Transport in Gabon
Modes of transport in Gabon include rail, road, water, and air. The one rail link, the Trans-Gabon Railway, connects the port of Owendo with the inland town of Franceville. Most but not all of the country is connected to the road network, much of which is unpaved, and which centres on seven "national routes" identified as N1 to N7. The largest seaports are Port-Gentil and the newer Owendo, and 1,600 km of inland waterways are navigable. There are three international airports, eight other paved airports, and over 40 with unpaved runways. Nearly 300km of pipelines carry petroleum products, mainly crude oil.
Railways in Gabon
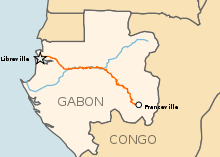
Until the 1970s, Gabon had no railroads. A 936 km railroad construction program, the Trans-Gabon Railway, began in October 1974. In its first stage, completed in 1983, the project linked the port of Owendo with the interior city of Booué (332 km). The second stage, completed in December 1986, linked Booué with Franceville (357 km) via Moanda, thus facilitating exports of manganese from the southeast and forestry exploitation in the same region. A proposed third stage would continue the line from Booué to Belinga in the northeast, where there are iron ore deposits.
In 2003, the railway began the process of installing a satellite based telecommunications system.[1] As of 2004, Gabon State Railways totalled 814 km of standard-gauge track.
total: 814 km (Gabon State Railways or OCTRA)
standard gauge: 814 km 1.435-m gauge; single track (1994)
Maps
- UN Map - shows line to Franceville
- UNHCR map - does not show line to Franceville
- TravelPortal map - shows major rivers
- UNJLC Rail map of Southern Africa - does not show line to Franceville
Cities served by rail
- Existing
- Libreville - capital
- Owendo - port
- Sahoué - port
- Franceville - railhead
- Ndjolé
- Lopé
- Booué - likely junction for branchline to Makokou
- Lastoursville
- Moanda
- Ntoum - proposed junction for iron ore traffic to Santa Clara
- Kango
- Four-Place
- Mounana - ?
- Proposed
- Makokou - iron ore
- Cape Santa Clara - proposed deep water port for Makokou iron ore.
- Bélinga - possible iron ore mine.
2007
- New rail line from Belinga will go 450 km all the way to the coast, rather than to be a branch off an existing line.[2]
- Pan-African issues[3]
2006
- China signs a deal for an iron ore mine with associated rail and port upgrades from Belinga to Santa Clara
Road transport
Main roads connect virtually all major communities, but maintenance work is difficult because of heavy rainfall. In 2002, the road network comprised 8,454 km, of which 838 km were paved, including 30 km of expressways. A north-south road runs the length of the country, from Bitam to Ndendé. This main north-south link continues into Cameroon in the north and the Congo in the south. An east–west road connects Libreville and Mékambo. Farther south, another road runs from Mayumba to Lastoursville and Franceville. In 1995 there were about 23,000 automobiles and 10,000 commercial vehicles in use.
total:
7,670 km
paved:
629 km (including 30 km of expressways)
unpaved:
7,041 km (1996 est.)
Roads in Gabon link most areas of the country, and many of the main roads are of a reasonable standard. However, remoter areas along the coast and in the east are often not connected to the road network. Major roads are denoted national routes and numbered, with a prefix "N" (sometimes "RN"):
- N1 road: Libreville – Kougouleu – Bifoun – Lambaréné – Mouila – Ndendé – Tchibanga - (Republic of Congo)
- N2 road: Bifoun – Alembe – Viate – Mitzic – Bibasse – Oyem – Bitam – Éboro – (Cameroon)
- N3 road: Alembe – Kazamabika – Lastoursville – Moanda – Franceville
- N4 road: Viate – Ekonlong – Makokou – Mékambo
- N5 road: Kougouleu – Bibasse
- N6 road: Mayumba – Tchibanga – Ndendé – Lebamba - Koulamoutou – Lastoursville
- N7 road: Makokou – Bakwaka – Okondja – Lékori - Akiéni – Ngouoni – Franceville
Water transport
Seaports and harbours
The busiest ports are Port-Gentil, the center for exports of petroleum products and imports of mining equipment, and Owendo, a new port that opened in 1974 on the Ogooué estuary, 10 km north of Libreville. Owendo’s capacity, initially 300,000 tons, reached 1.5 million tons in 1979, when the port was enlarged to include timber-handling facilities. The smaller port at Mayumba also handles timber, and a deepwater port is planned for the city.
Merchant marine
In 1998, Gabon’s merchant marine owned two vessels totalling 13,613 GRT. As of 2002, there was one merchant marine vessel, with a volume of 2,419 GRT/3,205 tonnes deadweight (DWT).
Waterways
Gabon has 1,600 km of perennially navigable waterways, including 310 km on the Ogooué River.
Air transport
Gabon had an estimated 56 airports in 2004, but only 11 of which had paved runways as of 2005. There are three international airports: Libreville, Port-Gentil, and Franceville. Numerous airlines provide international flights. Nouvelle Air Affaires Gabon handles scheduled domestic service. In 2003, about 386,000 passengers were carried on scheduled domestic and international airline flights.
Airports - with paved runways
total:
11
over 3,047 m:
1
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
8
914 to 1,523 m:
1 (1999 est.)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total:
45
1,524 to 2,437 m:
9
914 to 1,523 m:
16
under 914 m:
25 (1999 est.)
Pipelines
Crude oil 270 km; petroleum products 14 km
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook website https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html.
This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook website https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Transport in Gabon. |
