Flemish
Flemish (Vlaams),[1][2][3] also called Flemish Dutch (Vlaams-Nederlands), Belgian Dutch (Belgisch-Nederlands [ˈbɛlɣis ˈneːdərlɑnts]), or Southern Dutch (Zuid-Nederlands), is any of the varieties of the Dutch language dialects spoken in Flanders, the northern part of Belgium,[4][5][6][7] by approximately 6 million people.[8][9][10] They differ to some extent from the Dutch spoken in the Netherlands in terms of intonation and pronunciation, and there are minor differences in vocabulary, including loanwords from French and English not found in Standard Dutch.[3]
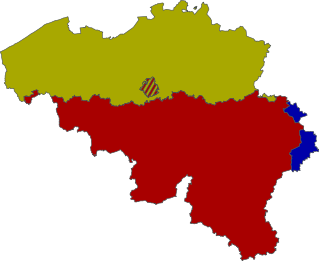
There are four principal Dutch dialects in the Flemish region (Flanders): Brabantian, East Flemish, West Flemish and Limburgish.[11] The latter two are sometimes considered separate (regional) languages.[12] Despite its name, Brabantian is the dominant contributor to the Flemish Dutch tussentaal. The combined region, culture, and people of Dutch-speaking Belgium (which consists of the provinces of West Flanders, East Flanders, Flemish Brabant, Antwerp, and Limburg, and historically of Brussels) has come to be known as "Flemish".[13] "Flemish" is also used to refer to one of the historical languages spoken in the former County of Flanders.[14]
Linguistically and formally, "Flemish" refers to the region, culture and people of (North) Belgium or Flanders. Flemish people speak (Belgian) Dutch in Flanders, the Flemish part of Belgium. "Belgian Dutch" is slightly different from Dutch spoken in The Netherlands, mainly in pronunciation, lexicon and expressions. Dutch speakers from the Netherlands and Dutch speakers from Belgium may not be able to communicate fluently with each other because Flemish uses different nouns and different pronunciation, and has evolved at a different pace from modern Dutch.[15] Similar differences exist within other languages, such as English (Australia, New Zealand, Canada, UK, USA, South Africa, etc.), French (Belgium, Canada, France, Switzerland, etc.), Spanish (Mexico,Chile, Spain, Argentina, Colombia etc.), and Portuguese (Brazil, Portugal, etc.). The differences are not significant enough to constitute an individual language (just as American English, Mexican Spanish, Canadian French and Brazilian Portuguese have not diverted enough from their European sources to be considered separate languages).[16]
Characteristics
Dutch is the majority language in northern Belgium, being spoken natively by three-fifths of the population. It is one of the three national languages of Belgium, together with French and German, and is the only official language of the Flemish Region.
The various Dutch dialects spoken in Belgium contain a number of lexical and a few grammatical features which distinguish them from the standard Dutch.[17] As in the Netherlands, the pronunciation of Standard Dutch is affected by the native dialect of the speaker.
All Dutch dialect groups spoken in Belgium are spoken in adjacent areas of the Netherlands as well. East Flemish forms a continuum with both Brabantic and West Flemish. Standard Dutch is primarily based on the Hollandic dialect [18] (spoken in the Western provinces of the Netherlands) and to a lesser extent on Brabantian, which is the dominant dialect in Flanders, as well as in the south of the Netherlands.
Phonological differences
Among vowels is the diphthong "ou" / "au." Ou as in bout (bolt) and au as in fauna is realized as [ɔ̞u] in formal situations. In informal situations, the sound tends to be pronounced as [ɔ̞u] or as a monophthong [ɔ̞ː], depending on the dialect. In contrast, these are generally pronounced as [ʌu] in the north and middle parts of the Netherlands. Among consonants, the northern Dutch pronunciation of "w" (as in wang cheek) is [ʋ], in some southern Dutch dialects it is [β̞] or [w]. Probably the most obvious difference between northern and southern Dutch is in the sounds spelled ⟨ch⟩ and ⟨g⟩. The sound spelled ⟨ch⟩ is a voiceless velar fricative [x] in northern Dutch and a voiceless prevelar fricative [x̟] in southern Dutch.[19] In the northern and western parts of the Netherlands the sound spelled ⟨g⟩ is usually realized as voiceless velar fricative [x] or voiceless uvular fricative [χ], whereas in the south, the distinction between voiced and unvoiced has been preserved and ⟨g⟩ is pronounced as voiced pre-velar fricative /ɣ̟/.
