League of Free Laconians
The League of Free Laconians (Greek: Κοινόν τῶν Ἐλευθερολακώνων, Koinon tōn Eleutherolakōnōn) was established in southern Greece in 21 BC by the Emperor Augustus,[1] giving formal structure to a group of cities that had been associated for almost two centuries.
History
The Eleutherolakones (Ἐλευθερολάκωνες, free Laconians) are first mentioned in 195 BC, after Sparta's defeat in the Roman-Spartan War. The Roman general Titus Quinctius Flamininus placed several coastal cities, inhabited by perioikoi, under the protection of the Achaean League, separating them from the rump Spartan state.[2] The most important of its cities was Gythium. A few years later, in 192 BC, Gythium was recaptured by Nabis of Sparta, but the Achean League immediately attacked the city. The city of Las was attacked and captured by the Spartans. The Achaean League retaliated and attacked Las and Sparta.
Following the dissolution of the Achaean League in 146 BC, the Eleutherolakones joined the Lacedaemonian League, until Emperor Augustus re-established the League of Free Laconians in 21 BC.[2]
Constitution
The highest officer in the Union was the strategos, who was assisted by the treasurer. At its height the koinon consisted of 24 cities; however, the number decreased to 18.[3] The koinon continued to exist into the second half of the 3rd century AD, as is demonstrated by the coins and inscriptions of its member states. It continued until 297 AD when the Emperor Diocletian reformed the provincial administration.
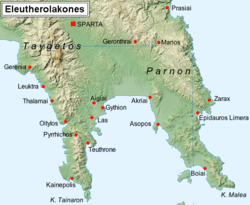
Member cities
According to Pausanias, the members of the koinon were:[4]
|
|
Notes
References
Primary Sources
- Pausanias, translated by W.H.S Jones, (1918). Pausanias Description of Greece. London: Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-14-044362-2.
Secondary Sources
- Peter Greenhalgh and Edward Eliopoulos, (1985). Deep into Mani: Journey to the southern tip of Greece. London: Trinity Press ISBN 0-571-13524-2
- "Eleutherolakones". The New Pauly. 4. Brill. p. 918.