Turmeric
| Turmeric | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Inflorescence of Curcuma longa | |
 | |
| Processed turmeric | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Clade: | Commelinids |
| Order: | Zingiberales |
| Family: | Zingiberaceae |
| Genus: | Curcuma |
| Species: | C. longa |
| Binomial name | |
| Curcuma longa L.[1] | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Curcurma domestica Valeton | |
Turmeric (/ˈtɜːrmərɪk/)[2] is a rhizomatous herbaceous perennial plant (Curcuma longa) of the ginger family, Zingiberaceae.[3] It is native to Southeast Asia, and requires temperatures between 20 and 30 °C (68 and 86 °F) and a considerable amount of annual rainfall to thrive. Plants are gathered annually for their rhizomes and propagated from some of those rhizomes in the following season.
When not used fresh, the rhizomes are boiled for about 30–45 minutes and then dried in hot ovens, after which they are ground into a deep-orange-yellow powder[4] commonly used as a coloring and flavoring agent in the cuisines of Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, Iran, and Pakistan, especially for curries, as well as for dyeing.
Although long-used in Ayurvedic medicine to treat various diseases, there is little high-quality clinical evidence for use of turmeric or its main constituent, curcumin, as a therapy.[5][6]
History
Turmeric has been used in Asia for thousands of years and is a major part of Ayurveda, Siddha medicine, Unani, and traditional Chinese medicine.[7] It was first used as a dye, and then later for its medicinal properties.[8]
Etymology
The origin of the name is uncertain. It possibly derives from Middle English or Early Modern English as turmeryte or tarmaret. It may be of Latin origin, terra merita ("meritorious earth").[9] The name of the genus, Curcuma, is derived from the Sanskrit kuṅkuma, referring to both turmeric and saffron, used in India since ancient times.[10]
Botanical description
Appearance
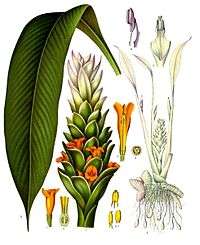
Turmeric is a perennial herbaceous plant that reaches up to 1 m (3 ft 3 in) tall. Highly branched, yellow to orange, cylindrical, aromatic rhizomes are found. The leaves are alternate and arranged in two rows. They are divided into leaf sheath, petiole, and leaf blade.[11] From the leaf sheaths, a false stem is formed. The petiole is 50 to 115 cm (20 to 45 in) long. The simple leaf blades are usually 76 to 115 cm (30 to 45 in) long and rarely up to 230 cm (91 in). They have a width of 38 to 45 cm (15 to 18 in) and are oblong to elliptic, narrowing at the tip.
Inflorescence, flower, and fruit


In China, the flowering time is usually in August. Terminally on the false stem is a 12 to 20 cm (4.7 to 7.9 in) long inflorescence stem containing many flowers. The bracts are light green and ovate to oblong with a blunt upper end with a length of 3 to 5 cm (1.2 to 2.0 in).
At the top of the inflorescence, stem bracts are present on which no flowers occur; these are white to green and sometimes, tinged reddish-purple, and the upper ends are tapered.[12]
The hermaphrodite flowers are zygomorphic and threefold. The three 0.8 to 1.2 cm (0.3 to 0.5 in) long sepals are fused, white, have fluffy hairs and the three calyx teeth are unequal. The three bright-yellow petals are fused into a corolla tube up to 3 cm (1.2 in) long. The three corolla lobes have a length of 1.0 to 1.5 cm (0.39 to 0.59 in) and are triangular with soft-spiny upper ends. While the average corolla lobe is larger than the two lateral, only the median stamen of the inner circle is fertile. The dust bag is spurred at its base. All other stamens are converted to staminodes. The outer staminodes are shorter than the labellum. The labellum is yellowish, with a yellow ribbon in its center and it is obovate, with a length from 1.2 to 2.0 cm (0.47 to 0.79 in). Three carpels are under a constant, trilobed ovary adherent, which is sparsely hairy. The fruit capsule opens with three compartments.[13][14][15]
Phytochemistry
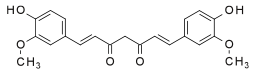

Phytochemical components of turmeric include compounds called curcuminoids, such as curcumin (diferuloylmethane), demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin. Curcumin constitutes 3.14% (on average) of powdered turmeric, having variations in content among the species of Curcuma longa.[16] In addition, volatile oils include turmerone, atlantone, and zingiberene. Other constituents are sugars, proteins, and resins.[17]
Uses
Traditional medicine
Turmeric grows wild in the forests of South and Southeast Asia where it is collected for use in Indian traditional medicine (also called Siddha or Ayurveda).[5] From clinical research, there is no high-quality evidence that turmeric has medicinal properties.[5]
Culinary




Turmeric is one of the key ingredients in many Asian dishes. Its use as a coloring agent is not of primary value in South Asian cuisine.
