2017 Pacific hurricane season
| 2017 Pacific hurricane season | |
|---|---|
|
Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed |
May 9, 2017 (record earliest in East Pacific) |
| Last system dissipated | Season ongoing |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Fernanda |
| • Maximum winds |
145 mph (230 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 947 mbar (hPa; 27.97 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 12 |
| Total storms | 10 |
| Hurricanes | 5 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) | 2 |
| Total fatalities | 7 total |
| Total damage | $3.9 million (2017 USD) |
| Related articles | |
The 2017 Pacific hurricane season is an ongoing event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. The season officially started on May 15 in the eastern Pacific, and on June 1 in the central Pacific; they will both end on November 30.[1] These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the basin. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year. This was demonstrated when the first storm, Tropical Storm Adrian, was named on May 10 and became the earliest-known tropical storm in the East Pacific since the advent of satellite imagery.
Seasonal forecasts
| Record | Named storms |
Hurricanes | Major hurricanes |
Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average (1981-2010): | 15.4 | 7.6 | 3.2 | [2] | |
| Record high activity: | 1992: 27 | 2015: 16 | 2015: 11 | [3] | |
| Record low activity: | 2010: 8 | 2010: 3 | 2003: 0 | [3] | |
| Date | Source | Named storms |
Hurricanes | Major hurricanes |
Ref |
| May 25, 2017 | NOAA | 14–20 | 6–11 | 3–7 | [4] |
| May 29, 2017 | SMN | 16 | 10 | 6 | [5] |
| Area | Named storms | Hurricanes | Major hurricanes | Ref | |
| Actual activity: | EPAC | 10 | 5 | 2 | |
| Actual activity: | CPAC | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Actual activity: | 10 | 5 | 2 | ||
On May 25, 2017, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration released its annual forecast, predicting a 80% chance of a near- to above-average season in both the Eastern and Central Pacific basins, with a total of 14–20 named storms, 6–11 hurricanes, and 3–7 major hurricanes.[nb 1][4] During May 28, the Servicio Meteorológico Nacional (SMN) issued its first forecast for the season, predicting a total of 16 named storms, 10 hurricanes and 6 major hurricanes to develop.[5]
Seasonal summary

The Accumulated Cyclone Energy for the 2017 Pacific hurricane season, as of 03:00 UTC August 11, is 72.6325 units (71.7 units from the East Pacific and 0.9325 units from the Central Pacific).[nb 2]
The season began with Tropical Storm Adrian on May 9, several days before the official start of the season. Two weeks later, Tropical Storm Beatriz developed and made landfall near Puerto Ángel, Mexico, on June 1, resulting in seven fatalities. The third storm, Calvin, formed about a week later in the same region, and made landfall on June 12. Unusually, the first three storms did not strengthen beyond 45 mph (75 km/h), a rare occurrence, which led to the least amount of ACE being produced by the first three storms on record.[6] In late June, the first hurricane, Dora, formed and remained away from land without any notable impacts. The first major hurricane of the season, Eugene, occurred in early July, with the second, Hurricane Fernanda, forming a few days later. During July, activity significantly increased with the development of Tropical Storm Greg, Tropical Depression Eight-E, Hurricane Hilary, and Hurricane Irwin in quick succession.
