Uniform tiling symmetry mutations
| Spherical tilings (n = 3..5) | ||
|---|---|---|
 *332 |
 *432 |
 *532 |
| Euclidean plane tiling (n = 6) | ||
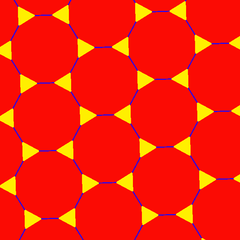 *632 | ||
| Hyperbolic plane tilings (n = 7...∞) | ||
 *732 |
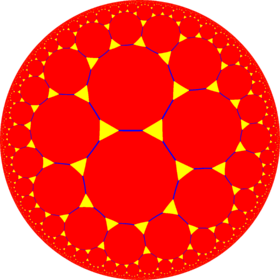 *832 |
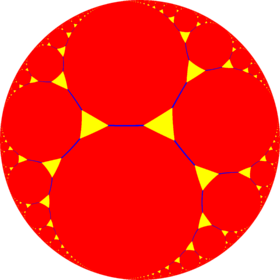 ... *∞32 |
In geometry, a symmetry mutation is a mapping of fundamental domains between two symmetry groups.[1] They are compactly expressed in orbifold notation. These mutations can occur from spherical tilings to Euclidean tilings to hyperbolic tilings. Hyperbolic tilings can also be divided between compact, paracompact and divergent cases.
The uniform tilings are the simplest application of these mutations, although more complex patterns can be expressed within a fundamental domain.
This article expressed progressive sequences of uniform tilings within symmetry families.
Mutations of orbifolds
Orbifolds with the same structure can be mutated between different symmetry classes, including across curvature domains from spherical, to Euclidean to hyperbolic. This table shows mutation classes.[1] This table is not complete for possible hyperbolic orbifolds.
| Orbifold | Spherical | Euclidean | Hyperbolic |
|---|---|---|---|
| o | - | o | - |
| pp | 22, 33 ... | ∞∞ | - |
| *pp | *22, *33 ... | *∞∞ | - |
| p* | 2*, 3* ... | ∞* | - |
| p× | 2×, 3× ... | ∞× | |
| ** | - | ** | - |
| *× | - | *× | - |
| ×× | - | ×× | - |
| ppp | 222 | 333 | 444 ... |
| pp* | - | 22* | 33* ... |
| pp× | - | 22× | 33×, 44× ... |
| pqq | 222, 322 ... , 233 | 244 | 255 ..., 433 ... |
| pqr | 234, 235 | 236 | 237 ..., 245 ... |
| pq* | - | - | 23*, 24* ... |
| pq× | - | - | 23×, 24× ... |
| p*q | 2*2, 2*3 ... | 3*3, 4*2 | 5*2 5*3 ..., 4*3, 4*4 ..., 3*4, 3*5 ... |
| *p* | - | - | *2* ... |
| *p× | - | - | *2× ... |
| pppp | - | 2222 | 3333 ... |
| pppq | - | - | 2223... |
| ppqq | - | - | 2233 |
| pp*p | - | - | 22*2 ... |
| p*qr | - | 2*22 | 3*22 ..., 2*32 ... |
| *ppp | *222 | *333 | *444 ... |
| *pqq | *p22, *233 | *244 | *255 ..., *344... |
| *pqr | *234, *235 | *236 | *237..., *245..., *345 ... |
| p*ppp | - | - | 2*222 |
| *pqrs | - | *2222 | *2223... |
| *ppppp | - | - | *22222 ... |
| ... |
*n22 symmetry
Regular tilings
| Space | Spherical | Euclidean | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiling |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Config. | 2.2 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 210 | 211 | 212 | 2∞ |
| Space | Spherical | Euclidean | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiling |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Config. | 2.2 | 3.3 | 4.4 | 5.5 | 6.6 | ...∞.∞ |
Prism tilings
| Space | Spherical | Euclidean | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiling | |||||||||||
| Config. | 3.4.4 | 4.4.4 | 5.4.4 | 6.4.4 | 7.4.4 | 8.4.4 | 9.4.4 | 10.4.4 | 11.4.4 | 12.4.4 | ...∞.4.4 |
Antiprism tilings
