Demography of the United States
| Demographics of the United States | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Population | 324,420,000 (3rd) |
| Density |
84.54 people/sq mi (180th) 32.54 people/km2 |
| Growth rate |
|
| Birth rate | 13.42 births/1,000 population (147th) |
| Death rate | 8.15/1,000 population (100th) |
| Life expectancy | 79.56 years (36th) |
| • male | 77.11 years |
| • female | 81.94 years |
| Fertility rate | 1.82 children/woman (123rd) |
| Infant mortality rate | 6.17 deaths/1,000 live births |
| Net migration rate | 2.45 migrants/1,000 population |
| Age structure | |
| 0–14 years | 19.4% |
| 15–64 years | 66.2% |
| 65 and over | 14.4% |
| Nationality | |
| Nationality | American |
| Language | |
| Official | None at the federal level |
| Spoken | English 80%, Spanish 12.4%, other Indo-European 3.7%, Asian and Pacific island languages 3%, other languages 0.9% |
As of July 1, 2017, the United States has a total resident population of 325,350,377 making it the third most populous country in the world.[1] It is very urbanized, with 81% residing in cities and suburbs as of 2014 (the worldwide urban rate is 54%).[2] California and Texas are the most populous states,[3] as the mean center of U.S. population has consistently shifted westward and southward.[4] New York City is the most populous city in the United States.[5]
The total fertility rate in the United States estimated for 2016 is 1.82 children per woman,[6][7] which is below the replacement fertility rate of approximately 2.1. Compared to other Western countries, in 2012, U.S. fertility rate was lower than that of France (2.01),[8] Australia (1.93) and the United Kingdom (1.92).[9] However, U.S. population growth is among the highest in industrialized countries,[10] because the differences in fertility rates are less than the differences in immigration levels, which are higher in the U.S.[11][12] The United States Census Bureau shows a population increase of 0.75% for the twelve-month period ending in July 2012. Though high by industrialized country standards, this is below the world average annual rate of 1.1%.[10]
There were about 125.9 million adult women in the United States in 2014. The number of men was 119.4 million. At age 85 and older, there were almost twice as many women as men (4 million vs. 2.1 million). People under 21 years of age made up over a quarter of the U.S. population (27.1%), and people age 65 and over made up one-seventh (14.5%).[13] The national median age was 37.8 years in 2015.[14]
The United States Census Bureau defines White people as those "having origins in any of the original peoples of Europe, the Middle East, or North Africa." It includes people who reported "White" or wrote in entries such as Irish, German, Italian, Lebanese, Near Easterner, Arab, or Polish."[15] Whites constitute the majority of the U.S. population, with a total of about 245,532,000 or 77.7% of the population as of 2013. Non-Hispanic whites make up 62.6% of the country's population. Despite major changes due to immigration since the 1960s, and the higher birth-rates of nonwhites, the overall current majority of American citizens are still white, and English-speaking, though regional differences exist.
The American population almost quadrupled during the 20th century—at a growth rate of about 1.3% a year—from about 76 million in 1900 to 281 million in 2000. It reached the 200 million mark in 1968, and the 300 million mark on October 17, 2006.[16][17] Population growth is fastest among minorities as a whole, and according to the Census Bureau's estimation for 2012, 50.4% of American children under the age of 1 belonged to minority groups.[18]
Hispanic and Latino Americans accounted for 48% of the national population growth of 2.9 million between July 1, 2005, and July 1, 2006.[19] Immigrants and their U.S.-born descendants are expected to provide most of the U.S. population gains in the decades ahead.[20]
The Census Bureau projects a U.S. population of 417 million in 2060, which is a 38% increase from 2007 (301.3 million).[21] However, the United Nations projects a U.S. population of 402 million in 2050, an increase of 32% from 2007.[22] In an official census report, it was reported that 54.4% (2,150,926 out of 3,953,593) of births in 2010 were non-Hispanic white. This represents an increase of 0.34% compared to the previous year, which was 54.06%.[23]
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 3,929,214 | — | |
| 1800 | 5,236,631 | 33.3% | |
| 1810 | 7,239,881 | 38.3% | |
| 1820 | 9,638,453 | 33.1% | |
| 1830 | 12,866,020 | 33.5% | |
| 1840 | 17,069,453 | 32.7% | |
| 1850 | 23,191,876 | 35.9% | |
| 1860 | 31,443,321 | 35.6% | |
| 1870 | 38,558,371 | 22.6% | |
| 1880 | 49,371,340 | 28.0% | |
| 1890 | 62,979,766 | 27.6% | |
| 1900 | 76,212,168 | 21.0% | |
| 1910 | 92,228,531 | 21.0% | |
| 1920 | 106,021,568 | 15.0% | |
| 1930 | 123,202,660 | 16.2% | |
| 1940 | 132,165,129 | 7.3% | |
| 1950 | 151,325,798 | 14.5% | |
| 1960 | 179,323,175 | 18.5% | |
| 1970 | 203,211,926 | 13.3% | |
| 1980 | 226,545,805 | 11.5% | |
| 1990 | 248,709,873 | 9.8% | |
| 2000 | 281,421,906 | 13.2% | |
| 2010 | 308,745,538 | 9.7% | |
| Est. 2017 | 324,700,000 | 5.2% | |
| Sources: United States Census Bureau[24][25][26] Note that the census numbers do not include American Indian natives before 1860. | |||
History

In 1900, when the U.S. population was 76 million, there were 66.8 million Whites in the United States, representing 88% of the total population,[27] 8.8 million Black Americans, with about 90% of them still living in Southern states,[28] and slightly more than 500,000 Hispanics.[29]
Under the law, the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965,[30] the number of first-generation immigrants living in the United States has increased,[31] from 9.6 million in 1970 to about 38 million in 2007.[32] Around a million people legally immigrated to the United States per year in the 1990s, up from 250,000 per year in the 1950s.[33] In 2009, 37% of immigrants originated in Asia, 42% in North America, and 11% in Africa.[34]
In 1900, non-Hispanic whites comprised almost 97% of the population of the 10 largest American cities.[35] The Census Bureau reported that minorities (including Hispanic whites) made up 50.4% of the children born in the U.S. between July 2010 and July 2011,[36] compared to 37% in 1990.[37]
In 2010 the state with the lowest fertility rate was Rhode Island, with a rate of 1.63, while Utah had the greatest rate with a rate of 2.45.[38] This correlates with the ages of the states' populations: Rhode Island has the ninth-oldest median age in the US—39.2—while Utah has the youngest—29.0.[39]
Vital statistics

The U.S. total fertility rate as of 2010 census is 1.931:
- 1.948 for White Americans (including White Hispanics)
- 1.791 for non-Hispanic Whites
- 1.972 for Black Americans (including Black Hispanics)
- 1.958 for non-Hispanic Blacks
- 1.404 for Native Americans (including Hispanics)
- 1.689 for Asian Americans (including Hispanics)
Other:[40]
- 2.350 for Hispanics (of all racial groups)
- 1.831 for non-Hispanics (of all racial groups)
(Note that ~95% of Hispanics are included as "white Hispanics" by CDC, which does not recognize the Census' "Some other race" category and counts people in that category as white.)
