Trams in Spain
Trams in Spain go back to an animal-drawn Madrid tramway network, which opened in 1871. Steam tramway traction started in Spain in 1879, and electric trams first operated in 1899.
Spanish tramway networks were dismantled in the 1960s and 1970s, but have gradually been reintroduced since 1994. At present, there are plans to add 13 new Spanish tram networks to the nine currently operating.
History
The history of tramways in Spain began with animal-drawn trams in the nineteenth century, in Madrid (1871), Barcelona and Bilbao (1872), Valencia (1876), Valladolid (1881), Zaragoza (1885), Sevilla (1887) and Palma de Mallorca (1891).
In 1879, the Madrid-Leganés tramway began working with steam traction, and in 1899 the first electrified line ran. In Barcelona, steam traction was introduced in 1877 (at Sant Andreu), and the first electrified line in 1899.
The first Spanish city to introduce an electric tram service was Bilbao, with the line Bilbao-Santurtzi, electrified in 1896 and managed by a predecessor of the current Transportes Colectivos. Steam trams began running in Valencia in 1892 and the first line was electrified in 1900. In Zaragoza, the Torrero line was electrified in 1902, and electric trams came to Palma de Mallorca in 1916. Valladolid network was totally electrified in 1911.
In many other cities, trams were common through much of the twentieth century. However, they were dismantled in the 1960s and 1970s, on the basis that they obstructed traffic on the streets of large cities. Then, in the late twentieth century, they were once again considered and, in some cities, began running again.
Today's tramway networks
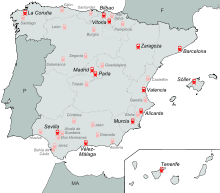
Valencia was the first Spanish city to reintroduce the tram, in 1994. The success of the modern tramway network in Valencia led to the extension of its lines on three occasions.
After Valencia came Bilbao (2002), Alicante (2003), Barcelona (2004) and, in October 2006, the inauguration of the 4.7 km long Vélez-Málaga tramway (which linked Vélez-Málaga with the coastal part of Torre del Mar).
These lines were followed by the Metro Ligero de Madrid (2007), in the Madrid districts of Sanchinarro and las Tablas (ML-1), and linking the capital with Boadilla del Monte and Pozuelo de Alarcón (ML2, ML3).
Then came Seville, where a tramway network named MetroCentro has been running since spring 2007, Tenerife (2007), Murcia (2007), the Madrid suburb of Parla (2007) and Vitoria (2008).
In Tenerife, the tramway is operated by the company Metropolitano de Tenerife. It runs through and connects the cities of Santa Cruz de Tenerife and San Cristóbal de La Laguna, and has a fleet of 26 Citadis trams, made by the French multinational Alstom. Line 1 (Santa Cruz interchange)–Avda. Trinidad (La Laguna) opened on 2 June 2007. The line connecting the two neighborhoods of Tincer (Santa Cruz) and La Cuesta (La Laguna) followed on 30 May 2009.
In Zaragoza, the commercial service began on 19 April 2011.
Projects
In Spain, 13 tram networks are currently planned to be added to the nine already operating.
New projects, in Cadiz, Cordoba and Toledo, total 160 km (99 mi) in length and two billion euros in investment.
Other networks are proposed for Granada, Jerez de la Frontera, Córdoba, Huelva, Pamplona, Almeria, León, Elche, Burgos, Salamanca, Toledo, Palma de Mallorca, Leioa-Sestao, Baracaldo, el Alto Deva, Jaén and Bahía de Cádiz.
There have also been plans to install a tramway in Oviedo (a project to implement this mode of transport, by the PSOE, was discarded after the PP defeated it at an election). In addition, Madrid is expanding its LRT (light rail) network on its outskirts.
Finally, an historic tramway has been operating in the city of A Coruña since 1997, following additions and alterations to the road.
See also
- History of rail transport in Spain
- List of town tramway systems in Spain
- List of trolleybus systems in Spain
- Rail transport in Spain
References
External links
![]() Media related to Trams in Spain at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Trams in Spain at Wikimedia Commons
This article is based upon a translation of the Spanish language version as at September 2011.