| Space | Spherical | Euclidean | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiling | ||||||||
| Config. | 2.3.3.3 | 3.3.3.3 | 4.3.3.3 | 5.3.3.3 | 6.3.3.3 | 7.3.3.3 | 8.3.3.3 | ...∞.3.3.3 |
*n32 symmetry
Regular tilings
| *n32 symmetry mutation of regular tilings: {3,n} | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spherical | Euclid. | Compact hyper. | Paraco. | Noncompact hyperbolic | |||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 3.3 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 | 3∞ | 312i | 39i | 36i | 33i |
| *n32 symmetry mutation of regular tilings: {n,3} | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperb. | Paraco. | Noncompact hyperbolic | |||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| {2,3} | {3,3} | {4,3} | {5,3} | {6,3} | {7,3} | {8,3} | {∞,3} | {12i,3} | {9i,3} | {6i,3} | {3i,3} |
Truncated tilings
| *n32 symmetry mutation of truncated tilings: t{n,3} | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry *n32 [n,3] |
Spherical | Euclid. | Compact hyperb. | Paraco. | Noncompact hyperbolic | ||||||
| *232 [2,3] |
*332 [3,3] |
*432 [4,3] |
*532 [5,3] |
*632 [6,3] |
*732 [7,3] |
*832 [8,3]... |
*∞32 [∞,3] |
[12i,3] | [9i,3] | [6i,3] | |
| Truncated figures |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Symbol | t{2,3} | t{3,3} | t{4,3} | t{5,3} | t{6,3} | t{7,3} | t{8,3} | t{∞,3} | t{12i,3} | t{9i,3} | t{6i,3} |
| Triakis figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||||
| Config. | V3.4.4 | V3.6.6 | V3.8.8 | V3.10.10 | V3.12.12 | V3.14.14 | V3.16.16 | V3.∞.∞ | |||
| *n32 symmetry mutation of truncated tilings: n.6.6 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sym. *n42 [n,3] |
Spherical | Euclid. | Compact | Parac. | Noncompact hyperbolic | |||||||
| *232 [2,3] |
*332 [3,3] |
*432 [4,3] |
*532 [5,3] |
*632 [6,3] |
*732 [7,3] |
*832 [8,3]... |
*∞32 [∞,3] |
[12i,3] | [9i,3] | [6i,3] | ||
| Truncated figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
| Config. | 2.6.6 | 3.6.6 | 4.6.6 | 5.6.6 | 6.6.6 | 7.6.6 | 8.6.6 | ∞.6.6 | 12i.6.6 | 9i.6.6 | 6i.6.6 | |
| n-kis figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||||
| Config. | V2.6.6 | V3.6.6 | V4.6.6 | V5.6.6 | V6.6.6 | V7.6.6 | V8.6.6 | V∞.6.6 | V12i.6.6 | V9i.6.6 | V6i.6.6 | |
Quasiregular tilings
| Quasiregular tilings: (3.n)2 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sym. *n32 [n,3] |
Spherical | Euclid. | Compact hyperb. | Paraco. | Noncompact hyperbolic | |||||||
| *332 [3,3] Td |
*432 [4,3] Oh |
*532 [5,3] Ih |
*632 [6,3] p6m |
*732 [7,3] |
*832 [8,3]... |
*∞32 [∞,3] |
[12i,3] | [9i,3] | [6i,3] | |||
| Figure |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||
| Figure |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||
| Vertex | (3.3)2 | (3.4)2 | (3.6)2 | (3.6)2 | (3.7)2 | (3.8)2 | (3.∞)2 | (3.12i)2 | (3.9i)2 | (3.6i)2 | ||
| Schläfli | r{3,3} | r{3,4} | r{3,5} | r{3,6} | r{3,7} | r{3,8} | r{3,∞} | r{3,12i} | r{3,9i} | r{3,6i} | ||
| Coxeter |
||||||||||||