Source: National Vital statistics report based on 2010 US Census data[23]
Vital statistics
| Average population (x 1,000)[41] | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1,000) | Crude death rate (per 1,000)[42] | Natural change (per 1,000) | Total fertility rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1935 | 127,362 | 2,377,000 | 1,392,752 | 984,248 | 18.7 | 10.9 | 7.7 | 2.19 |
| 1936 | 128,181 | 2,355,000 | 1,479,228 | 875,772 | 18.4 | 11.5 | 6.8 | 2.15 |
| 1937 | 128,961 | 2,413,000 | 1,450,427 | 962,573 | 18.7 | 11.2 | 7.5 | 2.17 |
| 1938 | 129,969 | 2,496,000 | 1,381,391 | 1,114,609 | 19.2 | 10.6 | 8.6 | 2.22 |
| 1939 | 131,028 | 2,466,000 | 1,387,897 | 1,078,103 | 18.8 | 10.6 | 8.2 | 2.17 |
| 1940 | 132,165 | 2,559,000 | 1,417,269 | 1,142,000 | 19.4 | 10.8 | 8.6 | 2.23 |
| 1941 | 133,002 | 2,703,000 | 1,397,642 | 1,305,358 | 20.3 | 10.5 | 9.8 | 2.33 |
| 1942 | 134,464 | 2,989,000 | 1,385,187 | 1,603,813 | 22.2 | 10.3 | 11.9 | 2.55 |
| 1943 | 136,003 | 3,104,000 | 1,459,544 | 1,644,306 | 22.8 | 10.7 | 12.1 | 2.64 |
| 1944 | 138,083 | 2,939,000 | 1,411,338 | 1,644,456 | 21.2 | 10.2 | 11.0 | 2.49 |
| 1945 | 139,994 | 2,858,000 | 1,401,719 | 1,456,281 | 20.4 | 10.0 | 10.4 | 2.42 |
| 1946 | 140,008 | 3,411,000 | 1,395,617 | 2,015,383 | 24.1 | 10.0 | 14.1 | 2.86 |
| 1947 | 145,023 | 3,817,000 | 1,445,370 | 2,371,630 | 26.6 | 10.0 | 16.6 | 3.18 |
| 1948 | 148,013 | 3,637,000 | 1,444,337 | 2,192,663 | 24.9 | 9.8 | 15.1 | 3.03 |
| 1949 | 149,336 | 3,649,000 | 1,443,607 | 2,205,393 | 24.5 | 9.7 | 14.8 | 3.04 |
| 1950 | 151,861 | 3,632,000 | 1,452,454 | 2,180,000 | 24.1 | 9.6 | 14.5 | 3.03 |
| 1951 | 154,056 | 3,823,000 | 1,482,099 | 2,340,901 | 24.8 | 9.6 | 15.2 | 3.20 |
| 1952 | 156,431 | 3,913,000 | 1,496,838 | 2,416,162 | 25.0 | 9.6 | 15.4 | 3.30 |
| 1953 | 159,047 | 3,965,000 | 1,447,459 | 2,517,541 | 25.2 | 9.1 | 16.1 | 3.36 |
| 1954 | 161,948 | 4,078,000 | 1,481,091 | 2,596,909 | 24.8 | 9.3 | 15.5 | 3.48 |
| 1955 | 163,476 | 4,097,000 | 1,528,717 | 2,568,283 | 25.0 | 9.3 | 14.3 | 3.52 |
| 1956 | 166,578 | 4,218,000 | 1,564,476 | 2,653,524 | 25.1 | 9.3 | 15.8 | 3.63 |
| 1957 | 169,637 | 4,308,000 | 1,633,128 | 2,666,872 | 25.3 | 9.5 | 15.8 | 3.71 |
| 1958 | 172,668 | 4,255,000 | 1,647,886 | 2,607,114 | 24.4 | 9.5 | 14.9 | 3.65 |
| 1959 | 175,642 | 4,244,796 | 1,656,814 | 2,587,982 | 24.0 | 9.4 | 14.7 | 3.66 |
| 1960 | 179,979 | 4,257,850 | 1,711,982 | 2,545,868 | 23.7 | 9.5 | 14.1 | 3.65 |
| 1961 | 182,992 | 4,268,326 | 1,701,522 | 2,566,804 | 23.3 | 9.3 | 14.0 | 3.62 |
| 1962 | 185,771 | 4,167,362 | 1,756,720 | 2,410,642 | 22.4 | 9.5 | 12.9 | 3.46 |
| 1963 | 188,483 | 4,098,020 | 1,813,549 | 2,284,471 | 21.7 | 9.6 | 12.1 | 3.32 |
| 1964 | 191,141 | 4,027,490 | 1,798,051 | 2,229,439 | 21.1 | 9.4 | 11.7 | 3.19 |
| 1965 | 193,526 | 3,760,358 | 1,828,136 | 1,932,222 | 19.4 | 9.5 | 9.9 | 2.91 |
| 1966 | 195,576 | 3,606,274 | 1,863,149 | 1,743,125 | 18.4 | 9.5 | 8.9 | 2.72 |
| 1967 | 197,457 | 3,520,959 | 1,851,323 | 1,669,636 | 17.8 | 9.4 | 8.4 | 2.56 |
| 1968 | 199,399 | 3,501,564 | 1,930,082 | 1,571,482 | 17.6 | 9.7 | 7.9 | 2.46 |
| 1969 | 201,385 | 3,600,206 | 1,921,990 | 1,678,216 | 17.9 | 9.5 | 8.4 | 2.46 |
| 1970 | 203,984 | 3,731,386 | 1,921,031 | 1,810,355 | 18.4 | 9.4 | 9.0 | 2.480 |
| 1971 | 206,827 | 3,555,970 | 1,927,542 | 1,628,428 | 17.2 | 9.3 | 7.9 | 2.266 |
| 1972 | 209,284 | 3,258,411 | 1,963,944 | 1,294,467 | 15.6 | 9.4 | 6.2 | 2.010 |
| 1973 | 211,357 | 3,136,965 | 1,973,003 | 1,163,962 | 14.8 | 9.5 | 5.3 | 1.879 |
| 1974 | 213,342 | 3,159,958 | 1,934,388 | 1,225,570 | 14.8 | 9.1 | 5.7 | 1.835 |
| 1975 | 215,465 | 3,144,198 | 1,892,879 | 1,251,319 | 14.6 | 8.8 | 5.8 | 1.774 |
| 1976 | 217,563 | 3,167,788 | 1,909,440 | 1,258,348 | 14.6 | 8.8 | 5.8 | 1.738 |
| 1977 | 219,760 | 3,326,632 | 1,899,597 | 1,427,035 | 15.1 | 8.6 | 6.5 | 1.789 |
| 1978 | 222,095 | 3,333,279 | 1,927,788 | 1,405,491 | 15.0 | 8.7 | 6.3 | 1.760 |
| 1979 | 224,567 | 3,494,398 | 1,913,841 | 1,580,557 | 15.6 | 8.5 | 7.1 | 1.808 |
| 1980 | 227,225 | 3,612,258 | 1,989,841 | 1,622,417 | 15.9 | 8.8 | 7.1 | 1.839 |
| 1981 | 229,466 | 3,629,238 | 1,977,981 | 1,651,257 | 15.8 | 8.6 | 7.2 | 1.812 |
| 1982 | 231,664 | 3,680,537 | 1,974,797 | 1,705,740 | 15.9 | 8.5 | 7.4 | 1.827 |
| 1983 | 233,792 | 3,638,933 | 2,019,201 | 1,619,732 | 15.6 | 8.6 | 6.9 | 1.799 |
| 1984 | 235,825 | 3,669,141 | 2,039,369 | 1,629,772 | 15.6 | 8.6 | 6.9 | 1.806 |
| 1985 | 237,924 | 3,760,561 | 2,086,440 | 1,674,121 | 15.8 | 8.8 | 7.0 | 1.844 |
| 1986 | 240,133 | 3,756,547 | 2,105,361 | 1,651,186 | 15.6 | 8.8 | 6.9 | 1.837 |
| 1987 | 242,289 | 3,809,394 | 2,123,323 | 1,686,071 | 15.7 | 8.8 | 7.0 | 1.872 |
| 1988 | 244,499 | 3,909,510 | 2,167,999 | 1,741,511 | 16.0 | 8.9 | 7.1 | 1.934 |
| 1989 | 246,819 | 4,040,958 | 2,150,466 | 1,890,492 | 16.4 | 8.7 | 7.7 | 2.014 |
| 1990 | 249,623 | 4,158,212 | 2,148,463 | 2,009,749 | 16.7 | 8.6 | 8.1 | 2.081 |
| 1991 | 252,981 | 4,110,907 | 2,169,518 | 1,941,389 | 16.2 | 8.6 | 7.7 | 2.062 |
| 1992 | 256,514 | 4,065,014 | 2,175,613 | 1,889,401 | 15.8 | 8.5 | 7.4 | 2.046 |
| 1993 | 259,919 | 4,000,240 | 2,268,553 | 1,731,687 | 15.4 | 8.7 | 6.7 | 2.019 |
| 1994 | 263,126 | 3,952,767 | 2,278,994 | 1,673,773 | 15.0 | 8.7 | 6.4 | 2.001 |
| 1995 | 266,278 | 3,899,589 | 2,312,132 | 1,587,457 | 14.6 | 8.7 | 6.0 | 1.978 |
| 1996 | 269,394 | 3,891,494 | 2,314,690 | 1,576,804 | 14.4 | 8.6 | 5.9 | 1.976 |
| 1997 | 272,647 | 3,880,894 | 2,314,245 | 1,566,649 | 14.2 | 8.5 | 5.7 | 1.971 |
| 1998 | 275,854 | 3,941,553 | 2,337,256 | 1,604,297 | 14.3 | 8.5 | 5.8 | 1.999 |
| 1999 | 279,040 | 3,959,417 | 2,391,399 | 1,568,018 | 14.2 | 8.6 | 5.6 | 2.007 |
| 2000 | 282,172 | 4,058,814 | 2,403,351 | 1,655,463 | 14.4 | 8.5 | 5.9 | 2.056 |
| 2001 | 285,082 | 4,025,933 | 2,416,425 | 1,609,508 | 14.1 | 8.5 | 5.6 | 2.030 |
| 2002 | 287,804 | 4,021,726 | 2,443,387 | 1,578,339 | 14.0 | 8.5 | 5.5 | 2.020 |
| 2003 | 290,326 | 4,089,950 | 2,448,288 | 1,641,662 | 14.1 | 8.4 | 5.5 | 2.047 |
| 2004 | 293,046 | 4,112,052 | 2,397,615 | 1,714,437 | 14.0 | 8.2 | 5.9 | 2.051 |
| 2005 | 295,753 | 4,138,349 | 2,448,017 | 1,690,332 | 14.0 | 8.3 | 5.7 | 2.057 |
| 2006 | 298,593 | 4,265,555 | 2,426,264 | 1,839,291 | 14.3 | 8.1 | 6.2 | 2.108 |
| 2007 | 301,580 | 4,316,234 | 2,423,712 | 1,892,522 | 14.3 | 8.0 | 6.3 | 2.120 |
| 2008 | 304,375 | 4,247,694 | 2,471,984 | 1,775,710 | 14.0 | 8.1 | 5.9 | 2.072 |
| 2009 | 307,007 | 4,130,665 | 2,437,163 | 1,693,502 | 13.5 | 7.9 | 5.6 | 2.002 |
| 2010 | 309,330 | 3,999,386 | 2,468,435 | 1,530,951 | 13.0 | 8.0 | 5.0 | 1.931 |
| 2011 | 311,583 | 3,953,590 | 2,515,458 | 1,438,412 | 12.7 | 8.1 | 4.6 | 1.894 |
| 2012 | 313,874 | 3,952,841 | 2,543,279 | 1,409,562 | 12.6 | 8.1 | 4.5 | 1.880 |
| 2013 | 316,129 | 3,932,181 | 2,596,993 | 1,336,183 | 12.4 | 8.2 | 4.2 | 1.857 |
| 2014 | 319,113 | 3,988,076 | 2,626,418 | 1,361,658 | 12.5 | 8.2 | 4.3 | 1.862 |
| 2015 | 321,442 | 3,978,497 | 2,712,630 | 1,265,867 | 12.4 | 8.4 | 4.0 | 1.843 |
| 2016 | 323,100 | 3,941,109 | 2,733,000 | 1,209,000 | 12.2 | 8.4 | 3.8 | 1.818 |
Population density
The most densely populated state is New Jersey (1,121/mi2 or 433/km2). See List of U.S. states by population density for maps and complete statistics.
The United States Census Bureau publishes a popular "dot" or "nighttime" map showing population distribution at resolutions of 1,000 and 7,500 people,[43] as well as complete listings of population density by place name.[44]
Cities
The United States has dozens of major cities, including 31 "global cities"[45] of all types, with 10 in the "alpha" group of global cities: New York City, Los Angeles, Chicago, Washington, DC, Boston, San Francisco, Miami, Philadelphia, Dallas, and Atlanta.[46] As of 2011, the United States had 51 metropolitan areas with a population of over 1,000,000 people each. (See Table of United States Metropolitan Statistical Areas.)