Consonants
- ⟨w⟩ realised as [β̞]
- ⟨ch⟩ and ⟨g⟩ pronounced as (voiceless resp. voiced) front-velars, not as palatals, as often claimed.
- alveolar consonants /n, t, d, s, z, l/ are pronounced as denti-alveolarsMap showing the dialects spoken in the Benelux: many people in Flanders speak a dialect and the common Flemish, and understand spoken Dutch; in writing, the dialects are hardly used, while Flemish and Dutch are nearly identical in this regard
Vowels
The difference between short and long vowels tends to be quantitative instead of qualitative, especially in the influential Brabantic pronunciation.
Diphthongs
Strong tendency towards monophthongisation.
- ⟨au⟩/⟨ou⟩ realized as [ɔ̞ː]
- ⟨ij⟩/⟨ei⟩ realized as [ɛ̞ː]
- ⟨ui⟩ realized as [œː]
Loanwords
Northern Dutch speakers tend to retain the foreign pronunciation of loanwords, whereas Belgian speakers tend to dutchify their pronunciation.[20]
Lexical differences
Belgian Dutch includes different French loanwords in its vocabulary compared to Netherlands Dutch.[21] There are also different Dutch terms for similar things: for example, the former Belgian gendarmerie was known as the Rijkswacht ("Guard of the Realm") in Belgium while the equivalent body in the Netherlands is the Koninklijke Marechaussee ("Royal Military Constabulary").
The traditionally most spoken Dutch dialect in Belgium, Brabantian, has had a large influence on the vocabulary used in Belgium.[22] Examples include beenhouwer (Brabantian) and slager (Hollandic), both meaning butcher (slager is however used in Belgium to mean the kind of butcher who sells salami, sausages, etc.: cf. the difference between beenhouwerij (butcher's shop) and slagerij (delicatessen)); also schoon (Brabantian) vs. mooi (Hollandic) "beautiful": in standard Dutch, schoon means clean, whereas in Belgium it is often used for pretty or beautiful. Another notable difference is ge / gij ("you" in Brabantian and "thou / thee" in the Dutch Bible, originally translated by Belgian Protestants fleeing the Inquisition under Philip II of Spain) vs. je / jij ("you" singular in Hollandic), jullie ("you" plural in Hollandic). The changes (isoglosses) from northern to southern Dutch dialects are somewhat gradual, both vocabulary-wise and phonetically, and the boundaries within coincide with mediaeval territorial borders. There is a distinct boundary located in the river area of the Netherlands, south of which northern variants of Brabantian are spoken, which share phonological traits with the southern variants spoken in Belgium. A second distinct border area is located around the border with the Belgian territories, where the transition is mostly lexical, but also with an intensification of the phonological diversion from northern Dutch. An exception to the border with the Belgian territories for this border is Zeelandic Flanders ("Zeeuws-Vlaanderen"), a part of the Netherlands where Flemish is spoken.
Flemish and Dutch television shows are occasionally subtitled for the other country in their standard language when using informal speech or dialects because of the differences in pronunciation, lexicon and expressions.[23]
In 2009, one of the main publishers of Dutch dictionaries, Prisma, published the first Dutch dictionary that distinguished between the two natiolectic varieties "Nederlands Nederlands" (or "Netherlandish Dutch") and "Belgisch Nederlands" ("Belgian Dutch"), treating both variations as equally correct. The selection of the "Flemish Dutch" words was based on the Referentiebestand Belgisch Nederlands (RBBN): an electronic database built under the supervision of Prof. Dr. W. Martin (Free University in Amsterdam, Netherlands) and Prof. Dr. W. Smedts (Catholic University in Leuven, Belgium).
Professor Willy Martin, one of the Flemish editors, claimed that the latter expressions are "just as correct" as the former. This formed a break with the previous lexicologists' custom of indicating Dutch words that are mostly only used in Flanders, while not doing the same for Dutch words mostly only used in the Netherlands, which could give the impression that only usage in the Netherlands defines the standard language.