Systems
Tropical Storm Adrian
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | May 9 – May 11 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 45 mph (75 km/h) (1-min) 1004 mbar (hPa) |
On May 5, the National Hurricane Center (NHC) indicated that an area of low pressure was forecast to form south of Mexico over subsequent days, with the possibility of tropical cyclone development thereafter.[7] A broad cyclonic circulation began to develop as expected late on May 7,[8] gradually organizing into the season's first tropical depression by 21:00 UTC on May 9.[9] Upon formation, at which point it was located about 545 mi (875 km) south-southeast of Salina Cruz, Mexico, the depression became the earliest-forming East Pacific tropical cyclone (east of 140°W) on record. The previous record was held by 1990's Hurricane Alma, which formed on May 12.[10] The depression intensified into Tropical Storm Adrian six hours later, the earliest-known formation of a named storm in eastern Pacific proper since the advent of the satellite era.[11] Initially, forecasts expected the small storm to intensify into a powerful hurricane. Shortly after reaching peak intensity early on May 10, an unexpected increase in mid-level wind shear caused Adrian to quickly weaken back to a tropical depression by 03:00 UTC on May 11.[12] Early on the next day, Adrian degenerated into a remnant low.[13]
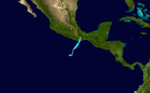
Tropical Storm Beatriz
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | May 31 – June 2 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 45 mph (75 km/h) (1-min) 1001 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical wave emerged off the western coast of Africa on May 18 and entered the East Pacific about a week later, where steady organization led to the formation of a tropical depression around 12:00 UTC on May 31. Embedded within southwesterly flow around a large upper-level trough across northern Mexico, the depression moved steadily northeast in a favorable environment, and it intensified into Tropical Storm Beatriz by 06:00 UTC on June 1. After attaining peak winds of 45 mph (75 km/h), the system made landfall around 00:00 UTC on June 2 about 25 miles (40 km) west of Puerto Ángel. The mountainous terrain of Mexico quickly disrupted Beatriz, and it ultimately dissipated twelve hours later.[14]
In the state of Oaxaca, flights out of Bahías de Huatulco International Airport were cancelled, and schools were closed until at least June 3. Dozens of roads were rendered impassable due to mudslides and flooding; numerous locales received over 4 in (102 mm) of rain, with a storm total of 19.07 in (484.4 mm) in Huatulco.[14] Numerous landslides caused significant disruption across the state, especially by blocking Federal Highway 200 at many areas. A landslide in San Marcial Ozolotepec killed two girls and buried several houses, while another in San Carlos Yautepec killed a woman.[15] As of June 4, a total of seven people have been killed—five in Oaxaca and two in Tehuantepec.[16] Less than two weeks after Beatriz, Tropical Storm Calvin affected similar areas of Mexico and inflicted additional damage. Combined damage from the two systems reached at least 70 million pesos (US$3.9 million) in Oaxaca.[17]
Tropical Storm Calvin
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | June 11 – June 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 40 mph (65 km/h) (1-min) 1005 mbar (hPa) |
In the second week of June, the NHC forecast the development of a broad area of low pressure a few hundred miles south of Mexico over the next several days.[18] This prediction came to fruition on June 9,[19] and the fledgling disturbance steadily organized into a tropical depression by 21:00 UTC on June 11 while located about 120 mi (190 km) south of Salina Cruz.[20] It was slow to organize initially amid moderate easterly wind shear;[21] by 21:00 UTC on June 12; however, the tropical depression intensified into Tropical Storm Calvin.[22] No further increase in strength occurred as Calvin made landfall halfway between Salina Cruz and Puerto Ángel, near Paja Blanca, around three hours later.[23] On June 13, Calvin dissipated into a remnant low, but the remnants of the storm were still expected to cause heavy rainfall in the area, with the potential for flash flooding.[24]
Hurricane Dora
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | June 25 – June 28 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 90 mph (150 km/h) (1-min) 981 mbar (hPa) |
On June 21, the NHC began monitoring a broad area of low pressure south of the Gulf of Tehuantepec for possible tropical cyclogenesis.[25] The disturbance organized into a tropical depression by 03:00 UTC on June 25,[26] and became a tropical storm six hours later, receiving the name Dora.[27] Progressing in a west-northwesterly direction at a steady speed, the storm began a 30-hour period of rapid intensification and became the first hurricane of the season at 09:00 UTC on June 26.[28] With impressive upper-level outflow and an eye apparent on satellite imagery,[29] the storm attained peak winds of 90 mph (150 km/h) by late on June 26.[30] Dora maintained its intensity for a number of hours before beginning to rapidly weaken over cooler sea surface temperatures and in an environment of drier air.[31] The storm later degenerated into a remnant low early on June 28, after all of the storm's deep convection had dissipated.[32]
The outer bands of Dora brought heavy rains to Guerrero, resulting in flash floods that inundated 20 homes. Overall damage was minor, however.[33]
Hurricane Eugene
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 7 – July 12 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 115 mph (185 km/h) (1-min) 965 mbar (hPa) |
Hurricane Eugene developed from a disturbance located 765 mi (1,230 km) south of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula on July 7.[34] On the following day, Eugene underwent a period of rapid intensification; in an 18-hour period starting at 21:00 UTC on July 8, Eugene intensified from a tropical storm with 70 mph (110 km/h) winds to a Category 3 hurricane with 115 mph (185 km/h) winds, making it the first major hurricane of the season.[35][36] However, by 12 hours later, the entrainment of dry air caused Eugene to weaken to a Category 2 hurricane,[37] and due to traveling over cooler waters, Eugene weakened to a tropical storm on the following day.[38] As the coverage of deep convection steadily dwindled, Eugene fell to tropical depression intensity around 15:00 UTC on July 12 and degenerated to a remnant low six hours later.[39][40]
Dangerous rip currents combined with swells of 4 to 8 ft (1.2 to 2.4 m) across southern California resulted in hundreds of rescues. On July 10 alone, lifeguards in Huntington Beach made 200 rescues while 600 were made in Los Angeles County; lifeguards also responded to 700 medical emergencies.[41]
Hurricane Fernanda
| Category 4 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 12 – July 22 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 145 mph (230 km/h) (1-min) 947 mbar (hPa) |
Late on July 10, the NHC began monitoring a broad area of low pressure several hundred miles southwest of Manzanillo. Contrary to predictions of gradual development,[42] the disturbance rapidly organized into a tropical depression by 03:00 UTC on July 12,[43] and further strengthened to become Tropical Storm Fernanda around 15:00 UTC that day.[44] The nascent cyclone initially battled moderate northeasterly wind shear, with its low-level circulation displaced to the northeastern edge of the deep convection.[45] This period of unfavorable upper-level winds was short-lived, and soon afterwards Fernanda commenced a period of rapid intensification, intensifying into a hurricane at 21:00 UTC on July 13.[46] A well-defined eye formed within a growing central dense overcast, and Fernanda further intensified into a major hurricane early on July 14.[47] Only six hours later, the system was upgraded to a Category 4 hurricane.[48] At 10.9°N, Fernanda became the second strongest hurricane to occur at such a low latitude in the Eastern Pacific, only behind 2015's Hurricane Olaf.[49]
With expansive upper-level outflow and spiral bands, a distinct eye, and a symmetric central dense overcast, Fernanda attained peak winds of 145 mph (230 km/h) around 03:00 UTC on July 15.[50] A series of microwave passes around that time began to indicate the formation of a secondary eyewall that halted the cyclone's development as it tracked west-northwest to northwest.[51] The eyewall replacement cycle concluded early on July 16, allowing Fernanda to remain a powerful hurricane amid favorable environmental conditions.[52] By late on July 18, however, cooler ocean temperatures and a more stable environment prompted the storm's weakening trend.[53] Fernanda fell below hurricane intensity shortly before entering the Central Pacific as it succumbed to stronger southwesterly wind shear,[54] and after failing to produce sustained deep convection, degenerated to a remnant low about 500 miles (805 km) east of Hilo, Hawaii, by 21:00 UTC on July 22.[55]
Tropical Storm Greg
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 17 – July 26 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min) 1001 mbar (hPa) |
On July 12, the NHC forecast the formation of a broad area of low pressure south of Mexico over subsequent days.[56] The disturbance formed two days later and slowly organized into a tropical depression by 15:00 UTC on July 17.[57][58] The cyclone battled strong west-northwesterly wind shear after formation, intensifying into Tropical Storm Greg by 09:00 UTC on July 18 as deep convection burst near the center, but remained steady state for several days thereafter despite continued predictions of intensification.[59][60] Ultimately, given global models' poor handling of the environment, NHC lowered their intensity forecast for Greg.[61] The cyclone continued west for the remainder of its life and maintained a similar convective structure, with intermittent bursts of deep convection near the center.[62] Approaching the Central Pacific, Greg's low-level circulation became increasingly difficult to locate as it moved into a cooler, drier environment intertwined by increasing southerly wind shear, and the system weakened to a tropical depression around 21:00 UTC on July 25.[63] It degenerated to a remnant low 24 hours later.[64]
Tropical Depression Eight-E
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 18 – July 20 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 35 mph (55 km/h) (1-min) 1007 mbar (hPa) |
A low-pressure trough began producing disorganized convection over the waters of the Pacific Ocean, well to the south of Baja California Peninsula, on July 14.[65] Despite only marginally conducive environmental conditions, the disturbance began to show signs of organization two days later,[66] and it attained tropical depression status by 15:00 UTC on July 18.[67] Strong west-northwesterly wind shear confined the storm's intermittent bursts of convection well to the southwest of its low-level circulation, and the depression consequently failed to produce winds above 35 mph (55 km/h).[68] The system's center later degenerated into a low-pressure trough within the Intertropical Convergence Zone, prompting the NHC to discontinue advisories at 21:00 UTC on July 20.[69]
Hurricane Hilary
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 21 – July 31 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 105 mph (165 km/h) (1-min) 972 mbar (hPa) |
Part of an exceptionally active July, the NHC began highlighting the far eastern reaches of the Pacific basin on July 19 for tropical development in later days.[70] A large area of disturbed weather progressed westward across Costa Rica later that day,[71] steadily organizing into a tropical depression by 15:00 UTC on July 21.[72] The cyclone failed to organize immediately after formation, and its low-level center migrated to the southern extent of associated convection.[73] By 03:00 UTC on July 23, though, better defined banding features and a more organized convective structure led the NHC to designate the system as Tropical Storm Hilary.[74] Over the coming hours, the cyclone's convective structure evolved into a small central dense overcast while hints of an eye became apparent;[75] in accordance with satellite estimates, Hilary was upgraded to a hurricane at 09:00 UTC on July 24.[76] A moist environment and warm ocean waters propelled Hilary to its peak as a Category 2 hurricane with winds of 105 mph (165 km/h) 24 hours later, at which time its core was most symmetric.[77] After maintaining its intensity, the hurricane began to weaken late on July 26 as northerly wind shear increased.[78]
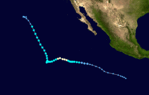
Hurricane Irwin
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 22 – August 1 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 90 mph (150 km/h) (1-min) 980 mbar (hPa) |
On July 16, the NHC highlighted the expected formation of an area of low pressure south of Mexico later that week.[79] A tropical wave began producing disorganized cloudiness three days later,[70] and the broad system slowly organized into a tropical depression by 15:00 UTC on July 22.[80] Its structure changed little after formation, impinged by strong wind shear; despite this, satellite wind data indicated the cyclone intensified into Tropical Storm Irwin by 09:00 UTC on July 23.[81] Over the next 24 hours, deep convection began to wrap around the center and a mid-level eye formed as environmental conditions improved;[82] by 09:00 UTC on July 25, Irwin intensified into a hurricane.[83] Although coolest cloudtops were located in the western semicircle of the system, a well-defined eye and convection in the eyewall propelled Irwin to its peak with winds of 90 mph (150 km/h) late on July 25.[84] Almost immediately, outflow from nearby Hurricane Hilary increased wind shear over the system and caused it to begin weakening.[85]
Tropical Depression Eleven-E
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
 | |
| Duration | August 4 – August 5 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 35 mph (55 km/h) (1-min) 1004 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical wave crossed into the East pacific basin in Late July, The wave became a disturbance and became a depression on August 4. It weakened on August 5 and became post-tropical on that day.
Tropical Storm Jova
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| As of: | 9:00 p.m. MDT August 11 (03:00 UTC August 12) | ||
| Location: |
19°18′N 109°48′W / 19.3°N 109.8°W ± 30 nm About 250 mi (400 km) S of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula | ||
| Sustained winds: |
35 kn (40 mph; 65 km/h) (1-min mean) gusting to 45 kn (50 mph; 85 km/h) | ||
| Pressure: | 1003 mbar (hPa; 29.62 inHg) | ||
| Movement: | WNW at 12 kn (14 mph; 22 km/h) | ||
| |||
Current storm information
As of 9:00 p.m. MDT August 11 (03:00 UTC August 12), Tropical Storm Jova is located within 30 nautical miles of 19°18′N 109°48′W / 19.3°N 109.8°W, about 250 miles (400 km) south of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula. Maximum sustained winds are 35 knots (40 mph; 65 km/h), with gusts up to 45 knots (50 mph; 85 km/h). The minimum barometric pressure is 1003 mbar (hPa; 29.62 inHg), and the system is moving west-northwest at 12 knots (14 mph; 22 km/h).
For latest official information, see:
- The NHC's latest public advisory on Tropical Storm Jova
- The NHC's latest forecast advisory on Tropical Storm Jova
- The NHC's latest forecast discussion on Tropical Storm Jova
Storm names
The following names will be used for named storms that form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean during 2017. Retired names, if any, will be announced by the World Meteorological Organization in the spring of 2018. The names not retired from this list will be used again in the 2023 season.[86] This is the same list used in the 2011 season.
|
|
|
For storms that form in the Central Pacific Hurricane Center's area of responsibility, encompassing the area between 140 degrees west and the International Date Line, all names are used in a series of four rotating lists.[87] The next four names slated for use are shown below.
|
|
|
|
Season effects
This is a table of all the storms that have formed in the 2017 Pacific hurricane season. It includes their duration, names, landfall(s), denoted in parentheses, damages, and death totals. Deaths in parentheses are additional and indirect (an example of an indirect death would be a traffic accident), but were still related to that storm. Damage and deaths include totals while the storm was extratropical, a wave, or a low, and all the damage figures are in 2017 USD.
| Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale | ||||||
| TD | TS | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
| Storm name |
Dates active | Storm category
at peak intensity |
Max 1-min wind mph (km/h) |
Min. press. (mbar) |
Areas affected | Damage (millions USD) |
Deaths | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adrian | May 9 – 11 | Tropical storm | 45 (75) | 1004 | None | None | None | |||
| Beatriz | May 31 – June 2 | Tropical storm | 45 (75) | 1001 | Southwestern Mexico | 3.9 | 7 | |||
| Calvin | June 11 – 13 | Tropical storm | 40 (65) | 1005 | Southwestern Mexico, Guatemala | Unknown | None | |||
| Dora | June 25 – 28 | Category 1 hurricane | 90 (150) | 981 | Southwestern Mexico, Revillagigedo Islands | Minimal | None | |||
| Eugene | July 7 – 12 | Category 3 hurricane | 115 (185) | 965 | Baja California Peninsula, California | None | None | |||
| Fernanda | July 12 – 22 | Category 4 hurricane | 145 (230) | 947 | Hawaii | None | None | |||
| Greg | July 17 – 26 | Tropical storm | 60 (95) | 1001 | None | None | None | |||
| Eight-E | July 18 – 20 | Tropical depression | 35 (55) | 1007 | None | None | None | |||
| Hilary | July 21 – 31 | Category 2 hurricane | 105 (165) | 972 | Southwestern Mexico | None | None | |||
| Irwin | July 22 – August 1 | Category 1 hurricane | 90 (150) | 980 | None | None | None | |||
| Eleven-E | August 4 – 5 | Tropical depression | 35 (55) | 1004 | Revillagigedo Islands | None | None | |||
| Jova | August 11 – Present | Tropical storm | 40 (65) | 1003 | Revillagigedo Islands | None | None | |||
| Season Aggregates | ||||||||||
| 12 systems | May 9 – Season ongoing | 145 (230) | 947 | 3.9 | 7 | |||||
See also
- List of Pacific hurricanes
- List of Pacific hurricane seasons
- 2017 Atlantic hurricane season
- 2017 Pacific typhoon season
- 2017 North Indian Ocean cyclone season
- South-West Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 2016–17, 2017–18
- Australian region cyclone seasons: 2016–17, 2017–18
- South Pacific cyclone seasons: 2016–17, 2017–18
Footnotes
- ↑ A major hurricane is a storm that ranks as Category 3 or higher on the Saffir–Simpson scale.
- ↑ The totals represent the sum of the squares for every (sub)tropical storm's intensity of over 33 knots (38 mph, 61 km/h), divided by 10,000. Calculations are provided at Talk:2017 Pacific hurricane season/ACE calcs.
References
- ↑ Dorst Neal. When is hurricane season? (Report). Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory. Archived from the original on 6 December 2010. Retrieved November 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Background Information: East Pacific Hurricane Season". Climate Prediction Center. College Park, Maryland: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. May 22, 2014. Retrieved May 29, 2014.
- 1 2 National Hurricane Center; Hurricane Research Division; Central Pacific Hurricane Center. "The Northeast and North Central Pacific hurricane database 1949–2016". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's National Weather Service. A guide on how to read the database is available here.
- 1 2 "Above-normal Atlantic hurricane season is most likely this year". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. May 25, 2017.
- 1 2 http://smn.cna.gob.mx/tools/DATA/Ciclones%20Tropicales/Proyecci%C3%B3n/2017.pdf
- ↑ https://mobile.twitter.com/philklotzbach/status/874627761461051394
- ↑ Stacy R. Stewart (May 5, 2017). "Special Tropical Weather Outlook". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved May 9, 2017.
- ↑ Scott Stripling (May 7, 2017). "Tropical Weather Discussion". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved May 9, 2017.
- ↑ Richard J. Pasch (May 9, 2017). Tropical Depression One-E Public Advisory Number 1 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved May 9, 2017.
- ↑ Doyle Rice (May 9, 2017). "Earliest Pacific tropical depression on record forms". USA Today. Retrieved May 9, 2017.
- ↑ Stacy R. Stewart (May 9, 2017). Tropical Storm Adrian Public Advisory Number 2 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved May 9, 2017.
- ↑ Stacy R. Stewart (May 9, 2017). Tropical Depression Adrian Public Advisory Number 6 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved May 9, 2017.
- ↑ Richard J. Pasch (May 11, 2017). Post-Tropical Cyclone Adrian Public Advisory Number 8 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 17, 2017.
- 1 2 Daniel P. Brown (July 13, 2017). Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Beatriz (PDF) (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. pp. 2, 5. Retrieved July 21, 2017.
- ↑ "UPDATE 1-Tropical Storm Beatriz nears Mexico's Pacific coast, kills 3". Thomson Reuters. June 2, 2017. Retrieved June 2, 2017.
- ↑ "Suman 7 muertos tras paso de tormenta tropical "Beatriz" en Oaxaca". Intolerancia. June 4, 2017. Retrieved June 11, 2017.
- ↑ Oscar Rodríguez (June 16, 2017). "Oaxaca necesita 70 mpd para reparar daños carreteros per lluvias" (in Spanish). Retrieved June 18, 2017.
- ↑ Lixion A. Avila (June 8, 2017). "Tropical Weather Outlook". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 11, 2017.
- ↑ John L. Beven II (June 9, 2017). "Tropical Weather Outlook". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 11, 2017.
- ↑ Richard J. Pasch (June 11, 2017). Tropical Depression Three-E Public Advisory Number 1 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 11, 2017.
- ↑ Richard J. Pasch (June 12, 2017). Tropical Depression Three-E Discussion Number 4 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 12, 2017.
- ↑ Richard J. Pasch; Stacy R. Stewart (June 12, 2017). Tropical Storm Calvin Public Advisory Number 5 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 12, 2017.
- ↑ Stacy R. Stewart (June 12, 2017). Tropical Storm Calvin Intermediate Advisory Number 5A (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 12, 2017.
- ↑ Cangialosi (June 13, 2017). Remnants Of Calvin Advisory Number 8 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 14, 2017.
- ↑ Robbie Berg (June 21, 2017). "Tropical Weather Outlook". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 24, 2017.
- ↑ Robbie Berg (June 24, 2017). Tropical Depression Four-E Public Advisory Number 1 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 24, 2017.
- ↑ Eric Blake (June 25, 2017). Tropical Storm Dora Public Advisory Number 2 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 25, 2017.
- ↑ Eric Blake (June 26, 2017). Hurricane Dora Public Advisory Number 6 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 26, 2017.
- ↑ Stacy R. Stewart (June 26, 2017). Hurricane Dora Discussion Number 7 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 27, 2017.
- ↑ Stacy R. Stewart (June 26, 2017). Hurricane Dora Public Advisory Number 8 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 27, 2017.
- ↑ Hurricane Dora Discussion Number 10 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. June 27, 2017. Retrieved June 27, 2017.
- ↑ Post-Tropical Cyclone Dora Discussion Number 15 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. June 28, 2017. Retrieved June 28, 2017.
- ↑ "'Dora' deja daños leves en Guerrero". Excelsior (in Spanish). June 26, 2017. Retrieved June 28, 2017.
- ↑ David P. Roberts (July 7, 2017). Tropical Storm Eugene Public Advisory Number 1 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 7, 2017.
- ↑ Lixion A. Avila (July 8, 2017). Tropical Storm Eugene Public Advisory Number 5 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 9, 2017.
- ↑ Christopher W. Landsea (July 9, 2017). Hurricane Eugene Public Advisory Number 8 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 9, 2017.
- ↑ John P. Cangialosi (July 9, 2017). Hurricane Eugene Discussion Number 10 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 10, 2017.
- ↑ Richard J. Pasch (July 10, 2017). Hurricane Eugene Discussion Number 14 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 10, 2017.
- ↑ Christopher W. Landsea (July 12, 2017). Tropical Depression Eugene Discussion Number 20 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 27, 2017.
- ↑ Christopher W. Landsea (July 12, 2017). Post-Tropical Cyclone Eugene Discussion Number 21 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 27, 2017.
- ↑ Darsha Philips and Jovana Lara (July 10, 2017). "More than 600 beachgoers rescued as strong rip currents hit SoCal beaches". KABC. Retrieved July 15, 2017.
- ↑ Daniel P. Brown (July 10, 2017). "Graphical Tropical Weather Outlook". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 11, 2017.
- ↑ Daniel P. Brown (July 12, 2017). Tropical Depression Six-E Public Advisory Number 1 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 12, 2017.
- ↑ John L. Beven II (July 12, 2017). Tropical Storm Fernanda Public Advisory Number 3 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 12, 2017.
- ↑ Daniel P. Brown (July 12, 2017). Tropical Storm Fernanda Discussion Number 5 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 13, 2017.
- ↑ John L. Beven II (July 13, 2017). Hurricane Fernanda Discussion Number 8 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 13, 2017.
- ↑ David A. Zelinsky (July 14, 2017). Hurricane Fernanda Public Advisory Number 11 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 14, 2017.
- ↑ Richard J. Pasch (July 14, 2017). Hurricane Fernanda Public Advisory Number 12 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 14, 2017.
- ↑ NHC E. Pacific Ops (July 14, 2017). "Fernanda is now a category 4 hurricane- the 2nd strongest storm so far south in the eastern Pacific". Twitter. Retrieved July 16, 2017.
- ↑ John L. Beven II (July 14, 2017). Hurricane Fernanda Discussion Number 13 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 23, 2017.
- ↑ David A. Zelinsky (July 15, 2017). Hurricane Fernanda Discussion Number 15 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 23, 2017.
- ↑ Daniel P. Brown (July 16, 2017). Hurricane Fernanda Discussion Number 19 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 23, 2017.
- ↑ David P. Roberts (July 18, 2017). Hurricane Fernanda Discussion Number 29 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 23, 2017.
- ↑ Stacy R. Stewart (July 20, 2017). Tropical Storm Fernanda Discussion Number 34 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 23, 2017.
- ↑ Tom Birchard (July 22, 2017). Post-Tropical Cyclone Fernanda Discussion Number 44 (Report). Miami, Florida: Central Pacific Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 23, 2017.
- ↑ Christopher W. Landsea (July 12, 2017). "Graphical Tropical Weather Outlook". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 21, 2017.
- ↑ Richard J. Pasch (July 14, 2017). "Graphical Tropical Weather Outlook". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 21, 2017.
- ↑ Daniel P. Brown (July 17, 2017). Tropical Depression Seven-E Public Advisory Number 1 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 21, 2017.
- ↑ Daniel P. Brown (July 18, 2017). Tropical Storm Greg Discussion Number 4 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 21, 2017.
- ↑ Robbie J. Berg (July 20, 2017). Tropical Storm Greg Discussion Number 15 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 21, 2017.
- ↑ Christopher W. Landsea; Nelsie A. Ramos (July 21, 2017). Tropical Storm Greg Discussion Number 19 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 21, 2017.
- ↑ Stacy R. Stewart (July 23, 2017). Tropical Storm Greg Discussion Number 27 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 27, 2017.
- ↑ Robbie J. Berg (July 25, 2017). Tropical Depression Greg Discussion Number 34 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 27, 2017.
- ↑ Richard Ballard (July 26, 2017). Post-Tropical Cyclone Greg Discussion Number 38 (Report). Honolulu, Hawaii: Central Pacific Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 27, 2017.
- ↑ Eric S. Blake (July 14, 2017). "Graphical Tropical Weather Outlook". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 21, 2017.
- ↑ Eric S. Blake (July 16, 2017). "Graphical Tropical Weather Outlook". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 21, 2017.
- ↑ Daniel P. Brown (July 18, 2017). Tropical Depression Eight-E Public Advisory Number 1 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 21, 2017.
- ↑ Robbie J. Berg (July 18, 2017). Tropical Depression Eight-E Discussion Number 3 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 21, 2017.
- ↑ John L. Beven II (July 20, 2017). Post-Tropical Cyclone Eight-E Discussion Number 10 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 21, 2017.
- 1 2 Daniel P. Brown (July 19, 2017). "Graphical Tropical Weather Outlook". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 23, 2017.
- ↑ Robbie J. Berg (July 19, 2017). "Graphical Tropical Weather Outlook". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 23, 2017.
- ↑ Lixion A. Avila (July 21, 2017). Tropical Depression Nine-E Public Advisory Number 1 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 23, 2017.
- ↑ Lixion A. Avila (July 22, 2017). Tropical Depression Nine-E Discussion Number 5 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 23, 2017.
- ↑ John L. Beven II (July 22, 2017). Tropical Storm Hilary Public Advisory Number 7 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 23, 2017.
- ↑ Eric S. Blake (July 23, 2017). Tropical Storm Hilary Discussion Number 10 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 27, 2017.
- ↑ Richard J. Pasch (July 22, 2017). Hurricane Hilary Public Advisory Number 12 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 27, 2017.
- ↑ Richard J. Pasch (July 25, 2017). Hurricane Hilary Discussion Number 16 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 27, 2017.
- ↑ John P. Cangialosi (July 26, 2017). Hurricane Hilary Discussion Number 23 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 27, 2017.
- ↑ Eric S. Blake (July 16, 2017). "Graphical Tropical Weather Outlook". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 23, 2017.
- ↑ Lixion A. Avila (July 22, 2017). Tropical Depression Ten-E Public Advisory Number 1 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 23, 2017.
- ↑ David A. Zelinsky (July 23, 2017). Tropical Storm Irwin Discussion Advisory Number 4 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 27, 2017.
- ↑ David A. Zelinsky (July 24, 2017). Tropical Storm Irwin Discussion Advisory Number 8 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 27, 2017.
- ↑ John L. Beven II (July 25, 2017). Hurricane Irwin Public Advisory Advisory Number 12 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 27, 2017.
- ↑ John P. Cangialosi (July 25, 2017). Hurricane Irwin Discussion Advisory Number 15 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 27, 2017.
- ↑ David P. Roberts (July 26, 2017). Hurricane Irwin Discussion Advisory Number 16 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 27, 2017.
- ↑ "Tropical Cyclone Names 2016-2021". National Hurricane Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on December 30, 2016.
- ↑ "Pacific Tropical Cyclone Names 2016-2021". Central Pacific Hurricane Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. May 12, 2016. Archived from the original (PHP) on December 30, 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 2017 Pacific hurricane season. |
- National Hurricane Center Website
- National Hurricane Center's Eastern Pacific Tropical Weather Outlook
- Servicio Meteorológico Nacional Website (in Spanish)