As of 2011, about 250 million Americans live in or around urban areas. That means more than three-quarters of the U.S. population shares just about three percent of the U.S. land area.[47]
The following table shows the populations of the top twenty metropolitan areas, at the time of the 2010 Census. Note Denver and Baltimore have over 2.5 million residents in their metro areas.
Race and ethnicity


The U.S. population's distribution by race and ethnicity in 2010 was as follows; due to rounding, percentage figures may not add up to the totals shown.[50]
Hispanic or Latino origin

The total population of Hispanic and Latino Americans comprised 50.5 million or 16.3% of the national total in 2010. The category of "Hispanic or Latino" is considered by the U.S. Census Bureau to be separate from racial categories, including all people who identify their ethnicity as Hispanic or Latino.[51] The U.S. Census Bureau defines Hispanic or Latino as "those who classify themselves in one of the specific Hispanic or Latino categories listed on the Census 2000 or ACS questionnaire"—"Mexican", "Puerto Rican", or "Cuban"—as well as those who indicate that they are "other Spanish, Hispanic, or Latino."[52] Persons whose ethnicity is identified as Hispanic or Latino may be of any race.
Breakdown by state/territory
| State or District | Population (2010) | Non-Hispanic White | Hispanic or Latino | Black | American Indian or Alaskan Native | Asian | Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander | Mixed race |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 4,779,736 | 67.0 | 3.9 | 26.2 | 0.6 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 1.5 |
| Alaska | 710,231 | 64.1 | 5.5 | 3.3 | 14.8 | 5.4 | 1.0 | 7.3 |
| American Samoa | 55,519 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.8 | 91.6 | 4.5 |
| Arizona | 6,392,017 | 57.8 | 29.6 | 4.1 | 4.6 | 2.8 | 0.2 | 3.4 |
| Arkansas | 2,915,918 | 74.5 | 6.4 | 15.4 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 2.0 |
| California | 37,253,956 | 40.1 | 37.6 | 6.2 | 1.0 | 13.0 | 0.4 | 4.9 |
| Colorado | 5,029,196 | 70.0 | 20.7 | 4.0 | 1.1 | 2.8 | 0.1 | 3.4 |
| Connecticut | 3,574,097 | 71.2 | 13.4 | 10.1 | 0.3 | 3.8 | 0.0 | 2.6 |
| Delaware | 897,934 | 65.3 | 8.2 | 21.4 | 0.5 | 3.2 | 0.0 | 2.7 |
| District of Columbia | 601,723 | 34.8 | 9.1 | 50.7 | 0.3 | 3.5 | 0.1 | 2.9 |
| Florida | 18,801,310 | 57.9 | 22.5 | 16.0 | 0.4 | 2.4 | 0.1 | 2.5 |
| Georgia | 9,687,653 | 55.9 | 8.8 | 30.5 | 0.3 | 3.2 | 0.1 | 2.1 |
| Guam | 159,358 | 6.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 32.6 | 37.1 | 12.1 |
| Hawaii | 1,360,301 | 22.7 | 8.9 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 38.6 | 10.0 | 23.6 |
| Idaho | 1,567,582 | 84.0 | 11.2 | 0.6 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 2.5 |
| Illinois | 12,830,632 | 63.7 | 15.8 | 14.5 | 0.3 | 4.6 | 0.0 | 2.3 |
| Indiana | 6,483,802 | 81.5 | 6.0 | 9.1 | 0.3 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 2.0 |
| Iowa | 3,046,355 | 88.7 | 5.0 | 2.9 | 0.4 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 1.8 |
| Kansas | 2,853,118 | 78.2 | 10.5 | 5.9 | 1.0 | 2.4 | 0.1 | 3.0 |
| Kentucky | 4,339,367 | 86.3 | 3.1 | 7.8 | 0.2 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 1.7 |
| Louisiana | 4,533,372 | 60.3 | 4.2 | 32.0 | 0.7 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 1.6 |
| Maine | 1,328,361 | 94.4 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 1.6 |
| Maryland | 5,773,552 | 54.7 | 8.2 | 29.4 | 0.4 | 5.5 | 0.1 | 2.9 |
| Massachusetts | 6,547,629 | 76.1 | 9.6 | 6.6 | 0.3 | 5.3 | 0.0 | 2.6 |
| Michigan | 9,883,640 | 76.6 | 4.4 | 14.2 | 0.6 | 2.4 | 0.0 | 2.3 |
| Minnesota | 5,303,925 | 83.1 | 4.7 | 5.2 | 1.1 | 4.0 | 0.0 | 2.4 |
| Mississippi | 2,967,297 | 58.0 | 2.7 | 37.0 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 1.1 |
| Missouri | 5,988,927 | 81.0 | 3.5 | 11.6 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 2.1 |
| Montana | 989,415 | 87.8 | 2.9 | 0.4 | 6.3 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 2.5 |
| Nebraska | 1,826,341 | 82.1 | 9.2 | 4.5 | 1.0 | 1.8 | 0.1 | 2.2 |
| Nevada | 2,700,551 | 54.1 | 26.5 | 8.1 | 1.2 | 7.2 | 0.6 | 4.7 |
| New Hampshire | 1,316,470 | 92.3 | 2.8 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 2.2 | 0.0 | 1.6 |
| New Jersey | 8,791,894 | 59.3 | 17.7 | 13.7 | 0.3 | 8.3 | 0.0 | 2.7 |
| New Mexico | 2,059,179 | 40.5 | 46.3 | 2.1 | 9.4 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 3.7 |
| New York | 19,378,102 | 58.3 | 17.6 | 15.9 | 0.6 | 7.3 | 0.0 | 3.0 |
| North Carolina | 9,535,483 | 65.3 | 8.4 | 21.5 | 1.3 | 2.2 | 0.1 | 2.2 |
| North Dakota | 672,591 | 88.9 | 2.0 | 1.2 | 5.4 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 1.8 |
| Northern Mariana Islands | 53,833 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50.0 | 34.9 | 12.7 |
| Ohio | 11,536,504 | 81.1 | 3.1 | 12.2 | 0.2 | 1.7 | 0.0 | 2.1 |
| Oklahoma | 3,751,351 | 68.7 | 8.9 | 7.4 | 8.6 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 5.9 |
| Oregon | 3,831,074 | 78.5 | 11.7 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 3.7 | 0.3 | 3.8 |
| Pennsylvania | 12,702,379 | 79.5 | 5.7 | 10.8 | 0.2 | 2.7 | 0.0 | 1.9 |
| Puerto Rico | 3,725,789 | 0.7 | 99.0 | 12.4 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 3.3 |
| Rhode Island | 1,052,567 | 76.4 | 12.4 | 5.7 | 0.6 | 2.9 | 0.1 | 3.3 |
| South Carolina | 4,625,364 | 64.1 | 5.1 | 27.9 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 0.1 | 1.7 |
| South Dakota | 814,180 | 84.7 | 2.7 | 1.3 | 8.8 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 2.1 |
| Tennessee | 6,346,105 | 75.6 | 4.6 | 16.7 | 0.3 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 1.7 |
| Texas | 25,145,561 | 45.3 | 37.6 | 11.8 | 0.7 | 3.8 | 0.1 | 2.7 |
| Utah | 2,763,885 | 80.4 | 13.0 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 2.0 | 0.9 | 2.7 |
| Vermont | 625,741 | 94.3 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 0.0 | 1.7 |
| Virginia | 8,001,024 | 64.8 | 7.9 | 19.4 | 0.4 | 5.5 | 0.1 | 2.9 |
| Virgin Islands | 106,405 | 13.5 | 17.4 | 66.1 | 0 | 1.4 | 0 | 0 |
| Washington | 6,724,540 | 72.5 | 11.2 | 3.6 | 1.5 | 7.2 | 0.6 | 4.7 |
| West Virginia | 1,852,994 | 93.2 | 1.2 | 3.4 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 1.5 |
| Wisconsin | 5,686,986 | 83.3 | 5.9 | 6.3 | 1.0 | 2.3 | 0.0 | 1.8 |
| Wyoming | 563,626 | 85.9 | 8.9 | 0.8 | 2.4 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 2.2 |
- All Data from 2010 U.S. Census Bureau[53]
Other groups
There were 22.1 million veterans in 2009,[54] meaning that less than 10% of Americans served in the Armed Forces.[55]
In 2010, The Washington Post estimated that there were 11 million undocumented immigrants in the country.[56]
There were about 2 million people in prison in 2010.[57]
The 2000 U.S. Census counted same-sex couples in an oblique way; asking the sex and the relationship to the "main householder", whose sex was also asked. One organization specializing in analyzing gay demographic data reported, based on this count in the 2000 census and in the 2000 supplementary survey, that same-sex couples comprised between 0.99% and 1.13% of U.S. couples in 2000.[58] A 2006 report issued by The Williams Institute on Sexual Orientation concluded that the number of same-sex couples in the U.S. grew from 2000 to 2005, from nearly 600,000 couples in 2000 to almost 777,000 in 2005. A 2006 UCLA study reported that 4.1% of Americans aged 18–45 identify as gay, lesbian, or bisexual.[59]
A 2011 report by the Institute estimated that 4 million adults identify as gay or lesbian, representing 1.7% of the population over 18. A spokesperson said that, until recently, few studies have tried to eliminate people who had occasionally undertaken homosexual behavior or entertained homosexual thoughts, from people who identified as lesbian or gay.[60] (Older estimates have varied depending on methodology and timing; see Demographics of sexual orientation for a list of studies.) The American Community Survey from the 2000 U.S. Census estimated 776,943 same-sex couple households in the country as a whole, representing about 0.5% of the population.[59]
Projections
| 2015 | 2050 | |
|---|---|---|
| White Americans1 | 77.4% | 70.8% |
| > Non-Hispanic Whites | 61.8% | 46.6% |
| Black Americans1 | 13.2% | 14.4% |
| Asian Americans1 | 5.3% | 7.7% |
| Multiracial Americans1 | 2.6% | 5.4% |
| Hispanics/Latinos (of any race) | 17.8% | 28.0% |
| 1 Including Hispanics | ||
A report by the U.S. Census Bureau projects a decrease in the ratio of Whites between 2010 and 2050, from 79.5% to 74.0%.[62] At the same time, Non-Hispanic Whites are projected to no longer make up a majority of the population by 2042, but will remain the largest single ethnic group. In 2050 they will compose 46.3% of the population. Non-Hispanic whites made up 85% of the population in 1960.[63]
The report foresees the Hispanic or Latino population rising from 16% today to 30% by 2050, the Black percentage barely rising from 12.9% to 13.1%, and Asian Americans upping their 4.6% share to 7.8%. The United States had a population of 310 million people in October 2010, and is projected to reach 400 million by 2039 and 439 million in 2050.[21][64][65][66] It is further projected that 82% of the increase in population from 2005 to 2050 will be due to immigrants and their children.[67]
Of the nation's children in 2050, 62% are expected to be of a minority ethnicity, up from 44% today. Approximately 39% are projected to be Hispanic or Latino (up from 22% in 2008), and 38% are projected to be single-race, non-Hispanic Whites (down from 56% in 2008).[68] Racial and ethnic minorities surpassed non-Hispanic whites as the largest group of American children under 5 years old in 2015.[69]
In 2008, the U.S. Census Bureau projected the future censuses as follows:[21]
| Year | Projection | Actual result |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 310,232,863 | 308,745,538 |
| 2020 | 325,896,000 | |
| 2030 | 350,471,000 | |
| 2040 | 380,015,000 | |
| 2050 | 389,803,000 |
Religion
Religious affiliations in 2004

The table below is based mainly on selected data as reported to the United States Census Bureau. It only includes the voluntary self-reported membership of religious bodies with 750,000 or more. The definition of a member is determined by each religious body.[70] In 2004, the US census bureau reported that about 13% of the population did not identify themselves as a member of any religion.[71]
In a Pew Research Survey performed in 2012, Americans without a religion (atheists, agnostics, nothing in particular, etc.) surpassed Evangelical Protestant Americans with almost 20% of Americans being nonreligious. If this current growth rate continues, by 2050, around 51% of Americans will not have a religion.[72]
A survey conducted in 2014 by the same organization indicated that the percentage of Americans unaffiliated with a religion rose to nearly 23% of the population, up from 16% in 2007.[73]
- Religious affiliation within each state that has the largest deviation compared to the national average, 2001.
