Morabaraba
|
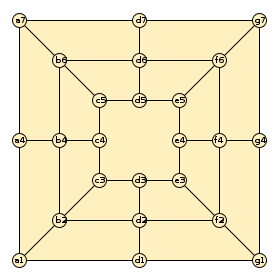
Morabaraba gameboard. Pieces move from intersection to intersection along marked lines. | |
| Genre(s) |
Board game Abstract strategy game |
|---|---|
| Players | 2 |
| Setup time | < 1 minute |
| Playing time | < 1 hour |
| Random chance | None |
| Skill(s) required | Strategy, tactics |
| Synonym(s) |
Mlabalaba, Mmela [in Setswana] Muravava, Umlabalaba Mororova |
Morabaraba is a traditional two-player strategy board game played in South Africa, Botswana and Lesotho. The game is also known as Mlabalaba, Mmela (in Setswana), Muravava, Umlabalaba. The game is similar to Twelve Men's Morris, a variation on the Roman board game Nine Men's Morris.
While some believe that Morabaraba was introduced to southern Africa by British settlers, Morris variants exist in many parts of the world; e.g. India (Char Bhar), Ghana (Achi), Kenya (Shisimia), Somalia (Shax), Zimbabwe (Tsoro Yemutwelve), the Philippines (Tapatan) and Mongolia (Gurgaldaj). It is claimed that Morabaraba boards carved in rock are dated to be at least 800 years old, which would exclude a European origin. However, many rock art images do not actually show Morabaraba, but the mancala game of Moruba (i.e. rows of cupules).
Morabaraba is today most popular amongst rural African youth in southern Africa. In South Africa it is also commonly known by the Xhosa form of the name Umlabalaba. In the traditional European game the counters are commonly referred to as "men", but in the South African game the counters are referred to as "cows", the game being particularly popular amongst youth who herd cattle.
According to the Oxford English Dictionary, the term "Morabaraba" is derived from the Southern Sotho moraba-raba, meaning "mill" or to "go round in a circle".
Gameplay
Morabaraba is accessible and easy to learn, and games can be played quickly, but the strategic and tactical aspects of the game run deep. While Morabaraba may be played on specially produced boards (or computer software), it is simple enough that a board can easily be scratched on a stone or into sand, with coins or pebbles (or whatever comes to hand) used as the pieces. The description below is compatible with Mind Sports South Africa's "Generally Accepted Rules".
There are three main phases to the game:
- Placing the cows
- Moving the cows
- Flying the cows
Placing the cows
- The board is empty when the game begins. Each player has 12 pieces, known as "cows"; one player has light cows and the other has dark cows.
- The player with the dark cows moves first.
- Each turn consists of placing a cow on an empty intersection on the board.
- The aim is to create a "mill": a row of three cows on any line drawn on the board.
- If a player forms a mill, he or she may remove or "shoot" one of the opponent's cows. The shot cow is removed from the board and not placed again. A cow in a mill may not be shot unless all of the opponent's cows are in mills, in which case any cow may be shot.
- Even if a move creates more than one mill, only one cow can be shot in a single move.
Moving the cows
- After all the cows have been placed, each turn consists of moving a cow to an empty adjacent intersection.
- As before, completing a mill allows a player to shoot one of the opponent's cows. Again, this must be a cow which is not in a mill, unless all of the opponent's cows are in mills.
- Players are allowed to "break" their own mills.
- A mill may be broken and remade repeatedly by shuffling cows back and forth. Each time the mill is remade, one of the opponent's cows is shot. Of course, by breaking the mill the player exposes the cows which were in a mill to the risk of being shot by the opponent on his or her next turn.
- In the "Generally Accepted Rules" published by Mind Sports South Africa, a mill which is broken to form a new mill can't be formed again on the next move.
Flying the cows
- When a player has only three cows remaining, desperate measures are called for. This player's cows are allowed to "fly" to any empty intersection, not just adjacent ones.
- If one player has three cows and the other player has more than three cows, only the player with three cows is allowed to fly.
Finishing the game
- You win if your opponent cannot move.
- You win if your opponent has just two cows.
- If either player has only three cows and neither player shoots a cow within ten moves, the game is drawn.
- One person cheats, then the other one wins by default.
Morabaraba as sport
Currently the International Wargames Federation is the international controlling body for the game, and Mind Sports South Africa is the South African controlling body for the game. Mind Sports South Africa is recognised by both the South African Department of Sports and Recreation and the South African Sports Confederation and Olympic Committee (SASCOC) .
Mind Sports South Africa has invested a great deal of time and effort into the different versions of Morabaraba which have borne fruit by having leagues played throughout the country as well as having adopted a notation system similar to Nine Men's Morris.
The game is an official discipline of the Traditional World Games, which are held every five years. Tournaments were not just in South Africa, but also in Bangkok (Thailand), Melbourne (Australia), New Orleans (United States), Athens (Greece) and at the Epsom College in England.
