Tunnel magnetoresistance
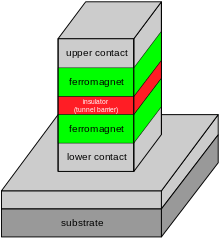
Tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) is a magnetoresistive effect that occurs in a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ), which is a component consisting of two ferromagnets separated by a thin insulator. If the insulating layer is thin enough (typically a few nanometers), electrons can tunnel from one ferromagnet into the other. Since this process is forbidden in classical physics, the tunnel magnetoresistance is a strictly quantum mechanical phenomenon.
Magnetic tunnel junctions are manufactured in thin film technology. On an industrial scale the film deposition is done by magnetron sputter deposition; on a laboratory scale molecular beam epitaxy, pulsed laser deposition and electron beam physical vapor deposition are also utilized. The junctions are prepared by photolithography.
Phenomenological description
The direction of the two magnetizations of the ferromagnetic films can be switched individually by an external magnetic field. If the magnetizations are in a parallel orientation it is more likely that electrons will tunnel through the insulating film than if they are in the oppositional (antiparallel) orientation. Consequently, such a junction can be switched between two states of electrical resistance, one with low and one with very high resistance.
History
The effect was originally discovered in 1975 by M. Jullière (University of Rennes, France) in Fe/Ge-O/Co-junctions at 4.2 K. The relative change of resistance was around 14%, and did not attract much attention.[1] In 1991 Terunobu Miyazaki (Tohoku University, Japan) found an effect of 2.7% at room temperature. Later, in 1994, Miyazaki found 18% in junctions of iron separated by an amorphous aluminum oxide insulator [2] and Jagadeesh Moodera found 11.8% in junctions with electrodes of CoFe and Co.[3] The highest effects observed to date with aluminum oxide insulators are around 70% at room temperature.
Since the year 2000, tunnel barriers of crystalline magnesium oxide (MgO) have been under development. In 2001 Butler and Mathon independently made the theoretical prediction that using iron as the ferromagnet and MgO as the insulator, the tunnel magnetoresistance can reach several thousand percent.[4][5] The same year, Bowen et al. were the first to report experiments showing a significant TMR in a MgO based magnetic tunnel junction [Fe/MgO/FeCo(001)].[6] In 2004, Parkin and Yuasa were able to make Fe/MgO/Fe junctions that reach over 200% TMR at room temperature.[7][8] In 2008, effects of up to 604% at room temperature and more than 1100% at 4.2 K were observed in junctions of CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB by S. Ikeda, H. Ohno group of Tohoku University in Japan.[9]
Applications
The read-heads of modern hard disk drives work on the basis of magnetic tunnel junctions. TMR, or more specifically the magnetic tunnel junction, is also the basis of MRAM, a new type of non-volatile memory. The 1st generation technologies relied on creating cross-point magnetic fields on each bit to write the data on it, although this approach has a scaling limit at around 90–130 nm.[10] There are two 2nd generation techniques currently being developed: Thermal Assisted Switching (TAS)[10] and Spin Torque Transfer (STT). Magnetic tunnel junctions are also used for sensing applications. For example, a TMR-Sensor can measure angles in modern high precision wind vanes, used in the wind power industry.
Physical explanation

The relative resistance change—or effect amplitude—is defined as
where is the electrical resistance in the anti-parallel state, whereas is the resistance in the parallel state.
The TMR effect was explained by Jullière with the spin polarizations of the ferromagnetic electrodes. The spin polarization P is calculated from the spin dependent density of states (DOS) at the Fermi energy:
The spin-up electrons are those with spin orientation parallel to the external magnetic field, whereas the spin-down electrons have anti-parallel alignment with the external field. The relative resistance change is now given by the spin polarizations of the two ferromagnets, P1 and P2:
If no voltage is applied to the junction, electrons tunnel in both directions with equal rates. With a bias voltage U, electrons tunnel preferentially to the positive electrode. With the assumption that spin is conserved during tunneling, the current can be described in a two-current model. The total current is split in two partial currents, one for the spin-up electrons and another for the spin-down electrons. These vary depending on the magnetic state of the junctions.
There are two possibilities to obtain a defined anti-parallel state. First, one can use ferromagnets with different coercivities (by using different materials or different film thicknesses). And second, one of the ferromagnets can be coupled with an antiferromagnet (exchange bias). In this case the magnetization of the uncoupled electrode remains "free".