 Percentage of state populations that identify with a religion rather than "no religion", 2001.
Percentage of state populations that identify with a religion rather than "no religion", 2001. Plurality religion by state, 2001. Data is unavailable for Alaska and Hawaii.
Plurality religion by state, 2001. Data is unavailable for Alaska and Hawaii.
Religions of American adults
The United States government does not collect religious data in its census. The survey below, the American Religious Identification Survey (ARIS) 2008, was a random digit-dialed telephone survey of 54,461 American residential households in the contiguous United States. The 1990 sample size was 113,723; 2001 sample size was 50,281.
Adult respondents were asked the open-ended question, "What is your religion, if any?". Interviewers did not prompt or offer a suggested list of potential answers. The religion of the spouse or partner was also asked. If the initial answer was "Protestant" or "Christian" further questions were asked to probe which particular denomination. About one-third of the sample was asked more detailed demographic questions.
Religious Self-Identification of the U.S. Adult Population: 1990, 2001, 2008[80]
Figures are not adjusted for refusals to reply; investigators suspect refusals are possibly more representative of "no religion" than any other group.
| Group | 1990 adults × 1,000 | 2001 adults × 1,000 | 2008 adults × 1,000 | Numerical Change 1990– 2008 as % of 1990 | 1990 % of adults | 2001 % of adults | 2008 % of adults | change in % of total adults 1990– 2008 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult population, total | 175,440 | 207,983 | 228,182 | 30.1% | ||||
| Adult population, Responded | 171,409 | 196,683 | 216,367 | 26.2% | 97.7% | 94.6% | 94.8% | –2.9% |
| Total Christian | 151,225 | 159,514 | 173,402 | 14.7% | 86.2% | 76.7% | 76.0% | –10.2% |
| Catholic | 46,004 | 50,873 | 57,199 | 24.3% | 26.2% | 24.5% | 25.1% | –1.2% |
| Non-Catholic Christian | 105,221 | 108,641 | 116,203 | 10.4% | 60.0% | 52.2% | 50.9% | –9.0% |
| Baptist | 33,964 | 33,820 | 36,148 | 6.4% | 19.4% | 16.3% | 15.8% | –3.5% |
| Mainline Protestant | 32,784 | 35,788 | 29,375 | –10.4% | 18.7% | 17.2% | 12.9% | –5.8% |
| Methodist | 14,174 | 14,039 | 11,366 | –19.8% | 8.1% | 6.8% | 5.0% | –3.1% |
| Lutheran | 9,110 | 9,580 | 8,674 | –4.8% | 5.2% | 4.6% | 3.8% | –1.4% |
| Presbyterian | 4,985 | 5,596 | 4,723 | –5.3% | 2.8% | 2.7% | 2.1% | –0.8% |
| Episcopalian/Anglican | 3,043 | 3,451 | 2,405 | –21.0% | 1.7% | 1.7% | 1.1% | –0.7% |
| United Church of Christ | 438 | 1,378 | 736 | 68.0% | 0.2% | 0.7% | 0.3% | 0.1% |
| Christian Generic | 25,980 | 22,546 | 32,441 | 24.9% | 14.8% | 10.8% | 14.2% | –0.6% |
| Jehovah's Witness | 1,381 | 1,331 | 1,914 | 38.6% | 0.8% | 0.6% | 0.8% | 0.1% |
| Christian Unspecified | 8,073 | 14,190 | 16,384 | 102.9% | 4.6% | 6.8% | 7.2% | 2.6% |
| Non-denominational Christian | 194 | 2,489 | 8,032 | 4040.2% | 0.1% | 1.2% | 3.5% | 3.4% |
| Protestant - Unspecified | 17,214 | 4,647 | 5,187 | –69.9% | 9.8% | 2.2% | 2.3% | –7.5% |
| Evangelical/Born Again | 546 | 1,088 | 2,154 | 294.5% | 0.3% | 0.5% | 0.9% | 0.6% |
| Pentecostal/Charismatic | 5,647 | 7,831 | 7,948 | 40.7% | 3.2% | 3.8% | 3.5% | 0.3% |
| Pentecostal - Unspecified | 3,116 | 4,407 | 5,416 | 73.8% | 1.8% | 2.1% | 2.4% | 0.6% |
| Assemblies of God | 617 | 1,105 | 810 | 31.3% | 0.4% | 0.5% | 0.4% | 0.0% |
| Church of God | 590 | 943 | 663 | 12.4% | 0.3% | 0.5% | 0.3% | 0.0% |
| Other Protestant Denomination | 4,630 | 5,949 | 7,131 | 54.0% | 2.6% | 2.9% | 3.1% | 0.5% |
| Seventh-Day Adventist | 668 | 724 | 938 | 40.4% | 0.4% | 0.3% | 0.4% | 0.0% |
| Churches of Christ | 1,769 | 2,593 | 1,921 | 8.6% | 1.0% | 1.2% | 0.8% | –0.2% |
| Mormon/Latter-Day Saints | 2,487 | 2,697 | 3,158 | 27.0% | 1.4% | 1.3% | 1.4% | 0.0% |
| Total non-Christian religions | 5,853 | 7,740 | 8,796 | 50.3% | 3.3% | 3.7% | 3.9% | 0.5% |
| Jewish | 3,137 | 2,837 | 2,680 | –14.6% | 1.8% | 1.4% | 1.2% | –0.6% |
| Eastern Religions | 687 | 2,020 | 1,961 | 185.4% | 0.4% | 1.0% | 0.9% | 0.5% |
| Buddhist | 404 | 1,082 | 1,189 | 194.3% | 0.2% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.3% |
| Muslim | 527 | 1,104 | 1,349 | 156.0% | 0.3% | 0.5% | 0.6% | 0.3% |
| New Religious Movements & Others | 1,296 | 1,770 | 2,804 | 116.4% | 0.7% | 0.9% | 1.2% | 0.5% |
| None/ No religion, total | 14,331 | 29,481 | 34,169 | 138.4% | 8.2% | 14.2% | 15.0% | 6.8% |
| Agnostic+Atheist | 1,186 | 1,893 | 3,606 | 204.0% | 0.7% | 0.9% | 1.6% | 0.9% |
| Did Not Know/ Refused to reply | 4,031 | 11,300 | 11,815 | 193.1% | 2.3% | 5.4% | 5.2% | 2.9% |
Marriage
In 2010, the median age for marriage for men was 27; for women, 26.[81]
Income
In 2006, the median household income in the United States was around $46,326. Household and personal income depends on variables such as race, number of income earners, educational attainment and marital status.
