Greater Tokyo Area
| Greater Tokyo Area | |
|---|---|
|
| |
 Yokohama | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 35°41′23″N 139°41′30″E / 35.68972°N 139.69167°ECoordinates: 35°41′23″N 139°41′30″E / 35.68972°N 139.69167°E | |
| Country |
|
| Major Cities |
Tokyo Metropolis (includes 23 special wards) Yokohama Kawasaki Saitama Chiba Sagamihara |
| Area | |
| • Urban | 3,925 km2 (1,515 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 14,034 km2 (5,419 sq mi) |
| Population (2016/7 only for total population) | |
| • City | 38,000,000 |
| • Urban | 37,832,892 |
| • Urban density | 8,790/km2 (22,765/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 37,832,892[1] |
| • Metro density | 2,631/km2 (6,814/sq mi) |
| GDP | 2008 estimate |
| Nominal[2] | $2.0 trillion (¥165 trillion, The One Metropolis and Three Prefectures) |
| PPP | $1.5 trillion[3] (1st in Japan; 1st in the world) |
The Greater Tokyo Area is the most populous metropolitan area in the world, consisting of the Kantō region of Japan, including the Tokyo Metropolis, as well as the prefecture of Yamanashi. In Japanese, it is referred to by various terms, the most common of which being National Capital Region (首都圏 Shuto-ken).
A 2016 United Nations estimate puts the total population at 38,000,000.[4] It covers an area of approximately 13,500 km² (5,200 mi²),[5] giving it a population density of 2,642 person/km². It is the second largest single metropolitan area in the world in terms of built-up or urban function landmass at 8,547 km² (3,300 mi²), behind only New York City at 11,642 km² (4,495 mi²).[6]
The area has the largest metropolitan economy in the world, with a total GDP (nominal) of approximately $2 trillion (¥165 trillion)[2] in 2008. According to research published by PricewaterhouseCoopers, the agglomeration of Tokyo had a total GDP of $1.5 trillion in 2008 (at purchasing power parity), ranking again as the largest urban agglomeration GDP in the world.[3]
Definition

There are various definitions of the Greater Tokyo Area, each of which tries to incorporate different aspects. Some definitions are clearly defined by law or government regulation, some are based coarsely on administrative areas, while others are for research purposes such as commuting patterns or distance from Central Tokyo. Each definition has a different population figure, granularity, methodology, and spatial association.
Various definitions of Tokyo, Greater Tokyo & Kantō
| Inner Tokyo and Tokyo | Details | Population 000's(Year) | Area (km2) | Population Density (People/km2) | Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area of former (dissolved) Tokyo City limits | 23 special wards, does not correspond to any single authority | 8,841 (1970CF), 8,135 (2000CF), 8,490 (2005CF), 8,949 (2010CF), 9,256 (2015-12CR) | 621.9 | 13,080 (2000) 14,390 (2010) 14,883 (2015-12) |  |
| Tokyo Metropolis | Prefectural-level jurisdiction (Tokyo-to), figures here subtract out Izu/Ogasawara Islands | 12,038 (2000CF), 12,541 (2005CF), 13,129 (2010CF), 13,479 (2015-12CR) | 1808 | 6,658(2000) 6,936 (2005) 7,216.5 (2010) 7,455 (2015-12) |  |
| Metropolitan Area Name | Details | Population 000's(Year) | Area (km2) | Population Density (People/km2) | Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tokyo Metropolitan Employment Area (東京大都市雇用圏 Tōkyō Dai-toshi Koyō-ken) | All municipalities that have at least 10% of their population commuting to the 23 special wards. Figures for this definition are complex to update without a major re-study. |
|
|
3,348.2 (2010) |  |
| One Metropolis, Three Prefectures (一都三県 Itto Sanken) | Coarse administrative definition. Misses many of the more-distant suburbs that lie outside the prefectural borders, especially in Ibaraki and Gunma. Incorporates sparsely settled rural districts like Nishitama. | 33,534 (2000CF), 35,623 (2010CF), 36,092 (2015-12CR) | 13,555.65 | 2,627.9 (2010), 2,662 (2015-12) |  |