The World Championships results:
| Year | SENIOR Winner | WOMEN Winner | JUNIOR Winner | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1997 | Gilbert Magabotse (Mind Sports South Africa) | Old Edwardian Society, Johannesburg, South Africa | ||
| 1999 | Amos Mavuso (Mind Sports South Africa) | The Castle, Cape Town, South Africa | ||
| 2000 | David Hlophe (Mind Sports South Africa) | Epsom College, Epsom, United Kingdom | ||
| 2001 | David Hlophe (Mind Sports South Africa) | Epsom College, Epsom, United Kingdom | ||
| 2002 | Simon Skhosana (Mind Sports South Africa) | Innocent Kubheka (Mind Sports South Africa) | Blue Waters Hotel, Durban, South Africa | |
| 2003 | Simphiwe Maphumulo (Mind Sports South Africa) | New Orleans, United States of America | ||
| 2004 | Simphiwe Maphumulo (Mind Sports South Africa) | Rome, Italy | ||
| 2005 | Medupe Sekao (Botswana Wargames Federation) | Teresa Chen (Mind Sports South Africa) | Teresa Chen (Mind Sports South Africa) | University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia |
| 2006 | Thanos Taktikos (Hellenic Wargames Federation) | Gazza, Athens, Greece | ||
| 2007 | Moses Rannyadi (Mind Sports South Africa) | Ledile Tshwane (Mind Sports South Africa) | Innocent Kubheka (Mind Sports South Africa) | Marine Hotel, Port Elizabeth, South Africa |
| 2008 | Hanna Melkko (Finnish Historical Wargames Association) | Hanna Melkko (Finnish Historical Wargames Association) | Helsinki, Finland | |
| 2012 | Simphiwe Maphumulo (Mind Sports South Africa) | Zama Latha (Mind Sports South Africa) | Blue Waters Hotel, Durban, South Africa | |
| 2013 | Simphiwe Maphumulo (Mind Sports South Africa) | Pretoria Boys High, Pretoria, South Africa | ||
| 2014 | Lejone Malikoe (Lesotho Mind Sports Association) | Victoria Hotel, Maseru, Lesotho | ||
| 2015 | Senane Gadlela (Swaziland Mind Sports Association) | Nipho Sipnepho (Swaziland Mind Sports Association) | Lugogo Sun, Mbabane, Swaziland | |
Variations
Sesotho Morabaraba
This is the variation typically played by Sesotho speaking children in South Africa. It differs from the standard form in that the board does not have diagonals between the center points of its sides and there is an additional intersection in the center of the board to prevent a draw.
Eleven Men's Morris
This is a European variation that uses the same board as Morabaraba but is played with eleven counters. This prevents a situation where the game can end in a draw in the placement phase.
Standard notation
The standard Welt-Mühlespiel-Dachverband notation for Nine Men's Morris works well for Morabaraba (see diagram). It is very similar to algebraic notation in chess. The board is laid out on a grid, with the columns in the grid being labelled a–g (from left to right), and rows in the grid being labelled from 1–7 (bottom to top). Each point is then referred to by its coordinate; for example, the top-left point in the middle (not inner) square is labelled b6. Moves are then formatted as in chess or draughts: placing a piece is denoted simply by the square where it is placed; moving a piece by the from and to squares (e.g. c5-d5); capturing by appending the captured piece to the move (e.g. c5-b6xe5 or c4xa1).
References
- Davie, K., The Little Golden Rhino. Peace Parks Foundation, Stellenbosch (South Africa) April 4, 2004.
- Dunton, C. Ntaote, B & Bulane, N., A Game for Two: Morabaraba. In: Sethlala (Lesotho) 1990; Issue March/April, 30–31.
- Futhwa, F., Setho: Afrikan Thought and Belief System. Nalane ka Fezekile Futhwa, Alberton (South Africa) 2011, 66
- Hamann, H., Herdboys' Game Moves into the Big Time. In: The Sunday Times (South Africa) February 13, 2000
- Hess, S., Playing the African Game. In: 1999 Guide to South African Arts, Culture and Heritage. 1999.
- Lehihi, M., The African Game. In: Sunday Times (South Africa) April 6, 2003.
- Mathys, C., Kids Learn to Be Game for Traditional Sports. In: Cape Argus, Independent News and Media April 26, 2005.
- Mosimege, M. D., Exploration of the Games of Malepa and Morabaraba in South African Secondary School Mathematics Education. University of the Western Cape, Cape Town (South Africa) 2000.
- Nkopodi, N. & Mosimege M. S., Incorporating the Indigenous Game of Morabaraba in the Learning of Mathematics. In: South African Journal of Education 2009; 29(3), 377–392.
- Russouw, S., Getting Morabaraba back on Board. In: Johannesburg News Agency September 20, 2002.
- Thokozile Mkonto, K., Indigenous Games Rule Book. Sport Recreation South Africa, Pretoria (South Africa) 2006: 22–23.
External links
- Mindsports South Africa – the South African National controlling body for Morabaraba
- International Wargames Federation
- Generally Accepted Rules for the game of Morabaraba