Turmeric is used mostly in savory dishes, but also is used in some sweet dishes, such as the cake sfouf. In India, turmeric plant leaf is used to prepare special sweet dishes, patoleo, by layering rice flour and coconut-jaggery mixture on the leaf, then closing and steaming it in a special copper steamer (goa).
In recipes outside South Asia, turmeric sometimes is used as an agent to impart a golden yellow color. It is used in canned beverages, baked products, dairy products, ice cream, yogurt, yellow cakes, orange juice, biscuits, popcorn color, cereals, sauces, gelatins, etc. It is a significant ingredient in most commercial curry powders.
Most turmeric is used in the form of rhizome powder. In some regions (especially in Maharashtra, Goa, Konkan, and Kanara), turmeric leaves are used to wrap and cook food. Turmeric leaves are mainly used in this way in areas where turmeric is grown locally, since the leaves used are freshly picked. Turmeric leaves impart a distinctive flavor.
Although typically used in its dried, powdered form, turmeric also is used fresh, like ginger. It has numerous uses in East Asian recipes, such as pickle that contains large chunks of soft turmeric, made from fresh turmeric.
Turmeric is used widely as a spice in South Asian and Middle Eastern cooking. Many Persian dishes use turmeric as a starter ingredient. Various Iranian khoresh dishes are started using onions caramelized in oil and turmeric, followed by other ingredients. The Moroccan spice mix ras el hanout typically includes turmeric.
In India and Nepal, turmeric is widely grown and extensively used in many vegetable and meat dishes for its color. It also is used in Nepal for its supposed value in traditional medicine.
In South Africa, turmeric is used to give boiled white rice a golden colour, known as geelrys (yellow rice) traditionally served with bobotie.
In Vietnamese cuisine, turmeric powder is used to color and enhance the flavors of certain dishes, such as bánh xèo, bánh khọt, and mi quang. The powder is used in many other Vietnamese stir-fried and soup dishes.
The staple Cambodian curry paste kroeung, used in many dishes including Amok, typically contains fresh turmeric.
In Indonesia, turmeric leaves are used for Minang or Padang curry base of Sumatra, such as rendang, sate padang, and many other varieties.
In Thailand, fresh turmeric rhizomes are used widely in many dishes, in particular in the southern Thai cuisine, such as the yellow curry and turmeric soup.
In medieval Europe, turmeric became known as Indian saffron because it was used widely as an alternative to the far more expensive saffron spice.
Dye
Turmeric makes a poor fabric dye, as it is not very light fast, but is commonly used in Indian and Bangladeshi clothing, such as saris and Buddhist monks's robes.[18] Turmeric (coded as E100, when used as a food additive),[19] is used to protect food products from sunlight. The oleoresin is used for oil-containing products. A curcumin and polysorbate solution or curcumin powder dissolved in alcohol is used for water-containing products. Over-coloring, such as in pickles, relishes, and mustard, is sometimes used to compensate for fading.