| Kantō Major Metropolitan Area (関東大都市圏 Kantō Dai-toshi-ken) | One of the two definitions the Japan Statistics Bureau uses. Consists of all municipalities that have at least 1.5% of their population aged 15 and above commuting to a designated city (Yokohama, Kawasaki, Sagamihara, Chiba, and Saitama) or the 23 special wards. Before Saitama became a designated city in 2001, the area was called Keihin'yō Major Metropolitan Area (京浜葉大都市圏 Keihin'yō Dai-toshi-ken). Excludes adjacent metropolitan areas of Gunma, Ibaraki, and Utsunomiya (ja:宇都宮都市圏) which are urbanized but have some small towns in between them and Tokyo. Most locally detailed definition, but hard to update without major re-study. | 36,923 (2010)[8] | - | - | 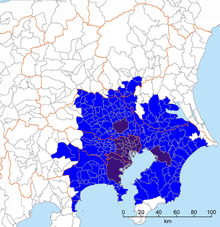 |
| Tokyo Major Metropolitan Area (東京大都市圏 Tōkyō Dai-toshi-ken) | Set of municipalities that are completely or mostly within 50 and 70 kilometres of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Buildings in Shinjuku. Suburbs tend to extend finger-like along major commuter train routes and density builds along express stops, not in a uniform fashion, and so this definition is of value. | 32,714 (<50 km, 2010), 36,303 (<70 km, 2010)[9] | - | - |  |
| Purely Administrative | Details | Population 000's(Year) | Area (km2) | Population Density (People/km2) | Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kantō region | Entire national region, includes many rural areas | 40,550 (2000CF) 42,607 (2010CF) 42,945 (2015-12CR) | 32,423.9 | 1,314.1 (2010) |  |
| National Capital Region | According to the National Capital Region Planning Act, very coarse administrative zone, essentially Kantō plus Yamanashi, includes large rural areas. | 41,438 (2000CF) 43,470 (2010CF) 43,785 (2015-12CR) | 36,889.28 | 1,178.4 (2010) |  |
Notes & Sources: All figures issued by Japan Statistics Bureau,[10][11] except for Metro Employment Area, a study by Center for Spatial Information Service, the University of Tokyo. Abbreviations: CF for National Census Final Data (every 5 years by JSB), CR for Civil Registry (compiled by local governments, monthly as per legal requirement), CP for Census Preliminary.
National Capital Region
The National Capital Region (首都圏 Shutoken) of Japan refers to the Greater Tokyo Area as defined by the National Capital Region Planning Act (首都圏整備法 Shutoken-seibi-hō) of 1956, which defines it as "Tokyo and its surrounding area declared by government ordinance."[12] The government ordinance defined it as Tokyo and all six prefectures in the Kantō region plus Yamanashi Prefecture. While this includes all of Greater Tokyo, it also includes sparsely populated mountain areas as well as far-flung Bonin Islands which are administered under Tokyo.
International comparison
Using the "One Metropolis Three Prefectures" definition, Tokyo is 13,555.65 square kilometres (5,233.87 sq mi), a similar size to that of Los Angeles County, and almost two-thirds smaller than the Combined Statistical Area of New York City, at 30,671 square kilometres (11,842 sq mi) and 21.9 million people. Other metropolitan areas such as Greater Jakarta are considerably more compact as well as more densely populated than Greater Tokyo.
Metropolitan Area definition ambiguities and issues
- The South Kantō region (南関東 Minami Kantō) is a potentially ambiguous term. Informally, it may mean the One Metropolis, Two Prefectures, or the area without Saitama Prefecture. Formally, it may mean the South Kantō Block, which is not the Greater Tokyo Area, but a proportional representation block of the national election, comprising Kanagawa, Chiba, and Yamanashi Prefectures.
- In informal occasions, the term National Capital Region (首都圏 Shuto-ken) often means Greater Tokyo Area. Officially, the term refers to a much larger area, namely the whole Kantō region and Yamanashi Prefecture.
- It should be noted that Tokyo as a metropolis includes some 394 km2
of islands (Izu Islands and Ogasawara Islands), as well as some mountainous areas to the far west (331 km2
), which are officially part of Greater Tokyo, but are wilderness or rustic areas.
Cities
(populations listed for those over 300,000)
Cities within Tokyo
Tokyo is legally classified as a to (都), which translates as "metropolis", and is treated as one of the forty-seven prefectures of Japan. The metropolis is administered by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government as a whole.
