Tympanic duct
| Tympanic duct | |
|---|---|
|
Inner ear, with tympanic duct labeled near bottom. | |
|
Cross section of the cochlea (scala tympani labeled at bottom) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Scala tympani |
| MeSH | A09.246.631.246.848 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | s_03/12721078 |
| TA | A15.3.03.043 |
| FMA | 61269 |
The tympanic duct or scala tympani is one of the perilymph-filled cavities in the inner ear of the human. It is separated from the cochlear duct by the basilar membrane, and it extends from the round window to the helicotrema, where it continues as vestibular duct.
The purpose of the perilymph-filled tympanic duct and vestibular duct is to transduce the movement of air that causes the tympanic membrane and the ossicles to vibrate, to movement of liquid and the basilar membrane. This movement is conveyed to the organ of Corti inside the cochlear duct, composed of hair cells attached to the basilar membrane and their stereocilia embedded in the tectorial membrane. The movement of the basilar membrane compared to the tectorial membrane causes the sterocilia to bend. They then depolarise and send impulses to the brain via the cochlear nerve. This produces the sensation of sound.
Additional images
 Interior of right osseous labyrinth. (Scala tympani labeled at right, inside cochlea.
Interior of right osseous labyrinth. (Scala tympani labeled at right, inside cochlea.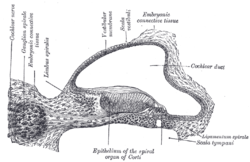 Transverse section of the cochlear duct of a fetal cat.
Transverse section of the cochlear duct of a fetal cat. The cochlea and vestibule, viewed from above.
The cochlea and vestibule, viewed from above. Diagrammatic longitudinal section of the cochlea.
Diagrammatic longitudinal section of the cochlea.