| Households | Persons, age 25 or older with earnings | Household income by race or ethnicity | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All households | Dual earner households |
Per household member |
Males | Females | Both sexes | Asian | Non-Hispanic White | Hispanic (of any race) |
Black |
| $46,326 | $67,348 | $23,535 | $39,403 | $26,507 | $32,140 | $57,518 | $48,977 | $34,241 | $30,134 |
| Measure | Some High School | High school graduate | Some college | Associate's degree | Bachelor's degree or higher | Bachelor's degree | Master's degree | Professional degree | Doctorate degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persons, age 25+ w/ earnings | $20,321 | $26,505 | $31,054 | $35,009 | $49,303 | $43,143 | $52,390 | $82,473 | $70,853 |
| Male, age 25+ w/ earnings | $24,192 | $32,085 | $39,150 | $42,382 | $60,493 | $52,265 | $67,123 | $100,000 | $78,324 |
| Female, age 25+ w/ earnings | $15,073 | $21,117 | $25,185 | $29,510 | $40,483 | $36,532 | $45,730 | $66,055 | $54,666 |
| Persons, age 25+, employed full-time | $25,039 | $31,539 | $37,135 | $40,588 | $56,078 | $50,944 | $61,273 | $100,000 | $79,401 |
| Household | $22,718 | $36,835 | $45,854 | $51,970 | $73,446 | $68,728 | $78,541 | $100,000 | $96,830 |
| Bottom 10% | Bottom 20% | Bottom 25% | Middle 33% | Middle 20% | Top 25% | Top 20% | Top 5% | Top 1.5% | Top 1% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $0 to $10,500 | $0 to $18,500 | $0 to $22,500 | $30,000 to $62,500 | $35,000 to $55,000 | $77,500 and up | $92,000 and up | $167,000 and up | $250,000 and up | $350,000 and up |
| Source: US Census Bureau, 2006; income statistics for the year 2005 | |||||||||
Economic class
Social classes in the United States lack distinct boundaries and may overlap. Even their existence (when distinguished from economic strata) is controversial. The following table provides a summary of some prominent academic theories on the stratification of American society:
| Dennis Gilbert, 2002 | William Thompson & Joseph Hickey, 2005 | Leonard Beeghley, 2004 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Typical characteristics | Class | Typical characteristics | Class | Typical characteristics |
| Capitalist class (1%) | Top-level executives, high-rung politicians, heirs. Ivy League education common. | Upper class (1%) | Top-level executives, celebrities, heirs; income of $500,000+ common. Ivy league education common. | The super-rich (0.9%) | Multi-millionaires whose incomes commonly exceed $350,000; includes celebrities and powerful executives/politicians. Ivy League education common. |
| Upper middle class[1] (15%) | Highly-educated (often with graduate degrees), most commonly salaried, professionals and middle management with large work autonomy. | Upper middle class[1] (15%) | Highly-educated (often with graduate degrees) professionals & managers with household incomes varying from the high 5-figure range to commonly above $100,000. | The rich (5%) | Households with net worth of $1 million or more; largely in the form of home equity. Generally have college degrees. |
| Middle class (plurality/ majority?; ca. 46%) |
College-educated workers with considerably higher-than-average incomes and compensation; a man making $57,000 and a woman making $40,000 may be typical. | ||||
| Lower middle class (30%) | Semi-professionals and craftsmen with a roughly average standard of living. Most have some college education and are white-collar. | Lower middle class (32%) | Semi-professionals and craftsmen with some work autonomy; household incomes commonly range from $35,000 to $75,000. Typically, some college education. | ||
| Working class (30%) | Clerical and most blue-collar workers whose work is highly routinized. Standard of living varies depending on number of income earners, but is commonly just adequate. High school education. | ||||
| Working class (32%) | Clerical, pink- and blue-collar workers with often low job security; common household incomes range from $16,000 to $30,000. High school education. | Working class (ca. 40–45%) |
Blue-collar workers and those whose jobs are highly routinized with low economic security; a man making $40,000 and a woman making $26,000 may be typical. High school education. | ||
| Working poor (13%) | Service, low-rung clerical and some blue-collar workers. High economic insecurity and risk of poverty. Some high school education. | ||||
| Lower class (ca. 14–20%) | Those who occupy poorly-paid positions or rely on government transfers. Some high school education. | ||||
| Underclass (12%) | Those with limited or no participation in the labor force. Reliant on government transfers. Some high school education. | The poor (ca. 12%) | Those living below the poverty line with limited to no participation in the labor force; a household income of $18,000 may be typical. Some high school education. | ||
Thompson, W. & Hickey, J. (2005). Society in Focus. Boston, MA: Pearson, Allyn & Bacon; Beeghley, L. (2004). The Structure of Social Stratification in the United States. Boston, MA: Pearson, Allyn & Bacon.
| |||||
Health
In 2010, the average man weighed 194.7 pounds (88.3 kg); the average woman 164.7 pounds (74.7 kg).[82] The height of an American man was 5 feet 9 inches (1.75 m)[83] and woman 5 feet 3.8 inches (1.621 m)[84] The average BMI is 27.3 for males (overweight) and 28.5 for females (overweight).[85]
According to a Gallup poll in 2012, an estimated 26% of the population were obese,[86] 21% smoked,[87] and 11% had diabetes.[88]
A nationwide study reported by The New York Times in 2010 indicated that 19.5% of teens, aged 12–19, had developed "slight" hearing loss. "Slight" was defined as an inability to hear at 16 to 24 decibels.[89]
According to the Centers for Disease Control in 2011, an estimated 1.2 million people were living with HIV/AIDS in the United States.[90]
Generational cohorts
A study by William Strauss and Neil Howe, in their books Generations and Fourth Turning, looked at generational similarities and differences going back to the 15th century and concluded that over 80-year spans, generations proceed through four stages of about 20 years each.
A definitive recent study of US generational cohorts was done by Schuman and Scott (2012) in which a broad sample of adults of all ages was asked, "What world events are especially important to you?"[91] They found that 33 events were mentioned with great frequency. When the ages of the respondents were correlated with the expressed importance rankings, seven (some put 8 or 9) distinct cohorts became evident.
Today the following descriptors are frequently used for these cohorts:
- Lost Generation – born from approximately 1883 to 1900.
- G.I. Generation – born from approximately 1901 to 1924 (depression cohort who fought and won World War II).
- Silent Generation – born from approximately 1925 to 1942[92] during the Great Depression and World War II.[93] The label was originally applied to people in North America but has also been applied to those in Western Europe, Australasia and South America. It includes most of those who fought during the Korean War.
- Baby Boomers – commentators use birth dates ranging approximately from the mid-1940s to the mid-1960s.
- Generation X – demographers and researchers typically use starting birth years ranging from the early-to-mid 1960s and ending birth years ranging from the late 1970s to early 1980s.[94]
- In the U.S., some called Generation Xers the "baby bust" generation because of the drop in the birth rate following the baby boom.[95] The drop in fertility rates in America began in the late 1950s. But according to authors and demographers William Strauss and Neil Howe (who use 1961 to 1981 for Gen X birth years), there are approximately 88.5 million Gen Xers in the U.S. today.[96][97]
- Millennials (also known as Generation Y) – demographers and researchers typically use the early 1980s as starting birth years and the mid-1990s to early 2000s as ending birth years.
- Generation Z (also known as Homelanders or Digital Natives) – demographers and researchers typically use starting birth years that range from the mid-1990s to early 2000s, and as of yet there is little consensus about ending birth years.
U.S. demographic birth cohorts
Subdivided groups are present when peak boom years or inverted peak bust years are present, and may be represented by a normal or inverted bell-shaped curve (rather than a straight curve). The boom subdivided cohorts may be considered as "pre-peak" (including peak year) and "post-peak". The year 1957 was the baby boom peak with 4.3 million births and 122.7 fertility rate. Although post-peak births (such as trailing edge boomers) are in decline, and sometimes referred to as a "bust", there are still a relatively large number of births. The dearth-in-birth bust cohorts include those up to the valley birth year, and those including and beyond, leading up to the subsequent normal birth rate. The Baby boom began around 1943 to 1946.
From the decline in U.S. birth rates starting in 1958 and the introduction of the birth control pill in 1960, the Baby Boomer normal distribution curve is negatively skewed. The trend in birth rates from 1958 to 1961 show a tendency to end late in the decade at approximately 1969, thus returning to pre-WWII levels, with 12 years of rising and 12 years of declining birth rates. Pre-war birth rates were defined as anywhere between 1939 and 1941 by demographers such as the Taeuber's, Philip M. Hauser and William Fielding Ogburn.[98]
Demographic statistics
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.[99]
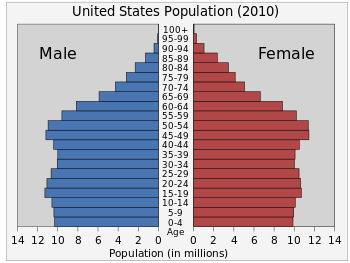
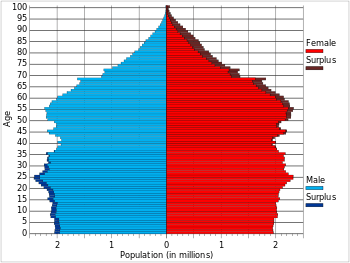
Ages
Median ages are 37.3 years; males are 36.1 years; females are 38.5 years estimated as of 2012.
As of 2012, people are distributed by age as follows:
- 0–14 years: 19.8% (male 31,639,127/female 30,305,704)
- 15–64 years: 66.8% (male 101,612,000/female 104,577,000)
- 65 years and over: 13.4% (male 18,332,000/female 23,174,000) (2012 est.)