Eastern Tokyo Metropolis
Central Tokyo, situated in the eastern portion of Tokyo Metropolis, was once incorporated as Tokyo City, which was dismantled during World War II. Its subdivisions have been reclassified as special wards (特別区 tokubetsu-ku). The twenty three special wards currently have the legal status of cities, with individual mayors and city councils, and they call themselves "cities" in English. However, when listing Japan's largest cities, Tokyo's twenty three wards are often counted as a single city.
Western Tokyo Metropolis
Western Tokyo, known as the Tama Area (Tama-chiiki 多摩地域) comprises a number of municipalities, including these suburban cities:
|
|
Cities outside Tokyo
The core cities of the Greater Tokyo Area outside Tokyo Metropolis are:
- Chiba (population 940,000)
- Kawasaki (population 1.36 million)
- Sagamihara (population 730,000)
- Saitama (population 1.19 million)
- Yokohama (population 3.62 million)
The other cities in Chiba, Kanagawa and Saitama Prefectures are:
|
source: stat.go.jp census 2005
Additional cities
In the major metropolitan area (MMA) definition used by the Japanese Statistics Bureau, the following cities in Ibaraki, Tochigi, Gunma, Yamanashi, and Shizuoka Prefectures are included:
Gunma Prefecture
Ibaraki Prefecture
Shizuoka Prefecture
Tochigi Prefecture
Yamanashi Prefecture
Border areas
Tighter definitions for Greater Tokyo do not include adjacent metropolitan areas of Numazu-Mishima (approx. 450,000) to the southwest, Maebashi-Takasaki-Ōta-Ashikaga (approx. 1,500,000 people) on the northwest, and Greater Utsunomiya (ja:宇都宮都市圏) approx. 1,000,000) to the north. If they are included, Greater Tokyo's population would be around 39 million.
Geography
At the centre of the main urban area (approximately the first 10 km from Tokyo Station) are the 23 special wards, formerly treated as a single city but now governed as separate municipalities, and containing many major commercial centres such as Shinjuku, Shibuya, Ikebukuro and Ginza. Around the 23 special wards are a multitude of suburban cities which merge seamlessly into each other to form a continuous built up area, circumnavigated by the heavily travelled Route 16 which forms a (broken) loop about 40 km from central Tokyo. Situated along the loop are the major cities of Yokohama (to the south of Tokyo), Hachiōji (to the west), Ōmiya (now part of Saitama City, to the north), and Chiba (to the east). Within the Route 16 loop, the coastline of Tokyo Bay is heavily industrialised, with the Keihin Industrial Area stretching from Tokyo down to Yokohama, and the Keiyō Industrial Zone from Tokyo eastwards to Chiba. Along the periphery of the main urban area are numerous new suburban housing developments such as the Tama New Town. The landscape is relatively flat compared to most of Japan, most of it comprising low hills.
Outside the Route 16 loop the landscape becomes more rural. To the southwest is an area known as Shōnan, which contains various cities and towns along the coast of Sagami Bay, and to the west the area is mountainous.
Many rivers run through the area, the major ones being Arakawa and Tama River.
Economy
Tokyo has the largest city economy in the world and is one of three major global centers of trade and commerce along with New York City and London.
Greater Tokyo Area 2005
- 2005 average exchange rate (1 US Dollar = 110.22 Yen)[13]
| Prefecture | Gross Prefecture Product (in billion Yen) |
Gross Prefecture Product (in billion US$) |
|---|---|---|
| Tokyo | |
|
| Kanagawa | |
|
| Saitama | |
|
| Chiba | |
|
| Ibaraki | |
|
| Tochigi | |
|
| Gunma | |
|
| Yamanashi | |
|
| The One Metropolis and Three Prefectures |
|
|
| National Capital Region | |
|
Source[2]
GDP (purchasing power parity)
The agglomeration of Tokyo is the world's largest economy, with the largest gross metropolitan product at purchasing power parity (PPP) in the world according to a study by PricewaterhouseCoopers.[14]
Metropolitan Employment Area
| Year | 2010 | 1995 | 1980 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employed Persons 000's | 16,234 | 16,381 | 12,760 |
| Production (billion US$) | 1,797 | 1,491 | 358 |
| Production Manufacturing (billion US$) | 216 | 476 | 159 |
| Private Capital Stock (billion US$) | 3,618 | 2,631 | 368 |
| Social Overhead Capital (billion US$) | 1,607 | 1,417 | 310 |
| 1 US Dollar (Japanese yen) | 87.780 | 94.060 | 226.741 |
Sources:,[7] Conversion rates - Exchange rates - OECD Data
Transportation

Air
The Greater Tokyo Area has two major airports, Tokyo International Airport, commonly known as Haneda Airport (previously chiefly domestic, now increasingly also international flights) and Narita International Airport (chiefly international). Minor facilities include the Chōfu, Ibaraki Airport, and Honda Airport. Tokyo Heliport serves helicopter traffic, including police, fire, and news. Various military facilities handle air traffic: Naval Air Facility Atsugi (United States Navy and Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force), Yokota Air Base (United States Air Force), and Camp Zama (United States Army).