It is obvious that the TMR becomes infinite if P1 and P2 equal 1, i.e. if both electrodes have 100% spin polarization. In this case the magnetic tunnel junction becomes a switch, that switches magnetically between low resistance and infinite resistance. Materials that come into consideration for this are called ferromagnetic half-metals. Their conduction electrons are fully spin-polarized. This property is theoretically predicted for a number of materials (e.g. CrO2, various Heusler alloys) but its experimental confirmation has been the subject of subtle debate. Nevertheless, if one considers only those electrons that enter into transport, measurements by Bowen et al. of up to 99.6%[11] spin polarization at the interface between La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 and SrTiO3 pragmatically amount to experimental proof of this property.
The TMR decreases with both increasing temperature and increasing bias voltage. Both can be understood in principle by magnon excitations and interactions with magnons, as well as due to tunnelling with respect to localized states induced by oxygen vacancies (see Symmetry Filtering section hereafter).[12]
Symmetry-filtering in Tunnel Barriers
Prior to the introduction of epitaxial magnesium oxide (MgO), amorphous aluminum oxide was used as the tunnel barrier of the MTJ, and typical room temperature TMR was in the range of tens of percent. MgO barriers increased TMR to hundreds of percent. This large increase reflects a synergetic combination of electrode and barrier electronic structures, which in turn reflects the achievement of structurally ordered junctions. Indeed, MgO filters the tunneling transmission of electrons with a particular symmetry that are fully spin-polarized within the current flowing across body-centered cubic Fe-based electrodes. Thus, in the MTJ's parallel (P) state of electrode magnetization, electrons of this symmetry dominate the junction current. In contrast, in the MTJ's antiparallel (AP) state, this channel is blocked, such that electrons with the next most favorable symmetry to transmit dominate the junction current. Since those electrons tunnel with respect to a larger barrier height, this results in the sizeable TMR.
Beyond these large values of TMR across MgO-based MTJs,[9] this impact of the barrier's electronic structure on tunnelling spintronics has been indirectly confirmed by engineering the junction's potential landscape for electrons of a given symmetry. This was first achieved by examining how the electrons of a LSMO half-metallic electrode with both full spin (P=+1 [11]) and symmetry polarization tunnel across an electrically biased SrTiO3 tunnel barrier.[13] The conceptually simpler experiment of inserting an appropriate metal spacer at the junction interface during sample growth was also later demonstrated[14][15] .
While theory, first formulated in 2001,[4][5] predicts large TMR values associated with a 4eV barrier height in the MTJ's P state and 12eV in the MTJ's AP state, experiments reveal barrier heights as low as 0.4eV.[7] This contradiction is lifted if one takes into account the localized states of oxygen vacancies in the MgO tunnel barrier. Extensive solid-state tunnelling spectroscopy experiments across MgO MTJs revealed in 2014[12] that the electronic retention on the ground and excited states of an oxygen vacancy, which is temperature-dependent, determines the tunnelling barrier height for electrons of a given symmetry, and thus crafts the effective TMR ratio and its temperature dependence. This low barrier height in turn enables the high current densities required for spin-transfer torque, discussed hereafter.
Spin-transfer torque in Magnetic Tunnel Junctions (MTJs)
The effect of spin-transfer torque (STT) has been studied and applied widely in MTJs, where there is a tunnelling barrier sandwiched between a set of two ferromagnetic electrodes such that there is (free) magnetization of the right electrode, while assuming that the left electrode (with fixed magnetization) acts as spin-polarizer. This may then be pinned to some selecting transistor in an MRAM device, or connected to a preamplifier in an HDD application.
The STT vector, driven by the linear response voltage, can be computed from the expectation value of the torque operator:
where is the gauge-invariant nonequilibrium density matrix for the steady-state transport, in the zero-temperature limit, in the linear-response regime,[16] and the torque operator is obtained from the time derivative of the spin operator:
Using the general form of a 1D tight-binding Hamiltonian:
where total magnetization (as macrospin) is along the unit vector and the Pauli matrices properties involving arbitrary classical vectors , given by
it is then possible to first obtain an analytical expression for (which can be expressed in compact form using , and the vector of Pauli spin matrices ).
