Tunica vaginalis
| Tunica vaginalis | |
|---|---|
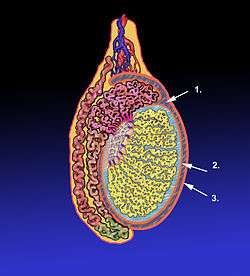 Diagram of a cross-section of a testicle. 1. Cavity of tunica vaginalis, 2. Visceral lamina, 3. Parietal lamina. | |
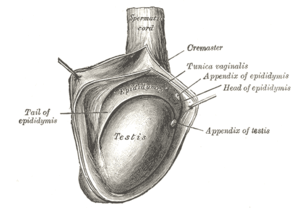 The right testis, exposed by laying open the tunica vaginalis. (Tunica vaginalis is labeled at upper right.) | |
| Details | |
| Latin | tunica vaginalis testis |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | t_22/12832403 |
The tunica vaginalis is the pouch of serous membrane that covers the testes. It is derived from the vaginal process of the peritoneum, which in the fetus precedes the descent of the testes from the abdomen into the scrotum.
After its descent, that portion of the pouch which extends from the abdominal inguinal ring to near the upper part of the gland becomes obliterated; the lower portion remains as a shut sac, which invests the surface of each testis, and is reflected on to the internal surface of the scrotum; hence it may be described as consisting of a visceral and a parietal lamina.
Visceral lamina
The visceral lamina (lamina visceralis) covers the greater part of the testis and epididymis, connecting the latter to the testis by means of a distinct fold. From the posterior border of the gland it is reflected on to the internal surface of the scrotum.
Parietal lamina
The parietal lamina (lamina parietalis) is far more extensive than the visceral, extending upward for some distance in front and on the medial side of the cord, and reaching below the testis. The inner surface of the tunica vaginalis is smooth, and covered by a layer of simple squamous mesothelial cells. The interval between the visceral and parietal laminæ constitutes the cavity of the tunica vaginalis.
Cavum vaginale
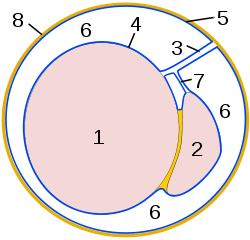
The cavum vaginale is the cavity of the tunica vaginalis. The testicle hangs suspended in a space, the cavum vaginale, from which is separated by the visceral layer of the tunica vaginalis. The latter is continued on to the epididymis, at the lateral margins of which it is reflected forward as the parietal layer, and as this is more extensive than the visceral layer, the cavum vaginale-named cavity results. The testicle is enclosed in a thick capsule of fibrous tissue, the tunica albuginea. The tunica albuginea sends prolongations inwards, dividing the testicle into lobules. Each lobule contains the seminiferous tubules, extending from the base where they end blindly, towards the apex.[1]
Diseases
- Mesothelioma
- Hydrocele[2]
- Cartilaginous Bodies[3]
- Hematocele[4]
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
![]() This article incorporates text from Spermatocele, by Edward T. Crossan, M.D., a publication from 1920 now in the public domain in the United States.
This article incorporates text from Spermatocele, by Edward T. Crossan, M.D., a publication from 1920 now in the public domain in the United States.
- ↑ DocCheck Medical Services GmbH. "Cavum vaginale". DocCheck Flexikon.
- ↑ Hydrocele in Emergency Medicine at eMedicine
- ↑ Paget, J (1855). "Account of a Growth of Cartilage in a Testicle and its Lymphatics, and in other parts". Medico-chirurgical transactions. 38: 247–260.9. PMC 2104299
 . PMID 20896046.
. PMID 20896046. - ↑ Garriga, Victoria; Serrano, Angel; Marin, Anna; Medrano, Santiago; Roson, Nuria; Pruna, Xavier (2009). "US of the Tunica Vaginalis Testis: Anatomic Relationships and Pathologic Conditions". RadioGraphics. 29 (7): 2017–32. PMID 19926760. doi:10.1148/rg.297095040.
External links
- Diagram at aspiruslibrary.org
- Anatomy photo:36:st-1502 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Inguinal Region, Scrotum and Testes: Tunic"
- Swiss embryology (from UL, UB, and UF) ugenital/diffmorpho04
- inguinalregion at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (testes)