Transport in Djibouti
Transport in Djibouti includes highways, airports, railways and seaports.
Railways
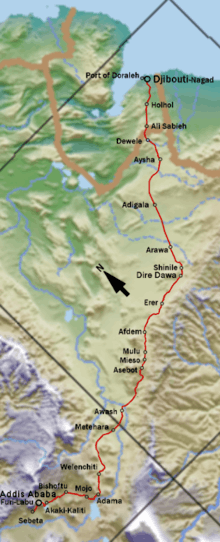
The country's first railway, Ethio-Djibouti Railway, was a metre gauge railway that connected Ethiopia to Djibouti. It was built between 1894 and 1917 by the French who ruled the country at the time as French Somaliland. The railway is no longer operational.
The Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway, a standard gauge railway built by two Chinese government firms, began operations in January 2017 and roughly parallels the route of the Ethio-Djibouti Railway.[1]
Roads
The Djiboutian highway system is named according to the road classification. Roads that are considered primary roads are those that are fully asphalted (throughout their entire length) and in general they connect all the major towns in Djibouti. There is a total of 3,065 kilometres (1,905 mi) of roads, with 1,379 kilometres (857 mi) paved and 1,686 kilometres (1,048 mi) unpaved, according to a 2000 estimate.
| Title | Start point | Intermediate point | End point | Road type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RN1 | Djibouti City | Dikhil | Galafi (border with Ethiopia) | Asphalt |
| RN2 | Djibouti City | n/a | Loyada (border with Somalia) | Asphalt |
| RN6 | Dikhil | As Eyla | Kouta Bouyya | Gravel |
Ports and harbors

Djibouti has an improved natural harbor that consists of a roadstead, outer harbor, and inner harbor, known as the Port of Djibouti. The roadstead is well protected by reefs and the configuration of the land. A quarter of Ethiopia’s imports and half of its exports move through the ports. Car ferries pass the Gulf of Tadjoura from Djibouti City to Tadjoura.
Merchant marine
Djibouti has one ship with a volume of 1,000 gross register tons (GRT) or over totaling 1,369 GRT/3,030 tonnes deadweight (DWT) according to a 1999 estimate.
Airports

In 2004, there were an estimated 13 airports, only 3 of which had paved runways as of 2005. Djibouti–Ambouli International Airport, which is situated about 6 km from the city of Djibouti, is the country's international air terminal. There are also local airports at Tadjoura and Obock. Beginning in 1963, the state-owned Air Djibouti also provided domestic service to various domestic centers and flew to many overseas destinations. The national carrier discontinued operations in 2002. Daallo Airlines, a Somali-owned private carrier, has also offered air transportation since its foundation in 1991. With its hub at the Djibouti–Ambouli International Airport, the airline provides flights to a number of domestic and overseas destinations.
Airports - with paved runways
total:
3
over 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 3,047 m:
2 (2013 est.)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total:
10
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
7
under 914 m:
2 (2013 est.)
References
- ↑ "Djibouti-Ethiopia Railway Officially Inaugurated". Awramba Times. 11 January 2017. Retrieved 11 January 2017.
Bibliography
- Michelon 745 Africa North East, Arabia 2007
- GeoCenter Africa North East 1999
- Maplanida.com
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook document "2015 edition".
This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook document "2015 edition".