Birth, growth, and death rates
The growth rate is 0.760% as estimated from 2014-2010 by the US Census
The birth rate is 12.5 births/1,000 population, estimated as of 2013. This was the lowest since records began. There were 3,957,577 births in 2013.[100]
- 13.9 births/1,000 population/year (Provisional Data for 2008)
- 14.3 births/1,000 population/year (Provisional Data for 2007)[101]
In 2009, Time magazine reported that 40% of births were to unmarried women.[102] The following is a breakdown by race for unwed births: 17% Asian, 29% White, 53% Hispanics, 66% Native Americans, and 72% Black American.[103]
The drop in the birth rate from 2007 to 2009 is believed to be associated with the Late-2000s recession.[104]
A study by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) found that more than half (51 percent) of live hospital births in 2008 and 2011 were male.[105]
Per U.S. federal government data released in March 2011, births fell 4% from 2007 to 2009, the largest drop in the U.S. for any two-year period since the 1970s.[106] Births have declined for three consecutive years, and are now 7% below the peak in 2007.[107] This drop has continued through 2010, according to data released by the U.S. National Center for Health Statistics in June 2011.[108] Numerous experts have suggested that this decline is largely a reflection of unfavorable economic conditions.[109] This connection between birth rates and economic downturns partly stems from the fact that American birth rates have now fallen to levels that are comparable to the Great Depression of the 1930s.[110] Teen birth rates in the U.S. are at the lowest level in U.S. history.[111] In fact, teen birth rates in the U.S. have consistently decreased since 1991 through 2011, except for a brief increase between 2005 and 2007.[111] The other aberration from this otherwise steady decline in teen birth rates is the 6% decrease in birth rates for 15- to 19-year-olds between 2008 and 2009.[111] Despite these years of decrease, U.S. teen birth rates are still higher than in other developed nations.[111] Racial differences prevail with teen birth and pregnancy rates as well. The American Indian/Alaska Native, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic black teen pregnancy rates are more than double the non-Hispanic white teen birth rate.[112]
Birth data
Note: Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.[113][7] Also note that growth arrows indicate an increase or decrease in the number of births, not in the fertility rate.
| Race of mother | Number of births in 2014 |
% of all born |
TFR (2014) |
Number of births in 2015 |
% of all born |
TFR (2015) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | |
75.72% | 1.876 | |
75.73% | 1.864 | |
| > Non-Hispanic | |
53.89 | 1.763 | |
53.54% | 1.746 | |
| Black | |
16.06% | 1.872 | |
16.09% | 1.853 | |
| > Non-Hispanic | |
14.77% | 1.874 | |
14.80% | 1.857 | |
| Asian and Pacific islander | |
7.09% | 1.715 | |
7.07% | 1.646 | |
| Native (incl. Alaska native) | |
1.13% | 1.289 | |
1.11% | 1.263 | |
| Total | |
100% | 1.862 | |
100% | 1.843 | |
NOTE:
- TFR = Total fertility rate.
- Growth arrows indicate an increase or decrease in the number of births, not in the fertility rate.
| Ethnicity of mother | Number of births in 2014 |
TFR (2014) |
Number of births in 2015 |
TFR (2015) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Hispanic (of any race) | |
1.793 | |
1.770 | |
| Hispanic (of any race) | |
2.131 | |
2.124 | |
| Race | 2008 | 2011 | 2013 |
|---|---|---|---|
| White | 2.29 | 2.01 | 1.94 |
| Black | 2.51 | 2.57 | 2.35 |
| Asian | 2.25 | 2.02 | 1.93 |
| Other | 1.80 | 2.04 | 2.06 |
| Hispanic (of any race) | 3.15 | 2.77 | 2.46 |
| Total | 2.75 | 2.45 | 2.22 |
| Age group | Total (of population) |
White alone (of race/age group) |
Black alone (of race/age group) |
Mixed and/or Some Other Race (of race/age group) |
Asian alone (of race/age group) |
Either American Indian or Alaska Native (of race/age group) |
Either Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander (of race/age group) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 308745538 (100%) | 223553265 (72.41%) | 38929319 (12.61%) | 28116441 (9.11%) | 14674252 (4.75%) | 2932248 (0.95%) | 540013 (0.17%) |
| 0–4 | 20201362 (6.5%) | 12795675 (5.7%/63.34%) | 2902590 (7.5%/14.37%) | 3315480 (11.8%/16.41%) | 898011 (6.1%/4.45%) | 244615 (8.3%/1.21%) | 44991 (8.3%/0.22%) |
| 5–9 | 20348657 (6.6%) | 13293799 (5.9%/65.33%) | 2882597 (7.4%/14.17%) | 2957487 (10.5%/14.53%) | 928248 (6.3%/4.56%) | 243259 (8.3%/1.20%) | 43267 (8.0%/0.21%) |
| 10–14 | 20677194 (6.7%) | 13737332 (6.1%/66.44%) | 3034266 (7.8%/14.67%) | 2736570 (9.7%/13.23%) | 881590 (6.0%/4.26%) | 245049 (8.4%/1.19%) | 42387 (7.8%/0.20%) |
| 15–19 | 22040343 (7.1%) | 14620638 (6.5%/66.35%) | 3448051 (8.9%/15.64%) | 2704571 (9.6%/12.27%) | 956028 (6.5%/4.34%) | 263805 (9.0%/1.20%) | 47250 (8.7%/0.21%) |
| 20–24 | 21585999 (7.0%) | 14535947 (6.5%/67.34%) | 3111397 (8.0%/14.41%) | 2538967 (9.0%/11.76%) | 1106222 (7.5%/5.12%) | 240716 (8.2%/1.12%) | 52750 (9.8%/0.24%) |
| 25–29 | 21101849 (6.8%) | 14345364 (6.4%/67.98%) | 2786254 (7.2%/13.20%) | 2464343 (8.8%/11.68%) | 1234322 (8.4%/5.85%) | 221654 (7.6%/1.05%) | 49912 (9.2%/0.24%) |
| 30–34 | 19962099 (6.5%) | 13573270 (6.1%/68.00%) | 2627925 (6.8%/13.16%) | 2273322 (8.1%/11.39%) | 1240906 (8.5%/6.22%) | 202928 (6.9%/1.02%) | 43748 (8.1%/0.22%) |
| 35–39 | 20179642 (6.5%) | 13996797 (6.3%/69.36%) | 2613389 (6.7%/12.95%) | 2038408 (7.2%/10.10%) | 1296301 (8.8%/6.42%) | 196017 (6.7%/0.97%) | 38730 (7.2%/0.19%) |
| 40–44 | 20890964 (6.8%) | 15052798 (6.7%/72.05%) | 2669034 (6.9%/12.78%) | 1782463 (6.3%/8.53%) | 1155565 (7.9%/5.53%) | 194713 (6.6%/0.93%) | 36391 (6.7%/0.17%) |
| 45–49 | 22708591 (7.4%) | 17028255 (7.6%/74.99%) | 2828657 (7.3%/12,46%) | 1532117 (5.4%/6.75%) | 1076060 (7.3%/4.74%) | 207857 (7.1%/0.92%) | 35645 (6.6%/0.16%) |
| 50–54 | 22298125 (7.2%) | 17178632 (7.7%/77.04%) | 2694247 (6.9%/12.08%) | 1222175 (4.3%/5.48%) | 980282 (6.7%/4.40%) | 191893 (6.5%/0.86%) | 30896 (5.7%/0.14%) |
| 55–59 | 19664805 (6.4%) | 15562187 (7.0%/79.14%) | 2205820 (5.7%/11.22%) | 873943 (3.1%/4.44%) | 844490 (5.8%/4.29%) | 154320 (5.3%/0.78%) | 24045 (4.5%/0.12%) |
| 60–64 | 16817924 (5.4%) | 13693334 (6.1%/81.42%) | 1686695 (4.3%/10.03%) | 611144 (2.2%/3.63%) | 689601 (4.7%/4.10%) | 118362 (4.0%/0.70%) | 18788 (3.5%/0.11%) |
| 65–69 | 12435263 (4.0%) | 10313002 (4.6%/82.93%) | 1162577 (3.0%/9.35%) | 394208 (1.4%/3.17%) | 474327 (3.2%/3.81%) | 79079 (2.7%/0.64%) | 12070 (2.2%/0.10%) |
| 70–74 | 9278166 (3.0%) | 7740932 (3.5%/83.43%) | 852317 (2.2%/9.19%) | 268574 (1.0%/2.89%) | 354268 (2.4%/3.82%) | 53926 (1.8%/0.58%) | 8149 (1.5%/0.09%) |
| 75–79 | 7317795 (2.4%) | 6224569 (2.8%/85.06%) | 616789 (1.6%/8.43%) | 184596 (0.7%/2.52%) | 251210 (1.7%/3.43%) | 35268 (1.2%/0.48%) | 5363 (1.0%/0.07%) |
| 80–84 | 5743327 (1.9%) | 5002427 (2.2%/87.10%) | 424592 (1.1%/7.39%) | 122249 (0.4%/2.13%) | 168879 (1.2%/2.94%) | 21963 (0.7%/0.38%) | 3217 (0.6%/0.06%) |
| 85+ | 5493433 (1.8%) | 4858307 (2.2%/88.44%) | 382122 (1.0%/6.96%) | 95824 (0.3%/1.74%) | 137942 (0.9%/2.51%) | 16824 (0.6%/0.31%) | 2414 (0.4%/0.04%) |
Death rate
As of July 2010, it was estimated that there were 8.18 deaths/1,000 population per year.[115]
Immigration and emigration
13% of the population was foreign-born in 2009 -- a rise of 350% since 1970 when foreign-born people accounted for 3.7% of the population,[116] including 11.2 million illegal aliens,[117] 80% of whom come from Latin America.[118] Latin America is the largest region-of-birth group, accounting for over half (53%) of all foreign born population in US,[119] and thus is also the largest source of both legal and illegal immigration to US.[120] In 2011, there are 18.1 million naturalized citizens in USA, accounting for 45% of the foreign-born population (40.4 million) and 6% of the total US population at the time,[121] and around 680,000 legal immigrants are naturalized annually.[122]
4.32 people migrate per 1,000 population, estimated in 2010.
| Country | 2011 |
|---|---|
| Mexico | 143,446 |
| China | 87,016 |
| India | 69,013 |
| Philippines | 57,011 |
| Dominican Rep. | 46,019 |
| Region | 2011 |
|---|---|
| Asia | 451,593 |
| Americas | 419,996 |
| Africa | 100,336 |
| Europe | 83,635 |
| All immigrants | 1,062,040 |
Sex ratios
- at birth: 1.048 male(s)/female
- under 15 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
- 15–64 years: 1 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over: 0.75 male(s)/female
- total population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
Infant mortality rate
- total: 6.22 deaths/1,000 live births
- male: 6.9 deaths/1,000 live births
- female: 5.53 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
- total population: 78.11 years
- male: 75.65 years
- female: 80.69 years (2010 est.)

<3.0% <3.5% <4.0% |
<4.5% <5.0% <5.5% |
<6.0% <6.5% ≥6.5% |
Total fertility rate
- 1.82 children born/woman (2016).
- Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention - National Vital Statistics System.