| Dual uniform figures | ||||||||||||
| Dual conf. |
 V(3.3)2 |
 V(3.4)2 |
 V(3.5)2 |
 V(3.6)2 |
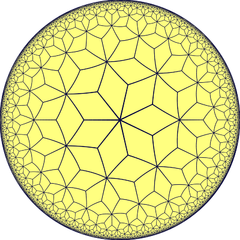 V(3.7)2 |
 V(3.8)2 |
 V(3.∞)2 |
|||||
| Symmetry mutations of dual quasiregular tilings: V(3.n)2 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *n32 | Spherical | Euclidean | Hyperbolic | ||||||||
| *332 | *432 | *532 | *632 | *732 | *832... | *∞32 | |||||
| Tiling |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||
| Conf. | V(3.3)2 | V(3.4)2 | V(3.5)2 | V(3.6)2 | V(3.7)2 | V(3.8)2 | V(3.∞)2 | ||||
Expanded tilings
| *n42 symmetry mutation of expanded tilings: 3.4.n.4 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry *n32 [n,3] |
Spherical | Euclid. | Compact hyperb. | Paraco. | Noncompact hyperbolic | |||||||
| *232 [2,3] |
*332 [3,3] |
*432 [4,3] |
*532 [5,3] |
*632 [6,3] |
*732 [7,3] |
*832 [8,3]... |
*∞32 [∞,3] |
[12i,3] |
[9i,3] |
[6i,3] | ||
| Figure |  |
 |
 |
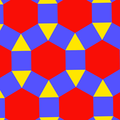 |
 |
 |
 |
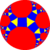 |
 |
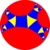 | ||
| Config. | 3.4.2.4 | 3.4.3.4 | 3.4.4.4 | 3.4.5.4 | 3.4.6.4 | 3.4.7.4 | 3.4.8.4 | 3.4.∞.4 | 3.4.12i.4 | 3.4.9i.4 | 3.4.6i.4 | |
| Symmetry *n32 [n,3] |
Spherical | Euclid. | Compact hyperb. | Paraco. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *232 [2,3] |
*332 [3,3] |
*432 [4,3] |
*532 [5,3] |
*632 [6,3] |
*732 [7,3] |
*832 [8,3]... |
*∞32 [∞,3] | |
| Figure Config. |
 V3.4.2.4 |
 V3.4.3.4 |
 V3.4.4.4 |
 V3.4.5.4 |
 V3.4.6.4 |
 V3.4.7.4 |
 V3.4.8.4 |
 V3.4.∞.4 |
Omnitruncated tilings
| *n32 symmetry mutations of omnitruncated tilings: 4.6.2n | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sym. *n32 [n,3] |
Spherical | Euclid. | Compact hyperb. | Paraco. | Noncompact hyperbolic | |||||||
| *232 [2,3] |
*332 [3,3] |
*432 [4,3] |
*532 [5,3] |
*632 [6,3] |
*732 [7,3] |
*832 [8,3] |
*∞32 [∞,3] |
[12i,3] |
[9i,3] |
[6i,3] |
[3i,3] | |
| Figures |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
| Config. | 4.6.4 | 4.6.6 | 4.6.8 | 4.6.10 | 4.6.12 | 4.6.14 | 4.6.16 | 4.6.∞ | 4.6.24i | 4.6.18i | 4.6.12i | 4.6.6i |
| Duals |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Config. | V4.6.4 | V4.6.6 | V4.6.8 | V4.6.10 | V4.6.12 | V4.6.14 | V4.6.16 | V4.6.∞ | V4.6.24i | V4.6.18i | V4.6.12i | V4.6.6i |
Snub tilings
| n32 symmetry mutations of snub tilings: 3.3.3.3.n | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry n32 |
Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperbolic | Paracomp. | ||||
| 232 | 332 | 432 | 532 | 632 | 732 | 832 | ∞32 | |
| Snub figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Config. | 3.3.3.3.2 | 3.3.3.3.3 | 3.3.3.3.4 | 3.3.3.3.5 | 3.3.3.3.6 | 3.3.3.3.7 | 3.3.3.3.8 | 3.3.3.3.∞ |
| Gryro figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
| Config. | V3.3.3.3.2 | V3.3.3.3.3 | V3.3.3.3.4 | V3.3.3.3.5 | V3.3.3.3.6 | V3.3.3.3.7 | V3.3.3.3.8 | V3.3.3.3.∞ |
*n42 symmetry
Regular tilings