In the Dutch language, around 3,500 words exist which are considered "Flemish Dutch", and 4,500 words which are considered "Netherlands Dutch".[24][25]
In November 2012 the Belgian radio channel Radio 1 wrote a text with words used in Flanders, and asked several Dutch-speaking people to "translate" it into general Dutch. Almost no inhabitant of the Netherlands was able to make a correct translation, whereas almost all Flemings succeeded.[26][27]
Tussentaal
The supra-regional, semi-standardized colloquial form (mesolect) of Dutch spoken in Belgium uses the vocabulary and the sound inventory of the Brabantic dialects. It is often called Tussentaal ("in-between-language" or "intermediate language", intermediate between dialects and standard Dutch).[28]
It is a rather informal variety of speech, which occupies an intermediate position between regional dialects and the standard language. It incorporates phonetic, lexical and grammatical elements not part of the standard language but drawn from local dialects.
It is a relatively new phenomenon that has been gaining popularity during the past decades. Some linguists note that it seems to be undergoing a process of (limited) standardisation[29][30] or that it is evolving into a Koiné language.[31]
Tussentaal is slowly gaining popularity in Flanders because it is used a lot in television dramas and comedies. Often, middle-class characters in a television series will be speaking tussentaal, lower-class characters use the dialect of the location where the show is set, and upper-class characters will speak Standard Dutch.[32] That has given tussentaal the status of normalcy in Flanders. It is slowly being accepted by the general population but has led to some controversy among linguists, who are afraid that it dilutes the usage of Standard Dutch.[33] Tussentaal is used in entertainment television but rarely in informative programmes (like the news), which normally use Standard Dutch.
Etymology
The English adjective Flemish (first attested as flemmysshe, c. 1325;[34] cf. Flæming, c. 1150),[35] meaning "from Flanders", was probably borrowed from Old Frisian.[36] The name Vlaanderen was probably formed from a stem flām-, meaning "flooded area", with a suffix -ðr- attached.[37] The Old Dutch form is flāmisk, which becomes vlamesc, vlaemsch in Middle Dutch and Vlaams in Modern Dutch.[38]
See also
- Afrikaans
- Belgian French
- French Flemish, the West Flemish dialect as spoken in France
- Languages of Belgium
- Walloon
- Zeelandic, a transitional dialect between West Flemish and Hollandic
References
- ↑ "Flemish, Vlaams". BBC. 14 October 2014. Retrieved 26 November 2016.
- ↑ "Flemish language policy in an era of globalisation by Barbara De Cock" (PDF). Gencat.cat. 2006. Retrieved 3 May 2017.
- 1 2 "Flemish language, alphabet and pronunciation". Omniglot. Retrieved 26 November 2016.
- ↑ "Belgium: A nation divided". The Independent. 18 December 2007. Retrieved 3 May 2017.
- ↑ Leidraad van de Taaltelefoon. Dienst Taaladvies van de Vlaamse Overheid (Department for Language advice of the Flemish government).
- ↑ Harbert, The Germanic Languages, CUP, 2007
- ↑ Jan Kooij, "Dutch", in Comrie, ed., The World's Major Languages, 2nd ed. 2009
- ↑ "ATLAS - Dutch: Who speaks it?". UCL. Retrieved 26 November 2016.
- ↑ "Belgium Bickering Over French and Dutch, Its Dual Languages". Los Angeles Times. 20 February 2005. Retrieved 26 November 2016.
- ↑ "About Belgium - Language Matters". Beer Tourism. Retrieved 26 November 2016.
- ↑ Ethnologue (1999-02-19). "Linguistic map of Benelux". Ethnologue.com. Retrieved 2013-10-17.
- ↑ Their ISO 639-3 codes are vls and lim, respectively.
- ↑ "Vlaams". Ethnologue. Retrieved 20 February 2013.
- ↑ König & Auwera, eds, The Germanic Languages, Routledge, 1994
- ↑ "Languages spoken in Brussels". Brussels.info. Retrieved 3 May 2017.
- ↑ "Language and territoriality in Flanders in a historical and international context". Flanders.be. Retrieved 2014-01-25.
Article 4 of the constitution stipulates that there are four language areas. The Dutch, French and German language areas are monolingual. The Brussels-Capital area is bilingual. (p. 27 of the pdf)
- ↑ G. Janssens and A. Marynissen, Het Nederlands vroeger en nu (Leuven/Voorburg 2005), 155 ff.
- ↑ "De gesproken standaardtaal: het Algemeen Beschaafd Nederlands". Structuur en geschiedenis van het Nederlands Een inleiding tot de taalkunde van het Nederlands (in Dutch). Niederländische Philologie, Freie Universität Berlin. 2014-06-10. Retrieved 2015-08-10.
- ↑ Pieter van Reenen; Nanette Huijs (2000). "De harde en de zachte g, de spelling gh versus g voor voorklinker in het veertiende-eeuwse Middelnederlands." (PDF). Taal en Tongval, 52(Thema nr.), 159-181 (in Dutch). Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ↑ https://dutchplusplus.ned.univie.ac.at/node/123
- ↑ G. Janssens and A. Marynissen, Het Nederlands vroeger en nu (Leuven/Voorburg 2005), 156
- ↑ Tussen spreek- en standaardtaal. Koen Plevoets. Katholieke Universiteit Leuven.
- ↑ "Vlaamse TV kijkers verstaan geen Hollands (Flemish TV viewers do not understand Hollandic)". Taalunieversum.org. 2010-01-26. Retrieved 2012-01-19.
- ↑ Auteur: Dirk Musschoot (2009-12-06). "Nederlands uit Nederland of uit Vlaanderen: het kan allebei - Primeur: Prisma-woordenboek duidt regionaal gebruik aan". Nieuwsblad.be. Retrieved 2012-01-19.
- ↑ "Belgisch-Nederlands in de vertaalpockets". Prismawoordenboeken.nl. Retrieved 2012-01-19.
- ↑ redactie. "Nieuwsblad: De voor Nederlanders meest onbegrijpelijke Vlaamse tekst". Demorgen.be. Retrieved 2013-10-17.
- ↑ donderdag 08 november 2012 (2012-11-08). "Radio 1: De voor Nederlanders meest onbegrijpelijke Vlaamse Tekst". Radio1.be. Retrieved 2013-10-17.
- ↑ "Geeraerts, Dirk. 2001. "Een zondagspak? Het Nederlands in Vlaanderen: gedrag, beleid, attitudes". Ons Erfdeel 44: 337-344" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-01-19.
- ↑ G. Janssens and A. Marynissen, Het Nederlands vroeger en nu (Leuven/Voorburg 2005), 196.
- ↑ "Algemeen Vlaams". VlaamseTaal.be. Retrieved 2013-04-14.
- ↑ Rys, K. & J. Taeldeman (2007). Fonologische ingrediënten van Vlaamse tussentaal. In: D. Sandra, R. Rymenans, P. Cuvelier et al. (red.), Tussen taal, spelling en onderwijs. Essays bij het emeritaat van Frans Daems. Gent: Academia Press, 1-9, p.2.
- ↑ "Standaardtaal of tussentaal op televisie" (PDF). Universiteit Gent. Retrieved 2014-08-28.
- ↑ "Actie tegen onverstaanbare Vlaamse 'tussentaal' op televisie". volkskrant.nl. Retrieved 2014-08-28.
- ↑ "entry Flēmish". Middle English Dictionary (MED).
- ↑ "MED, entry "Flēming"". Quod.lib.umich.edu. Retrieved 2013-10-17.
- ↑ "entry Flemish". Online Etymological Dictionary. Etymonline.com. which cites Flemische as an Old Frisian form; but cf. "entry FLĀMISK, which gives flēmisk". Oudnederlands Woordenboek (ONW). Gtb.inl.nl.
- ↑ "Entry VLAENDREN; ONW, entry FLĀMINK; Woordenboek der Nederlandsche Taal (WNT), entry VLAMING". Vroeg Middelnederlandsch Woordenboek (VMNW). Gtb.inl.nl.
- ↑ ONW, entry FLĀMISK.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Languages of Belgium. |