Control and Apoptosis". Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2013: 1. doi:10.1155/2013/247504.
- ↑ Cerdá, Begoña; Periago, Paula; Espín, Juan Carlos; Tomás-Barberán, Francisco A. (2005). "Identification of Urolithin a as a Metabolite Produced by Human Colon Microflora from Ellagic Acid and Related Compounds". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 53 (14): 5571–5576. PMID 15998116. doi:10.1021/jf050384i.
- ↑ Bialonska D, Kasimsetty SG, Khan SI, Ferreira D (11 November 2009). "Urolithins, intestinal microbial metabolites of Pomegranate ellagitannins, exhibit potent antioxidant activity in a cell-based assay". J Agric Food Chem. 57 (21): 10181–6. PMID 19824638. doi:10.1021/jf9025794.
- ↑ Larrosa M, González-Sarrías A, Yáñez-Gascón MJ, Selma MV, Azorín-Ortuño M, Toti S, Tomás-Barberán F, Dolara P, Espín JC (19 July 2009). "Anti-inflammatory properties of a pomegranate extract and its metabolite urolithin-A in a colitis rat model and the effect of colon inflammation on phenolic metabolism". J Nutr Biochem. 21 (8): 717–25. PMID 19616930. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.04.012.
- ↑ Giménez-Bastida, Juan A.; González-Sarrías, Antonio; Larrosa, Mar; Tomás-Barberán, Francisco; Espín, Juan C.; García-Conesa, María-Teresa (2012). "Ellagitannin metabolites, urolithin a glucuronide and its aglycone urolithin A, ameliorate TNF-α-induced inflammation and associated molecular markers in human aortic endothelial cells". Molecular Nutrition & Food Research. 56 (5): 784–796. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201100677.
External links
- Urolithin A at Phenol-Explorer.eu
- Urolithin A at the Human Metabolome Database
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.