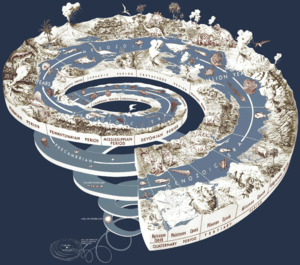
Timeline of the evolutionary history of life
Orange labels: known ice ages.
Also see: Human timeline and Nature timeline
This timeline of the evolutionary history of life represents the current scientific theory outlining the major events during the development of life on planet Earth. In biology, evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organization, from kingdoms to species, and individual organisms and molecules, such as DNA and proteins. The similarities between all present day organisms indicate the presence of a common ancestor from which all known species, living and extinct, have diverged through the process of evolution. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species,[1] that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct.[2][3] Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million,[4] of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.[5]
While the dates given in this article are estimates based on scientific evidence, there has been controversy between more traditional views of increased biodiversity through a cone of diversity with the passing of time and the view that the basic pattern on Earth has been one of annihilation and diversification and that in certain past times, such as the Cambrian explosion, there was great diversity.[6][7]
Extinction
Species go extinct constantly as environments change, organisms compete for environmental niches, and genetic mutation leads to the rise of new species from older ones. Occasionally biodiversity on the planet takes a hit in the form of a mass extinction in which the extinction rate is much higher than usual.[8] A large extinction event often represents an accumulation of smaller extinction events that take place in a relatively brief period of time.[9]
The first known mass extinction in earth's history was the Great Oxygenation Event 2.4 billion years ago. The event led to the loss of most of the planet's obligate anaerobes. The five largest extinction events in earth's history since are these:[10]
- End of the Ordovician: 440 million years ago, 86% of all species lost, including graptolites
- Late Devonian: 375 million years ago, 75% of species lost, including trilobites
- End of the Permian, "The Great Dying": 251 million years ago, 96% of species lost, including tabulate corals, and most extant trees and synapsids
- End of the Triassic: 200 million years ago, 80% of species lost, including all of the conodonts
- End of the Cretaceous: 66 million years ago, 76% of species lost, including all of the ammonites, mosasaurs, ichthyosaurs, plesiosaurs, pterosaurs, and nonavian dinosaurs
(Dates and percentages represent estimates.)
Smaller extinction events have occurred in the periods between these larger catastrophes, with some standing at the delineation points of the periods and epochs recognized by scientists in geologic time. The Holocene extinction event is currently under way.[11]
Factors in mass extinctions include continental drift, changes in atmospheric and marine chemistry, volcanism and other aspects of mountain formation, changes in glaciation, changes in sea level, and impact events.[9]
Detailed timeline
In this timeline, Ma (for megaannum) means "million years ago," ka (for kiloannum) means "thousand years ago," and ya means "years ago."
Hadean Eon
4000 Ma and earlier.
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 4600 Ma | The planet Earth forms from the accretion disc revolving around the young Sun with organic compounds (complex organic molecules) necessary for life having perhaps formed in the protoplanetary disk of cosmic dust grains surrounding it before the formation of the Earth.[12] |
| 4500 Ma | According to the giant impact hypothesis, the Moon was formed when the planet Earth and the hypothesized planet Theia collided, sending a very large number of moonlets into orbit around the young Earth which eventually coalesce to form the Moon.[13] The gravitational pull of the new Moon stabilised the Earth's fluctuating axis of rotation and set up the conditions in which abiogenesis occurred.[14] |
| 4404 Ma | First appearance of liquid water on Earth. |
| 4280 Ma | Earliest appearance of life on Earth.[15][16][17][18] |
Archean Eon



4000 Ma – 2500 Ma
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 4000 Ma | Formation of a greenstone belt of the Acasta Gneiss of the Slave craton in Northwest Territories, Canada, the oldest rock belt in the world.[19] |
| 4100–3800 Ma | Late Heavy Bombardment (LHB): extended barrage of impact events upon the inner planets by meteoroids. Thermal flux from widespread hydrothermal activity during the LHB may have been conducive to abiogenesis and life's early diversification.[20] "Remains of biotic life" were found in 4.1 billion-year-old rocks in Western Australia.[21][22] According to one of the researchers, "If life arose relatively quickly on Earth ... then it could be common in the universe."[21] |
| 3900–2500 Ma | Cells resembling prokaryotes appear.[23] These first organisms are chemoautotrophs: they use carbon dioxide as a carbon source and oxidize inorganic materials to extract energy. Later, prokaryotes evolve glycolysis, a set of chemical reactions that free the energy of organic molecules such as glucose and store it in the chemical bonds of ATP. Glycolysis (and ATP) continue to be used in almost all organisms, unchanged, to this day.[24][25] |