Unemployment rate
As of July 2016, the U.S. unemployment rate was 4.9 percent (U3 Rate).[125]
As of July 2015, the U.S. unemployment rate was 5.3 percent (U3 Rate).[126]
As of July 2014, the U.S. unemployment rate was 6.2 percent (U3 Rate).[125]
As of April 2017, the U6 unemployment rate is 8.6 percent.[127] The U6 unemployment rate counts not only people without work seeking full-time employment (the more familiar U-3 rate), but also counts "marginally attached workers and those working part-time for economic reasons." Note that some of these part-time workers counted as employed by U-3 could be working as little as an hour a week. And the "marginally attached workers" include those who have gotten discouraged and stopped looking, but still want to work. The age considered for this calculation is 16 years and over.[128]
Mobility
In 2013, about 15% of Americans moved. Most of these, 67%, moved within the same county. Of the 33% who moved beyond local county boundaries, 13% of those moved more than 200 miles (320 km).[129]
See also
| This article is part of a series on |
| Income in the United States of America |
|---|
 |
|
Lists by income |
|
|
- Outline of the United States
- Index of United States articles
- Book:United States
- Maps of American ancestries
- Languages of the United States
- Immigration to the United States
- Emigration from the United States
- Places in the United States with notable demographic characteristics
- Demographic history of the United States
- Historical racial and ethnic demographics of the United States
- Race and ethnicity in the United States
- Urbanization in the United States
- Historical Statistics of the United States
- Hispanic and Latino Americans
Lists:
- Lists of U.S. cities with non-white majority populations
- List of metropolitan areas in the Americas
- List of U.S. states and territories by population
Income:
- Household income in the United States
- Personal income in the United States
- Affluence in the United States
- Highest-income places in the United States
- Lowest-income counties in the United States
Population:
- United States
- Demographics of the United States
- United States Census Bureau
- United States Office of Management and Budget
- The OMB has defined 1098 statistical areas comprising 388 MSAs, 541 μSAs, and 169 CSAs
- United States urban area – List of United States urban areas
Notes
- ↑ "Population Clock". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 23, 2017.
- ↑ "United Nations - Population Division". un.org.
- ↑ "Table 13. State Population - Rank, Percent Change, and Population Density" (Excel). U.S. Census Bureau. 2008. Retrieved 2010-10-24.
- ↑ "Mean Center of Population for the United States: 1790 to 2000" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2001-11-03. Retrieved 2010-10-24.
- ↑ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Incorporated Places over 110,000, Ranked by July 1, 2009 Population: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2009 (SUB-EST2009-01)". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2011-05-19.
- ↑ National Vital Statistics Reports. Births: Preliminary Data for 2016
- 1 2 National Vital Statistics Reports. Births: Final Data for 2015
- ↑ "Fécondité, France hors Mayotte". INSEE. Retrieved 2014-04-27.
- ↑ "Vital Statistics: Population and Health Reference Tables (February 2014 Update): Annual Time Series Data". ONS. Retrieved 2014-04-27.
- 1 2 "CIA - The World Factbook -- Field Listing - Population growth rate". CIA. Retrieved 2012-01-09.
- ↑ "CIA - The World Factbook -- Rank Order - Total fertility rate". CIA. Retrieved 2010-02-01.
- ↑ "CIA - The World Factbook -- Rank Order - Net migration rate". CIA. Retrieved 2009-02-23.
- ↑ Bureau, U.S. Census. "American FactFinder - Results". census.gov.
- ↑ "Median age of the U.S. population 1960-2015 - Statistic". statista.com.
- ↑ "The White Population: 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. August 2001. Retrieved 10 March 2011.
- ↑ "Statistical Abstract of the United States" (PDF). United States Census Bureau.
- ↑ "U.S. population hits 300 million mark". MSNBC. Associated Press. 2006-10-17. Retrieved 2006-10-17.
- ↑ Morello, Carol and Mellnik, Ted. "Census: Minority Babies Are Now Majority in United States." Washington Post. May 17, 2012. Accessed 2012-05-17.
- ↑ "U.S. Census Bureau: Minority Population Tops 100 Million". Archived from the original on September 18, 2008.
- ↑ "U.S. Population Projections: 2005-2050 - Pew Hispanic Center". Pewhispanic.org. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- 1 2 3 "Projected Population by Single Year of Age, Sex, Race, and Hispanic Origin for the United States: July 1, 2000 to July 1, 2050". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2009-12-08.
- ↑ "World Population Prospects: The 2006 Revision, Highlights, Working Paper No. ESA/P/WP.202; Table A.2" (PDF). United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2007). Retrieved 2009-01-10.
- 1 2 http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr61/nvsr61_01.pdf
- ↑ 2-11-Z-COLONIAL & PRE-FEDERAL.pdf. (PDF). Retrieved on 2013-06-16.
- ↑ Resident Population Data. "Resident Population Data – 2010 Census". www.census.gov. Retrieved February 22, 2013.
- ↑ Historical Census Statistics on Population Totals By Race, 1790 to 1990.... U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2013-05-28.
- ↑ "Demographics Trends in the 20th Century". U.S. Census Bureau.
- ↑ "We the Americans: Blacks". Census.gov.
- ↑ "Latinos and the Changing Face of America - Population Reference Bureau"
- ↑ "Not Just Black and White: Historical and Contemporary Perspectives on Immigration, Race, and Ethnicity in the United States". Nancy Foner, George M. Fredrickson (2005). p.120. ISBN 0-87154-270-6
- ↑ "Immigrants in the United States and the Current Economic Crisis", Demetrios G. Papademetriou and Aaron Terrazas, Migration Policy Institute, April 2009.
- ↑ "Immigration Worldwide: Policies, Practices, and Trends". Uma A. Segal, Doreen Elliott, Nazneen S. Mayadas (2010). Oxford University Press US. p. 32. ISBN 0-19-538813-5
- ↑ Borjas, George J (2003). "Welfare reform, labor supply, and health insurance in the immigrant population". Journal of Health Economics. 22 (6): 933–958. ISSN 0167-6296. doi:10.1016/j.jhealeco.2003.05.002.
- ↑ "CBO: 748,000 Foreign Nationals Granted U.S. Permanent Residency Status in 2009 Because They Had Immediate Family Legally Living in America Archived January 14, 2011, at the Wayback Machine.". CNSnews.com. January 11, 2011
- ↑ ""The First Measured Century: An Illustrated Guide to Trends in America, 1900–2000"". Public Broadcasting Service (PBS).
- ↑ Exner, Rich (2012-07-03). "Americans under age 1 now mostly minorities, but not in Ohio: Statistical Snapshot". The Plain Dealer. Retrieved 2012-07-29.
- ↑ "Non-white births outnumber white births for the first time in US". The Daily Telegraph. May 17, 2012.
- ↑ ["http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr61/nvsr61_01.pdf" "Births: Final Data for 2010"]
- ↑ ["http://factfinder2.census.gov/faces/tableservices/jsf/pages/productview.xhtml?pid=ACS_10_3YR_GCT0101.US01PR&prodType=table" "American FactFinder: Median age by state"]
- ↑ http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr64/nvsr64_12.pdf
- ↑ "UNITED STATES OF AMERICA: historical demographical data of the whole country". POPULATION STATISTICS. Jan Lahmeyer. 2000-01-22. Retrieved 2013-10-16.
- ↑ 1960 to 2011"United States - Death rate: Death rate, crude (per 1,000 people)". Index Mundi. IndexMundi. Retrieved 2013-10-24.
- ↑ Census 2010 Population Distribution in the United States and Puerto Rico. U.S. Census Bureau.
- ↑ Density Using Land Area For States, Counties, Metropolitan Areas, and Places. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2007-12-14.
- ↑ "The 2012 Global Cities Index". Retrieved 2013-01-05.
- ↑ "The World According to GaWC - Classification of cities 2010". 2010. Archived from the original on October 10, 2013. Retrieved 2013-01-05.
- ↑ "American cities on the rebound". Cbsnews.com. August 5, 2011. Retrieved 2013-05-08.
- ↑ "Appendix A. Census 2000 Geographic Terms and Concepts – Figure A–3. Census Regions, Census Divisions, and Their Constituent States" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. 2000. p. 27. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 14, 2007. Retrieved February 25, 2017.
- ↑ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2015". United States Census Bureau, Population Division. March 2016. Retrieved 2016-04-25.
- ↑ "Overview of Race and Hispanic Origin: 2010" (PDF). Retrieved 2013-05-08.
- ↑ "U.S. Census Bureau Guidance on the Presentation and Comparison of Race and Hispanic Origin Data". Retrieved 2007-04-05.
Race and Hispanic origin are two separate concepts in the federal statistical system. People who are Hispanic may be of any race. People in each race group may be either Hispanic or Not Hispanic. Each person has two attributes, their race (or races) and whether or not they are Hispanic.
- ↑ "American FactFinder Help: Hispanic or Latino origin". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-06-13.
- ↑ "U.S. Census Bureau Data". U.S. Census Bureau. 2010. Retrieved 2011-07-13.
- ↑ Kanell, Michael E. (16 November 2009). "Number of veterans, October". Atlanta Constitution-Journal. Atlanta, Georgia. pp. A6. quoting the Bureau of Labor Statistics
- ↑ Davenport, Christian (20 April 2010). "A disconnect at Magruder". Washington Post. Washington, DC. pp. B1.
- ↑ Hsu, Spencer S. (2 May 2010). "Senate Democrats' plan highlights nation's shift to the right on immigration". Washington Post. Washington, DC. pp. A3.
- ↑ Gerson, Michael (5 January 2010). "Column:More second chances". Florida Today. Melbourne, Florida. pp. 7A.
- ↑ "2000 Census information on Gay and Lesbian Couples". gaydemographics.org. Archived from the original on July 1, 2009.
- 1 2 Gary J. Gates "Same-sex Couples and the Gay, Lesbian, Bisexual Population: New Estimates from the American Community Survey" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on July 2, 2007. (2.07 MB). The Williams Institute on Sexual Orientation Law and Public Policy, UCLA School of Law October 2006. Retrieved April 20, 2007.
- ↑ Press, Associated (March 1, 2011). "Research 4M adults in US identify as gay". Florida Today. Melbourne, Florida. pp. 1A.