The STT vector in general MTJs has two components: a parallel and perpendicular component:
A parallel component:
And a perpendicular component:
In symmetric MTJs (made of electrodes with the same geometry and exchange splitting), the STT vector has only one active component, as the perpendicular component disappears:
.[17]
Therefore, only vs. needs to be plotted at the site of the right electrode to characterise tunnelling in symmetric MTJs, making them appealing for production and characterisation at an industrial scale.
Note: In these calculations the active region (for which it is necessary to calculate the retarded Green's function) should consist of the tunnel barrier + the right ferromagnetic layer of finite thickness (as in realistic devices). The active region is attached to the left ferromagnetic electrode (modeled as semi-infinite tight-binding chain with non-zero Zeeman splitting) and the right N electrode (semi-infinite tight-binding chain without any Zeeman splitting), as encoded by the corresponding self-energy terms.
Discrepancy between theory and experiment
Theoretically tunnelling magneto resistances of 3400%[18] have been predicted however, the largest magneto-resistances which have been observed are only 604%.[19] One suggestion is that grain boundaries could be affecting the insulating properties of the MgO barrier, however the structure of films in buried stack structures is difficult to determine.[20] The grain boundaries may act as short circuit conduction paths through the material reducing the resistance of the device. Recently using new STEM techniques the grain boundaries within FeCoB/MgO/FeCoB MTJs has been atomically resolved, this has allowed for first principles calculations in the formalism of DFT to be performed on structural units which are present in real films, such calculations have shown that the band gap can be reduced by as much as 45%.[21]
See also
References
- ↑ M. Julliere (1975). "Tunneling between ferromagnetic films". Phys. Lett. 54A: 225–226. Bibcode:1975PhLA...54..225J. doi:10.1016/0375-9601(75)90174-7.
- ↑ T. Miyazaki & N. Tezuka (1995). "Giant magnetic tunneling effect in Fe/Al2O3/Fe junction". J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 139: L231–L234. Bibcode:1995JMMM..139L.231M. doi:10.1016/0304-8853(95)90001-2.
- ↑ J. S. Moodera; et al. (1995). "Large Magnetoresistance at Room Temperature in Ferromagnetic Thin Film Tunnel Junctions". Phys. Rev. Lett. 74 (16): 3273–3276. Bibcode:1995PhRvL..74.3273M. PMID 10058155. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.74.3273.
- 1 2 W. H. Butler; X.-G. Zhang; T. C. Schulthess & J. M. MacLaren (2001). "Spin-dependent tunneling conductance of Fe/MgO/Fe sandwiches". Phys. Rev. B. 63 (5): 054416. Bibcode:2001PhRvB..63e4416B. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.63.054416.
- 1 2 J. Mathon & A. Umerski (2001). "Theory of tunneling magnetoresistance of an epitaxial Fe/MgO/Fe (001) junction". Phys. Rev. B. 63 (22): 220403. Bibcode:2001PhRvB..63v0403M. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.63.220403.
- ↑ M. Bowen; et al. (2001). "Large magnetoresistance in Fe/MgO/FeCo(001)
epitaxial tunnel junctions on GaAs(001
)". Appl. Phys. Lett. 79 (11): 1655. Bibcode:2001ApPhL..79.1655B. doi:10.1063/1.1404125. C1 control character in
|title=at position 44 (help) - 1 2 S Yuasa; T Nagahama; A Fukushima; Y Suzuki & K Ando (2004). "Giant room-temperature magnetoresistance in single-crystal Fe/MgO/Fe magnetic tunnel junctions". Nat. Mat. 3 (12): 868–871. Bibcode:2004NatMa...3..868Y. PMID 15516927. doi:10.1038/nmat1257.
- ↑ S. S. P. Parkin; et al. (2004). "Giant tunnelling magnetoresistance at room temperature with MgO (100) tunnel barriers". Nat. Mat. 3 (12): 862–867. Bibcode:2004NatMa...3..862P. PMID 15516928. doi:10.1038/nmat1256.
- 1 2 S. Ikeda, J. Hayakawa, Y. Ashizawa, Y.M. Lee, K. Miura, H. Hasegawa, M. Tsunoda, F. Matsukura and H. Ohno (2008). "Tunnel magnetoresistance of 604% at 300 K by suppression of Ta diffusion in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB pseudo-spin-valves annealed at high temperature". Appl. Phys. Lett. 93 (8): 082508. Bibcode:2008ApPhL..93h2508I. doi:10.1063/1.2976435.