| 3800 Ma | Formation of a greenstone belt of the Isua complex of the western Greenland region, whose rocks show an isotope frequency suggestive of the presence of life.[19] The earliest evidences for life on Earth are 3.8 billion-year-old biogenic hematite in a banded iron formation of the Nuvvuagittuq Greenstone Belt in Canada,[26] graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in western Greenland[27] and microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia.[28][29] |
| 3500 Ma | Lifetime of the last universal common ancestor (LUCA);[30][31] the split between bacteria and archaea occurs.[32]
Bacteria develop primitive forms of photosynthesis which at first did not produce oxygen.[33] These organisms generated Adenosine triphosphate by exploiting a proton gradient, a mechanism still used in virtually all organisms.[34] |
| 3000 Ma | Photosynthesizing cyanobacteria evolved; they used water as a reducing agent, thereby producing oxygen as a waste product.[35] The oxygen initially oxidizes dissolved iron in the oceans, creating iron ore. The oxygen concentration in the atmosphere slowly rose, acting as a poison for many bacteria and eventually triggering the Great Oxygenation Event. The Moon, still very close to Earth, caused tides 1,000 feet (305 m) high. The Earth was continually wracked by hurricane-force winds. These extreme mixing influences are thought to have stimulated evolutionary processes.. Life on land likely developed at this time.[36] |
Proterozoic Eon
.svg.png)


2500 Ma – 542 Ma. Contains the Palaeoproterozoic, Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic eras.
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 2500 Ma | Great Oxygenation Event led by cyanobacteria's oxygenic photosynthesis.[35] Commencement of plate tectonics with old marine crust dense enough to subduct.[19] |
| 2000 Ma | Diversification and expansion of acritarchs.[37] |
| By 1850 Ma | Eukaryotic cells appear. Eukaryotes contain membrane-bound organelles with diverse functions, probably derived from prokaryotes engulfing each other via phagocytosis. (See Symbiogenesis and Endosymbiont). Bacterial viruses (bacteriophage) emerge before, or soon after, the divergence of the prokaryotic and eukaryotic lineages.[38] The appearance of red beds show that an oxidising atmosphere had been produced. Incentives now favoured the spread of eukaryotic life.[39][40][41] |
| 1400 Ma | Great increase in stromatolite diversity. |
| By 1200 Ma | Meiosis and sexual reproduction are present in single-celled eukaryotes, and possibly in the common ancestor of all eukaryotes.[42] Sex may even have arisen earlier in the RNA world.[43] Sexual reproduction first appears in the fossil records; it may have increased the rate of evolution.[44] |
| 800 Ma | First multicellular organism may have arisen.[45] |
| 750 Ma | First protozoa (ex: Melanocyrillium) |
| 850–630 Ma | A global glaciation may have occurred.[46][47] Opinion is divided on whether it increased or decreased biodiversity or the rate of evolution.[48][49][50] |
| 600 Ma | The accumulation of atmospheric oxygen allows the formation of an ozone layer.[51] Prior to this, land-based life would probably have required other chemicals to attenuate ultraviolet radiation enough to permit colonisation of the land.[36] |
| 580–542 Ma | The Ediacara biota represent the first large, complex multicellular organisms — although their affinities remain a subject of debate.[52] |
| 580–500 Ma | Most modern phyla of animals begin to appear in the fossil record during the Cambrian explosion.[53][54] |
| 560 Ma | Earliest fungi |
| 550 Ma | First fossil evidence for Ctenophora (comb jellies), Porifera (sponges), Anthozoa (corals and sea anemones) |
Phanerozoic Eon
542 Ma – present
The Phanerozoic Eon, literally the "period of well-displayed life," marks the appearance in the fossil record of abundant, shell-forming and/or trace-making organisms. It is subdivided into three eras, the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic, which are divided by major mass extinctions.
Palaeozoic Era
542 Ma – 251.0 Ma and contains the Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian periods.
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 535 Ma | Major diversification of living things in the oceans: chordates, arthropods (e.g. trilobites, crustaceans), echinoderms, molluscs, brachiopods, foraminifers and radiolarians, etc. |
| 530 Ma | The first known footprints on land date to 530 Ma, indicating that early animal explorations may have predated the development of terrestrial plants.[55] |
| 525 Ma | Earliest graptolites |
| 510 Ma | First cephalopods (nautiloids) and chitons |
| 505 Ma | Fossilization of the Burgess Shale |
| 485 Ma | First vertebrates with true bones (jawless fishes) |
| 450 Ma | First complete conodonts and echinoids appear |
| 440 Ma | First agnathan fishes: Heterostraci, Galeaspida, and Pituriaspida |
| 434 Ma | The first primitive plants move onto land,[56] having evolved from green algae living along the edges of lakes.[57] They are accompanied by fungi, which may have aided the colonization of land through symbiosis. |
| 420 Ma | Earliest ray-finned fishes, trigonotarbid arachnids, and land scorpions[58] |
| 410 Ma | First signs of teeth in fish. Earliest Nautilida, lycophytes, and trimerophytes. |
| 395 Ma | First lichens, stoneworts. Earliest harvestmen, mites, hexapods (springtails) and ammonoids. The first known tetrapod tracks on land. |
| 363 Ma | By the start of the Carboniferous Period, the Earth begins to resemble its present state. Insects roamed the land and would soon take to the skies; sharks swam the oceans as top predators,[59] and vegetation covered the land, with seed-bearing plants and forests soon to flourish.