Rail
Greater Tokyo has an extensive railway network comprising high-speed rail, commuter rails, subways, monorails, private lines, trams and others. There are around 136 individual rail lines in the Greater Tokyo Area, and between 1,000 and 1,200 railway stations depending on one's definition of the area, most designed for heavy use, usually long enough to accommodate 10-car trains. Stations are designed to accommodate hundreds of thousands of passengers at any given time, with miles of connecting tunnels linking vast department stores and corporate offices. Tokyo Station has underground connections that stretch well over 4 kilometers, and Shinjuku Station has well over 200 exits. Greater Tokyo's Railway Network is easily considered the world's largest in terms of both daily passenger throughput with a daily trips of over 40 million (20 million different passengers) as well as physical extent with approximately 2,578 kilometers of track. Shinjuku station is used by an average of 3.34 million people per day, making it the world's busiest train station. Some 57 percent of all Greater Tokyo residents used rail as their primary means of transport in 2001.[15]
JR East and many other carriers crisscross the region with a network of rail lines. (See this map showing the Suica/PASMO accepting area that roughly corresponds with Greater Tokyo). The most important carriers include Keihin Kyūkō Electric Railway (Keikyū), Keisei Electric Railway, Keiō Electric Railway, Odakyū Electric Railway, Seibu Railway, Tōbu Railway, and Tōkyū Corporation. In addition to Tokyo's two subway systems — Tokyo Metro and Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation (Toei and Toden lines), Yokohama operates three lines. The Tokyo Monorail provides service to Haneda Airport and other destinations.
Other
The Shuto Expressway system connects other national expressways in the capital region.
Tokyo and Yokohama are major commercial seaports, and both the Maritime Self-Defense Force and United States Navy maintain naval bases at Yokosuka.
See also
- List of metropolitan areas in Asia by population
- List of metropolitan areas in Japan by population
- National Capital Region (Japan) briefly shows the two definitions of the "Capital Area" (Shuto-ken.)
References
- ↑ "Megacities in 2014 and 2030". GeoHive. Retrieved 9 January 2016.
- 1 2 3 平成19年度県民経済計算
- 1 2 "Global city GDP rankings 2008-2025". Pricewaterhouse Coopers. Archived from the original on 31 May 2013. Retrieved 27 November 2009.
- ↑ United Nations (March 12, 2017). "The World's Cities in 2016" (PDF). United Nations.
- ↑ Japan Statistics Bureau - Keihin'yō Major Metropolitan Area
- ↑ demographia.com - World urban areas
- 1 2 3 Yoshitsugu Kanemoto. "Metropolitan Employment Area (MEA) Data". Center for Spatial Information Science, The University of Tokyo.
- ↑ Japan Statistics Bureau - Population figures for metropolitan areas
- ↑ Japan Statistics Bureau - Population figures for range of distance
- ↑ http://www.e-stat.go.jp/SG1/estat/XlsdlE.do?sinfid=000008640424
- ↑ http://www.e-stat.go.jp/SG1/estat/XlsdlE.do?sinfid=000008640423
- ↑ http://www.metro.tokyo.jp/ENGLISH/PROFILE/overview02.htm
- ↑ U.S.-Japan Annual Average Exchange Rate
- ↑ The 150 richest cities in the world by GDP in 2005
- ↑ Urban Transport Fact Book - Tokyo-Yokohama suburban rail summary