In combination with annatto (E160b), turmeric has been used to color cheeses, yogurt, dry mixes, salad dressings, winter butter, and margarine. Turmeric also is used to give a yellow color to some prepared mustards, canned chicken broths, and other foods (often as a much cheaper replacement for saffron).[20]
Indicator
Turmeric paper, also called curcuma paper or in German literature, Curcumapapier, is paper steeped in a tincture of turmeric and allowed to dry. It is used in chemical analysis as an indicator for acidity and alkalinity.[21] The paper is yellow in acidic and neutral solutions and turns brown to reddish-brown in alkaline solutions, with transition between pH of 7.4 and 9.2.[22]
Traditional uses

In Ayurvedic and Siddha practices, turmeric has been used as an attempted treatment for a variety of internal disorders, such as indigestion, throat infections, common colds, or liver ailments, as well as topically, to cleanse wounds or treat skin sores.[5][6]
In Eastern India, the plant is used as one of the nine components of navapatrika along with young plantain or banana plant, taro leaves, barley (jayanti), wood apple (bilva), pomegranate (darimba), asoka, manaka or manakochu, and rice paddy. The Navapatrika worship is an important part of Durga festival rituals.[23]
Haldi ceremony (called Gaye holud in Bengal) (literally "yellow on the body") is a ceremony observed during Hindu wedding celebrations in many parts of India including Bengal, Punjab, Maharashtra, and Gujarat.[24]
In Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh, as a part of the Tamil/Telugu marriage ritual, dried turmeric tuber tied with string is used to create a Thali necklace, the equivalent of marriage rings in western cultures. In western and coastal India, during weddings of the Marathi and Konkani people, Kannada Brahmins turmeric tubers are tied with strings by the couple to their wrists during a ceremony, Kankanabandhana.[25]
Friedrich Ratzel reported in The History of Mankind during 1896, that in Micronesia, turmeric powder was applied for embellishment of body, clothing, utensils, and ceremonial uses.[26]
Adulteration
As turmeric and other spices are commonly sold by weight, the potential exists for powders of toxic, cheaper agents with a similar color to be added, such as lead(II,IV) oxide, giving turmeric an orange-red color instead of its native gold-yellow.[27] Another common adulterant in turmeric, metanil yellow (also known as acid yellow 36), is considered an illegal dye for use in foods by the British Food Standards Agency.[28]
Research
Claims that curcumin in turmeric may help to reduce inflammation have not been supported by strong studies.[5][6]
Turmeric or its principal constituent, curcumin, has been studied in numerous clinical trials for various human diseases and conditions, but the conclusions have either been uncertain or negative.[5][29][30]
See also
References
- ↑ "Curcuma longa information from NPGS/GRIN". ars-grin.gov. Retrieved 2008-03-04.
- ↑ "Turmeric (pronunciation)". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. 2015.
- ↑ Priyadarsini, KI (2014). "The chemistry of curcumin: from extraction to therapeutic agent". Molecules. 19 (12): 20091–112. PMID 25470276. doi:10.3390/molecules191220091.
- ↑ "Turmeric processing". Kerala Agricultural University, Kerala, India. 2013. Retrieved 10 October 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Nelson, K. M.; Dahlin, J. L.; Bisson, J; Graham, J; Pauli, G. F.; Walters, M. A. (2017). "The Essential Medicinal Chemistry of Curcumin: Miniperspective". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 60 (5): 1620–1637. PMC 5346970
 . PMID 28074653. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00975.
. PMID 28074653. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00975. - 1 2 3 "Turmeric". National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH). National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH). Retrieved 31 January 2017.
- ↑ Chattopadhyay, Ishita; Kaushik Biswas; Uday Bandyopadhyay; Ranajit K. Banerjee (10 July 2004). "Turmeric and curcumin: Biological actions and medicinal applications" (PDF). Current Science. Indian Academy of Sciences. 87 (1): 44–53. ISSN 0011-3891. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
- ↑ "Herbs at a Glance: Turmeric, Science & Safety". National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH), National Institutes of Health. 2012. Retrieved 11 October 2012.
- ↑ "Turmeric". Dictionary.com; Unabridged Random House Dictionary. 2013. Retrieved 11 October 2012.
- ↑ Tawney, C. H. (1924). The Ocean of Story, chapter 104. p. 13.