- ↑ "2012 National Population Projections: Summary Tables - People and Households - U.S. Census Bureau - Table 6: Percent Distribution of the Projected Population by Race and Hispanic Origin for the United States: 2015 to 2060 (middle series)". census.gov.
- ↑ "Table 4. Projections of the Population by Sex, Race, and Hispanic Origin for the United States: 2010 to 2050". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original (Excel) on 2010-03-27. Retrieved 2010-10-24.
- ↑ U.S. Hispanic population to triple by 2050, USATODAY.com
- ↑ White Americans no longer a majority by 2042 Archived August 24, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Aizenman, N.C. (August 13, 2008). "U.S. to Grow Grayer, More Diverse". Washington Post. Retrieved 2013-05-08.
- ↑ Passel, Jeffrey (February 11, 2008). "Pew Research Center: Immigration to Play Lead Role In Future U.S. Growth". Pewresearch.org. Retrieved 2013-05-08.
- ↑ Whites to become minority in U.S. by 2050, Reuters
- ↑ Archived copy at the Library of Congress (September 17, 2008)., U.S. Census Press Releases, 14 August 2008 (archived from the original on 2008-08-22)
- ↑ The Majority of American Babies Are Now Minorities, Bloomberg, 25 July 2015.
- ↑ Table No. 68. Religious Bodies—Selected Data (p. 59), "Statistical Abstract of the United States: 2004–2005 (tables 67–69)" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau.
- ↑ "Statistical Abstract of the United States: 2004–2005 (tables 67-69)" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau.
- ↑ "Statistics on Religion in America Report -- Pew Forum on Religion & Public Life". pewforum.org.
- ↑ "America’s Changing Religious Landscape". Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project. 2015-05-12. Retrieved 2016-10-09.
- ↑ "Latest Episcopal Church Stats Reveal Fewer Parishes, Members". Juicy Ecumenism. 2012-10-12. Retrieved 2016-10-09.
- 1 2 3 "The Decline of Decline? Alarming Rate of Mainline Protestants Leaving Church May Be Slowing Down". Christian Post. Retrieved 2016-10-09.
- 1 2 "Always Declining: The Evangelical Lutheran Church in America’s Stillborn Quarter Century of Existence". Juicy Ecumenism. 2013-08-14. Retrieved 2016-10-09.
- ↑ "Adherents.com". Adherents.com. Retrieved September 19, 2011.
- ↑ "Section 1. Population" (PDF). Statistical Abstract of the United States: 2004–2005. U.S. Census Bureau. p. 55. Retrieved 2008-06-29. (Table No. 67. Self-described religious identification of adult population: 1990 and 2001; data for 2001).
- 1 2 King/LifeWay, Marty. "Southern Baptist Churches Growing in Numbers, Declining in Membership". charismanews.com.
- 1 2 Barry A. Kosmin and Ariela Keysar (2009). "AMERICAN RELIGIOUS IDENTIFICATION SURVEY (ARIS) 2008" (PDF). Hartford, Connecticut, USA: Trinity College. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 7, 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-01.
- ↑ Riley, Naomi Schaefer (6 June 2010). "Interfaith marriages are rising fast, but they're failing fast too". Washington Post. Washington, DC. pp. B1, B4.
- ↑ Larry Copeland (2011-03-22). "Caution: Wide Load (and Just Getting Wider)". Florida Today. Archived from the original on April 4, 2015.
- ↑ "Average Height of a Man". Buzzle.com. 2012-12-07. Retrieved 2013-05-08.
- ↑ "Average Height for Women Worldwide". Buzzle.com. 2012-01-31. Retrieved 2013-05-08.
- ↑ "Calculate Your BMI - Standard BMI Calculator". Nhlbisupport.com. 2012-02-15. Retrieved 2013-05-08.
- ↑ "In U.S., Obesity Up in Nearly All Age Groups Since 2008". Gallup.com. 2012-10-24. Retrieved 2013-05-08.
- ↑ Saad, Lydia (August 22, 2012). "One in Five U.S. Adults Smoke, Tied for All-Time Low". Gallup. Retrieved 10 November 2012.
- ↑ "U.S. Diabetes Rate Levels Off in 2011". Gallup.com. December 16, 2011. Retrieved 2013-05-08.
- ↑ Caryn, Roni (2011-09-15). "Childhood - Hearing Loss Grows Among Teenagers". New York Times. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- ↑ "HIV in the United States". Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 21 November 2011.
- ↑ Schuman, H. and Scott, J. (1989), Generations and collective memories, American Sociological Review, vol. 54, 1989, pp. 359–81.
- ↑ Strauss, William; Neil Howe (1991). Generations: The History of Americas Future, 1584 to 2069. New York, NY: Harper Perennial. p. 279. ISBN 0-688-11912-3.
- ↑ "People: THE YOUNGER GENERATION". time.com. 5 November 1951.
- ↑ Miller, Jon D. "The Generation X Report: Active, Balanced, and Happy: These Young Americans are not bowling alone" (PDF). University of Michigan, Longitudinal Study of American Youth, funded by the National Science Foundation. Retrieved October 30, 2012.
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Identity By Ronald L. Jackson, II
- ↑ William Strauss, Neil Howe (1991). Generations. New York, NY: Harper Perennial. p. 318. ISBN 0-688-11912-3.
- ↑ The Gen X Files. "Latest Numbers for Generation X". Retrieved October 24, 2012.
- ↑ Tuttle, William M. (1993-09-16). "Daddy's Gone to War": The Second World War in the Lives of America's Children. Oxford University Press, USA. p. 25. ISBN 9780195096491. Retrieved 17 March 2014.
- ↑ "CIA - The World Factbook -- United States". CIA. Retrieved 2010-02-16.
- ↑ Marchione, Marilynn (August 27, 2010). "Recession may have pushed U.S. birth rate to a new low". USA Today. Associated Press. Retrieved 2010-10-09.
- ↑ Births, Marriages, Divorces, and Deaths: Provisional Data for 2009 National Vital Statistics Reports Volume 58, Number 25, accessed August 28, 2010
- ↑ Amy Sullivan (March 20, 2009). "Behind the Boom in Adult Single Motherhood". Time.
- ↑ "Blacks rank highest in unwed births". Florida Today. Melbourne, Florida. Associated Press. 7 November 2010. pp. 9A.
- ↑ "Birthrate Is Lowest in a Century" Associated Press article printed in The New York Times August 27, 2010, accessed August 28, 2010
- ↑ Kowlessar N.M., Jiang H.J., and Steiner C. "Hospital Stays for Newborns, 2011." HCUP Statistical Brief #163. October 2013. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD.
- ↑ Roan, Shari (March 31, 2011). "Drop in U.S. birth rate is the biggest in 30 years" – via LA Times.
- ↑ "America's Birth Rate Declined For The Third Year Running". businessinsider.com.
- ↑ "America's Birth Rate Declined For The Third Year Running". businessinsider.com.
- ↑ "Health and Wellness - USATODAY.com". usatoday.com.
- ↑ Lower birth rate blamed on the economy | wzzm13.com
- 1 2 3 4 CDC Data & Statistics | Feature: Teen Birth Rates Declined Again in 2009 Archived July 31, 2011, at WebCite
- ↑ "CDC Features - Teen Birth Rates Drop, But Disparities Persist". cdc.gov.
- ↑ Births: Final Data for 2014
- ↑ http://cis.org/sites/cis.org/files/camarota-declining-fertility.pdf
- ↑ Data file for downloading, United Nations, Department of Economics and Social Affair, Population Division, file with demographic indicators, line #28862
- ↑ Starr, Tena (28 April 2010). "Mexican farmworker's life like living in a "golden cage"". The Chronicle. Barton, Vermont. p. 12.
- ↑ "Homeward Bound: Recent Immigration Enforcement and the Decline in the Illegal Alien Population". Center for Immigration Studies.
- ↑ "Illegal immigration to U.S. drops after rising for decade". cbsnews.com. 6 December 2012.
- ↑ Largest region-of-birth group of immigrants in US
- ↑ Largest source of legal and illegal immigrants to US,
- ↑ "Frequently Requested Statistics on Immigrants and Immigration in the United States". migrationpolicy.org.
- ↑ "Homepage - USCIS". uscis.gov.
- 1 2 "United States: Inflow of foreign-born population by country of birth, by year (table available by menu selection)". Migration Policy Institute. 2007.
- ↑ Current Unemployment Rates for States and Historical Highs/Lows, U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
- 1 2 "Seasonally Adjusted Unemployment Rate". U.S. Dept. of Labor. Retrieved 2016-09-19.
- ↑ "Employment Situation Summary". U.S. Dept. of Labor. 2015-07-02. Retrieved 2015-12-26.
- ↑ "Table A-15. Alternative measures of labor underutilization". U.S. Bureau of Labor. Retrieved 2011-11-13.
- ↑ "U6 Unemployment Rate". Portal Seven. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- ↑ Fishkind, Hank (March 15, 2014). "Harsh winters make Florida attractive for visitors, moves,". Florida Today. Melbourne, Florida. pp. 4A. Retrieved March 28, 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Demographics of the United States. |
| Wikinews has related news: US population reaches 300 million |
- United States Census Bureau
- Quick demographics lookup
- New York Times: "Mapping the 2010 U.S. Census"
- 2000 Census of Population and Housing United States, U.S. Census Bureau
- U.S. Demographics and State Rankings
- Asian-Nation: Demographics of Asian American /2006-07-04-us-population_x.htm?csp=34 Countdown to 300 million
- Census Ancestry Map
- USA Today 2004 Election County by County Map
- BeliefNet State by State Religious Affiliation at the Wayback Machine (archived April 21, 2008) (archived from the original on 2008-04-21)
- Health by State
- U.S. Demographics and Maps
- America's Changing Demographics a Nightly Business Report special
- The Realignment of America - The Wall Street Journal
- Religion U.S. Census Bureau
- Google - public data "Population in the U.S.A."
- Population projection charts Population projections USA till 2100 by United Nations