- 1 2 Barry Hoberman The Emergence of Practical MRAM. Crocus Technologies
- 1 2 Bowen, M; Barthélémy, A; Bibes, M; Jacquet, E; Contour, J P; Fert, A; Wortmann, D; Blügel, S (2005-10-19). "Half-metallicity proven using fully spin-polarized tunnelling". Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 17 (41): –407–L409. Bibcode:2005JPCM...17L.407B. ISSN 0953-8984. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/17/41/L02. Retrieved 2014-12-15.
- 1 2 Schleicher, F.; Halisdemir, U.; Lacour, D.; Gallart, M.; Boukari, S.; Schmerber, G.; Davesne, V.; Panissod, P.; Halley, D.; Majjad, H.; Henry, Y.; Leconte, B.; Boulard, A.; Spor, D.; Beyer, N.; Kieber, C.; Sternitzky, E.; Cregut, O.; Ziegler, M.; Montaigne, F.; Beaurepaire, E.; Gilliot, P.; Hehn, M.; Bowen, M. (2014-08-04). "Localized states in advanced dielectrics from the vantage of spin- and symmetry-polarized tunnelling across MgO". Nature Communications. 5: 4547. Bibcode:2014NatCo...5E4547S. ISSN 2041-1723. PMID 25088937. doi:10.1038/ncomms5547. Retrieved 2014-12-15.
- ↑ Bowen, M.; Barthélémy, A.; Bellini, V.; Bibes, M.; Seneor, P.; Jacquet, E.; Contour, J.-P.; Dederichs, P. (2006-04). "Observation of Fowler–Nordheim hole tunneling across an electron tunnel junction due to total symmetry filtering". Physical Review B. 73 (14). Bibcode:2006PhRvB..73n0408B. ISSN 1098-0121. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.73.140408. Retrieved 2014-12-15. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Greullet, F.; Tiusan, C.; Montaigne, F.; Hehn, M.; Halley, D.; Bengone, O.; Bowen, M.; Weber, W. (2007-11). "Evidence of a Symmetry-Dependent Metallic Barrier in Fully Epitaxial MgO Based Magnetic Tunnel Junctions". Physical Review Letters. 99 (18): 187202. Bibcode:2007PhRvL..99r7202G. ISSN 0031-9007. PMID 17995434. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.187202. Retrieved 2014-12-15. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Matsumoto, Rie; Fukushima, Akio; Yakushiji, Kay; Nishioka, Shingo; Nagahama, Taro; Katayama, Toshikazu; Suzuki, Yoshishige; Ando, Koji; Yuasa, Shinji (2009). "Spin-dependent tunneling in epitaxial Fe/Cr/MgO/Fe magnetic tunnel junctions with an ultrathin Cr(001) spacer layer". Physical Review B. 79 (17): 174436. Bibcode:2009PhRvB..79q4436M. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.79.174436. Retrieved 2015-01-12.
- ↑ [F. Mahfouzi, N. Nagaosa, and B. K. Nikolić, Spin-orbit coupling induced spin-transfer torque and current polarization in topological-insulator/ferromagnet vertical heterostructures, Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 166602 (2012). Eq. (13)]
- ↑ [S.-C. Oh et. al., Bias-voltage dependence of perpendicular spin-transfer torque in a symmetric MgO-based magnetic tunnel junctions, Nature Phys. 5, 898 (2009). [PDF]
- ↑ Tsymbal, E. Y., Mryasov, O. N., & LeClair, P. R. (2003). Spin-dependent tunnelling in magnetic tunnel junctions. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 15(4), R109–R142. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/15/4/201
- ↑ Ikeda, S., Hayakawa, J., Ashizawa, Y., Lee, Y. M., Miura, K., Hasegawa, H., … Ohno, H. (2008). Tunnel magnetoresistance of 604% at 300 K by suppression of Ta diffusion in CoFeBMgOCoFeB pseudo-spin-valves annealed at high temperature. Applied Physics Letters, 93(8), 39–42. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2976435
- ↑ Benedetti, S., Torelli, P., Valeri, S., Benia, H. M., Nilius, N., & Renaud, G. (2008). Structure and morphology of thin MgO films on Mo(001). Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 78(19), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.78.195411
- ↑ Bean, J. J., Saito, M., Fukami, S., Sato, H., & Ikeda, S. (2017). Atomic structure and electronic properties of MgO grain boundaries in tunnelling magnetoresistive devices. Nature Publishing Group, (January), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep45594