| *n42 symmetry mutation of regular tilings: {4,n} | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperbolic | Paracompact | ||||||||
 {4,3} |
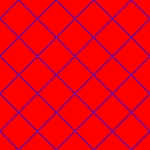 {4,4} |
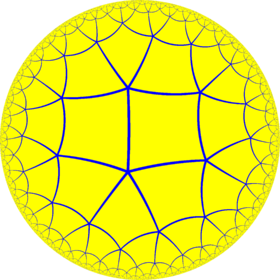 {4,5} |
 {4,6} |
 {4,7} |
 {4,8}... |
 {4,∞} | |||||
| *n42 symmetry mutation of regular tilings: {n,4} | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spherical | Euclidean | Hyperbolic tilings | |||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
| 24 | 34 | 44 | 54 | 64 | 74 | 84 | ...∞4 |
Quasiregular tilings
| *n42 symmetry mutations of quasiregular tilings: (4.n)2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry *4n2 [n,4] |
Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperbolic | Paracompact | Noncompact | |||
| *342 [3,4] |
*442 [4,4] |
*542 [5,4] |
*642 [6,4] |
*742 [7,4] |
*842 [8,4]... |
*∞42 [∞,4] |
[ni,4] | |
| Figures |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Config. | (4.3)2 | (4.4)2 | (4.5)2 | (4.6)2 | (4.7)2 | (4.8)2 | (4.∞)2 | (4.ni)2 |
| *n42 symmetry mutations of quasiregular dual tilings: V(4.n)2 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry *4n2 [n,4] |
Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperbolic | Paracompact | Noncompact | ||||||
| *342 [3,4] |
*442 [4,4] |
*542 [5,4] |
*642 [6,4] |
*742 [7,4] |
*842 [8,4]... |
*∞42 [∞,4] |
[iπ/λ,4] | ||||
| Tiling Conf. |
 V4.3.4.3 |
 V4.4.4.4 |
 V4.5.4.5 |
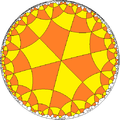 V4.6.4.6 |
 V4.7.4.7 |
 V4.8.4.8 |
 V4.∞.4.∞ |
V4.∞.4.∞ | |||
Truncated tilings
| *n42 symmetry mutation of truncated tilings: 4.2n.2n | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry *n42 [n,4] |
Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperbolic | Paracomp. | |||||||
| *242 [2,4] |
*342 [3,4] |
*442 [4,4] |
*542 [5,4] |
*642 [6,4] |
*742 [7,4] |
*842 [8,4]... |
*∞42 [∞,4] | ||||
| Truncated figures |
 |
 |
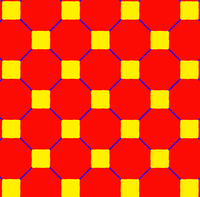 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |||
| Config. | 4.4.4 | 4.6.6 | 4.8.8 | 4.10.10 | 4.12.12 | 4.14.14 | 4.16.16 | 4.∞.∞ | |||
| n-kis figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |||
| Config. | V4.4.4 | V4.6.6 | V4.8.8 | V4.10.10 | V4.12.12 | V4.14.14 | V4.16.16 | V4.∞.∞ | |||
| *n42 symmetry mutation of truncated tilings: n.8.8 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry *n42 [n,4] |
Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperbolic | Paracompact | |||||||
| *242 [2,4] |
*342 [3,4] |
*442 [4,4] |
*542 [5,4] |
*642 [6,4] |
*742 [7,4] |
*842 [8,4]... |
*∞42 [∞,4] | ||||
| Truncated figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |||
| Config. | 2.8.8 | 3.8.8 | 4.8.8 | 5.8.8 | 6.8.8 | 7.8.8 | 8.8.8 | ∞.8.8 | |||
| n-kis figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
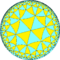 |
 |
 |
 | |||
| Config. | V2.8.8 | V3.8.8 | V4.8.8 | V5.8.8 | V6.8.8 | V7.8.8 | V8.8.8 | V∞.8.8 | |||
Expanded tilings
| *n42 symmetry mutation of expanded tilings: n.4.4.4 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry [n,4], (*n42) |
Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperbolic | Paracomp. | |||||||
| *342 [3,4] |
*442 [4,4] |
*542 [5,4] |
*642 [6,4] |
*742 [7,4] |
*842 [8,4] |
*∞42 [∞,4] | |||||
| Expanded figures |
 |
 |
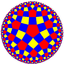 |
 |
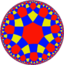 |
 |
 | ||||
| Config. | 3.4.4.4 | 4.4.4.4 | 5.4.4.4 | 6.4.4.4 | 7.4.4.4 | 8.4.4.4 | ∞.4.4.4 | ||||
| Rhombic figures config. |
 V3.4.4.4 |
 V4.4.4.4 |
 V5.4.4.4 |
 V6.4.4.4 |
 V7.4.4.4 |
 V8.4.4.4 |
 V∞.4.4.4 | ||||
Omnitruncated tilings
| *n42 symmetry mutation of omnitruncated tilings: 4.8.2n | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry *n42 [n,4] |
Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperbolic | Paracomp. | ||||
| *242 [2,4] |
*342 [3,4] |
*442 [4,4] |
*542 [5,4] |
*642 [6,4] |
*742 [7,4] |
*842 [8,4]... |
*∞42 [∞,4] | |
| Omnitruncated figure |
 4.8.4 |
 4.8.6 |
 4.8.8 |
 4.8.10 |
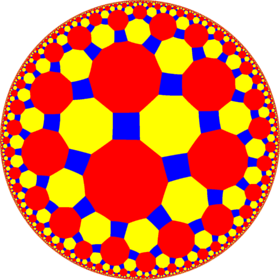 4.8.12 |
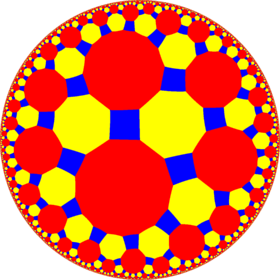 4.8.14 |
 4.8.16 |
 4.8.∞ |
| Omnitruncated duals |
 V4.8.4 |
 V4.8.6 |
 V4.8.8 |
 V4.8.10 |
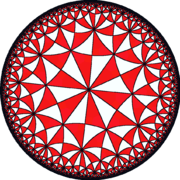 V4.8.12 |
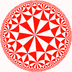 V4.8.14 |
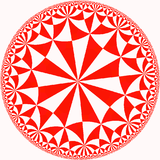 V4.8.16 |
 V4.8.∞ |
Snub tilings
| 4n2 symmetry mutations of snub tilings: 3.3.4.3.n | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry 4n2 |
Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperbolic | Paracomp. | ||||
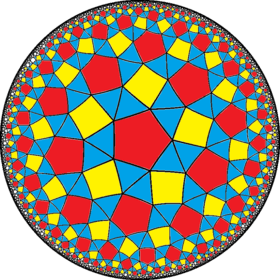
| 242 | 342 | 442 | 542 | 642 | 742 | 842 | ∞42 | |
| Snub figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Config. | 3.3.4.3.2 | 3.3.4.3.3 | 3.3.4.3.4 | 3.3.4.3.5 | 3.3.4.3.6 | 3.3.4.3.7 | 3.3.4.3.8 | 3.3.4.3.∞ |
| Gyro figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||
| Config. | V3.3.4.3.2 | V3.3.4.3.3 | V3.3.4.3.4 | V3.3.4.3.5 | V3.3.4.3.6 | V3.3.4.3.7 | V3.3.4.3.8 | V3.3.4.3.∞ |
*n52 symmetry
Regular tilings
| Sphere | Hyperbolic plane | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 {5,3} |
 {5,4} |
 {5,5} |
 {5,6} |
 {5,7} |
 {5,8} |
 ...{5,∞} |
*n62 symmetry
Regular tilings
| *n62 symmetry mutation of regular tilings: {6,n} | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spherical | Euclidean | Hyperbolic tilings | ||||||
 {6,2} |
 {6,3} |
 {6,4} |
 {6,5} |
 {6,6} |
 {6,7} |
 {6,8} |
... |  {6,∞} |
*n82 symmetry
Regular tilings
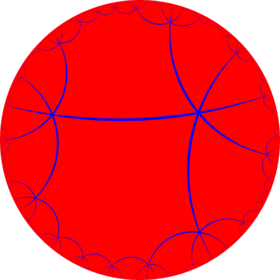
| Space | Spherical | Compact hyperbolic | Paracompact | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiling |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
| Config. | 8.8 | 83 | 84 | 85 | 86 | 87 | 88 | ...8∞ |
References
- John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strass, The Symmetries of Things 2008, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5
- From hyperbolic 2-space to Euclidean 3-space: Tilings and patterns via topology Stephen Hyde