- ↑ Grieve, M. "Turmeric". botanical.com. Retrieved April 14, 2017.
- ↑ "Curcuma longa Linn". efloras.org. Flora of China, South China Botanical Garden. Retrieved November 30, 2013.
- ↑ Siewek, Fred (2013). Exotische Gewürze Herkunft Verwendung Inhaltsstoffe (in German). Springer-Verlag. p. 72. ISBN 978-3-0348-5239-5.
- ↑ "Kurkuma kaufen in Ihrem" (in German). Archived from the original on November 20, 2016. Retrieved November 20, 2016.
- ↑ Hänsel, Rudolf; Keller, Konstantin; Rimpler, Horst; Schneider, Gerhard, eds. (2013). Drogen A-D (in German). Springer-Verlag. p. 1085. ISBN 978-3-642-58087-1.
- ↑ Tayyem RF, Heath DD, Al-Delaimy WK, Rock CL (2006). "Curcumin content of turmeric and curry powders". Nutr Cancer. 55 (2): 126–131. PMID 17044766. doi:10.1207/s15327914nc5502_2.
- ↑ Nagpal M, Sood S (2013). "Role of curcumin in systemic and oral health: An overview". J Nat Sci Biol Med. 4 (1): 3–7. PMC 3633300
 . PMID 23633828. doi:10.4103/0976-9668.107253.
. PMID 23633828. doi:10.4103/0976-9668.107253. - ↑ Brennan, James (15 Oct 2008). "Turmeric". Lifestyle. The National. Retrieved 13 May 2012.
- ↑ "E100: Curcumin". UKfoodguide.net. Retrieved 14 April 2017.
- ↑ NIIR Board of Consultants & Engineers (2006). Complete book on spices & condiments : (with cultivation, Processing & uses). Delhi: Asia Pacific Business Press. pp. 188–191. ISBN 9788178330389.
- ↑ Ravindran, P. N., ed. (2007). The genus Curcuma. Boca Raton, FL: Taylor & Francis. p. 244. ISBN 9781420006322.
- ↑ Berger, S; Sicker, D (2009). Classics in Spectroscopy. Wiley & Sons. p. 208. ISBN 978-3-527-32516-0.
- ↑ "Nabapatrika or Navapatrika – Nine leaves of plants used during Durga Puja". Hindu Blog. Retrieved 3 April 2015.
- ↑ "A Bangladeshi Wedding Journal – Gaye Holud: Pre-Wedding Ceremony". The Daily Star. November 11, 2014. Retrieved February 22, 2017.
- ↑ Singh K, S; Bhanu, BV (2004). People of India: Maharashtra, Volume 1. Popular Prakashan. p. 487. ISBN 9788179911006.
- ↑ Ratzel, Friedrich (1896). The History of Mankind. London: MacMillan.
- ↑ "Detention without physical examination of turmeric due to lead contamination". FDA.gov. US Food and Drug Administration. 3 December 2014. Retrieved 9 December 2015.
- ↑ "Producing and distributing food – guidance: Chemicals in food: safety controls; Sudan dyes and industrial dyes not permitted in food". gov.uk. Food Standards Agency, UK Government. 8 October 2012. Retrieved 12 December 2015.
- ↑ Daily, J. W.; Yang, M; Park, S (2016). "Efficacy of Turmeric Extracts and Curcumin for Alleviating the Symptoms of Joint Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials". Journal of Medicinal Food. 19 (8): 717–29. PMC 5003001
 . PMID 27533649. doi:10.1089/jmf.2016.3705.
. PMID 27533649. doi:10.1089/jmf.2016.3705. - ↑ Vaughn, A. R.; Branum, A; Sivamani, R. K. (2016). "Effects of Turmeric (Curcuma longa) on Skin Health: A Systematic Review of the Clinical Evidence". Phytotherapy Research. 30 (8): 1243–64. PMID 27213821. doi:10.1002/ptr.5640.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Curcuma longa. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Curcuma longa |
| Look up turmeric in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |