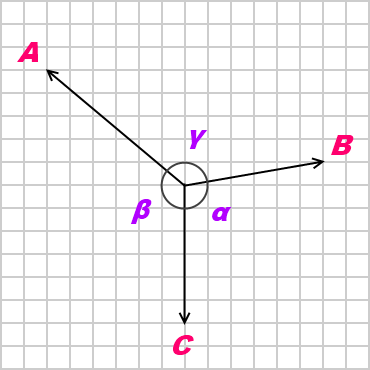
Lami's theorem
In statics, Lami's theorem is an equation relating the magnitudes of three coplanar, concurrent and non-collinear forces, which keeps an object in static equilibrium, with the angles directly opposite to the corresponding forces. According to the theorem,
- where A, B and C are the numerical values of three coplanar, concurrent and non-collinear forces, which keep the object in static equilibrium, andl
- α, β and γ are the angles directly opposite to the forces A, B and C respectively.
Lami's theorem is applied in static analysis of mechanical and structural systems. The theorem is named after Bernard Lamy.
See also
Further reading
- R.K. Bansal (2005). "A Textbook of Engineering Mechanics". Laxmi Publications. p. 4. ISBN 978-81-7008-305-4.
- I.S. Gujral (2008). "Engineering Mechanics". Firewall Media. p. 10. ISBN 978-81-318-0295-3
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.