Mucous membrane
| Mucous membrane | |
|---|---|
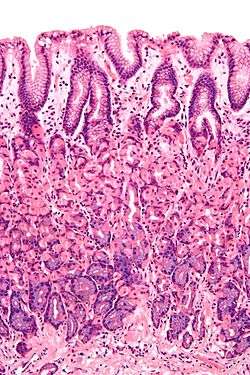 Histological section taken from the gastric antrum, showing the mucosa of the stomach | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | ectoderm |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tunica mucosa |
| MeSH | D009092 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | Mucous membrane |
 |
| This article is one of a series on the |
| Gastrointestinal wall |
|---|
|
General structure |
|
Specific |
|
Organs |
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body and surrounds internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at various body openings such as the eyes, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lip, the urethral opening and the anus, frenulum of tongue, tongue. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated.
Structure and function
Developmentally, the majority of mucous membranes are of endodermal origin.[1] Exceptions include the palate, cheeks, floor of the mouth, gums, lips and the portion of the anal canal below the pectinate line, which are all ectodermal in origin.[2][3] They are composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue.[4] The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract.[5]
Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory, and reproductive tracts and are the primary barrier between the external world and the interior of the body; in an adult human the total surface area of the mucosa is about 400 square meters while the surface area of the skin is about 2 square meters.[6]:1 They are at several places contiguous with skin: at the nostrils, the lips of the mouth, the eyelids, the ears, the trachea, the stomach, the genital area, and the anus.[4] Along with providing a physical barrier, they also contain key parts of the immune system and serves as the interface between the body proper and the microbiome.[5]:437
One of its functions is to keep the tissue moist (for example in the respiratory tract, including the mouth and nose).[5]:480 It also plays a role in absorbing and transforming nutrients.[5]:5,813 Mucous membranes also protect the body from itself; for instance mucosa in the stomach protects it from stomach acid,[5]:384,797 and mucosa lining the bladder protects the underlying tissue from urine.[7] In the uterus, the mucous membrane is called the endometrium, and it swells each month and is then eliminated during menstruation.[5]:1019
Examples
Some examples include:
- Bronchial mucosa and the lining of vocal folds
- Endometrium: the mucosa of the uterus
- Esophageal mucosa
- Gastric mucosa
- Intestinal mucosa
- Nasal mucosa
- Olfactory mucosa
- Oral mucosa
- Penile mucosa
- Vaginal mucosa
- Frenulum of tongue
- Tongue
- Anal canal
Nutrition
Niacin[5]:876 and vitamin A are essential nutrients that help maintain mucous membranes.[8]
See also
References
- ↑ "Chapter 25. Germ Layers and Their Derivatives - Review of Medical Embryology Book - LifeMap Discovery". discovery.lifemapsc.com. Retrieved 2017-02-18.
- ↑ Squier, Christopher; Brogden, Kim (2010-12-29). "Chapter 7, Development and aging of the oral mucosa". Human Oral Mucosa: Development, Structure and Function. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9780470959732.
- ↑ Schoenwolf, Gary C.; Bleyl, Steven B.; Brauer, Philip R.; Francis-West, Philippa H. (2014-12-01). Larsen's Human Embryology. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 372. ISBN 9781455727919.
- 1 2 "Mucous membrane". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Guyton, Arthur C.; Hall, John E. (2005). Textbook of medical physiology (11th ed.). Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-0240-1.
- ↑ Sompayrac, Lauren (2012). How the Immune System Works (4th ed.). John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. ISBN 9781118290446.
- ↑ Fry, CH; Vahabi, B (October 2016). "The Role of the Mucosa in Normal and Abnormal Bladder Function.". Basic & clinical pharmacology & toxicology. 119 Suppl 3: 57–62. PMID 27228303. doi:10.1111/bcpt.12626.
- ↑ "Vitamin A". MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. February 2, 2015. Retrieved 16 February 2017.