Four-limbed tetrapods gradually gain adaptations which will help them occupy a terrestrial life-habit. |
| 360 Ma | First crabs and ferns. Land flora dominated by seed ferns. |
| 350 Ma | First large sharks, ratfishes, and hagfish |
| 340 Ma | Diversification of amphibians |
| 330 Ma | First amniote vertebrates (Paleothyris) |
| 320 Ma | Synapsids (precursors to mammals) separate from sauropsids (reptiles) in late Carboniferous.[60] |
| 305 Ma | Earliest diapsid reptiles (e.g. Petrolacosaurus) |
| 280 Ma | Earliest beetles, seed plants and conifers diversify while lepidodendrids and sphenopsids decrease. Terrestrial temnospondyl amphibians and pelycosaurs (e.g. Dimetrodon) diversify in species. |
| 275 Ma | Therapsid synapsids separate from pelycosaur synapsids |
| 251.4 Ma | The Permian–Triassic extinction event eliminates over 90-95% of marine species. Terrestrial organisms were not as seriously affected as the marine biota. This "clearing of the slate" may have led to an ensuing diversification, but life on land took 30 million years to completely recover.[61] |
Mesozoic Era

From 251.4 Ma to 66 Ma and containing the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous periods.
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| The Mesozoic Marine Revolution begins: increasingly well adapted and diverse predators pressurize sessile marine groups; the "balance of power" in the oceans shifts dramatically as some groups of prey adapt more rapidly and effectively than others. | |
| 248 Ma | Sturgeon and paddlefish (Acipenseridae) first appear. |
| 245 Ma | Earliest ichthyosaurs |
| 240 Ma | Increase in diversity of gomphodont cynodonts and rhynchosaurs |
| 225 Ma | Earliest dinosaurs (prosauropods), first cardiid bivalves, diversity in cycads, bennettitaleans, and conifers. First teleost fishes. First mammals (Adelobasileus). |
| 220 Ma | Seed-producing Gymnosperm forests dominate the land; herbivores grow to huge sizes to accommodate the large guts necessary to digest the nutrient-poor plants. First flies and turtles (Odontochelys). First coelophysoid dinosaurs. |
| 205
Ma |
the Massive extinction of Triassic/Jurassic, that wiped out most of the group of pseudosuchians and was given the opportunity of dinosaurs including the Apatosaurus, Tyrannosaurus, Perrotasaurus, and Stegosaurus to enter its golden age. |
| 200 Ma | The first accepted evidence for viruses that infect eukaryotic cells (at least, the group Geminiviridae) existed.[62] Viruses are still poorly understood and may have arisen before "life" itself, or may be a more recent phenomenon.
Major extinctions in terrestrial vertebrates and large amphibians. Earliest examples of armoured dinosaurs |
| 195 Ma | First pterosaurs with specialized feeding (Dorygnathus). First sauropod dinosaurs. Diversification in small, ornithischian dinosaurs: heterodontosaurids, fabrosaurids, and scelidosaurids. |
| 190 Ma | Pliosauroids appear in the fossil record. First lepidopteran insects (Archaeolepis), hermit crabs, modern starfish, irregular echinoids, corbulid bivalves, and tubulipore bryozoans. Extensive development of sponge reefs. |
| 176 Ma | First members of the Stegosauria group of dinosaurs |
| 170 Ma | Earliest salamanders, newts, cryptoclidids, elasmosaurid plesiosaurs, and cladotherian mammals. Sauropod dinosaurs diversify. |
| 165 Ma | First rays and glycymeridid bivalves |
| 163 Ma | Pterodactyloid pterosaurs first appear[63] |
| 161 Ma | Ceratopsian dinosaurs appear in the fossil record (Yinlong) and the oldest known Eutherian Mammal appear in the fossil record: Juramaia. |
| 160 Ma | Multituberculate mammals (genus Rugosodon) appear in eastern China |
| 155 Ma | First blood-sucking insects (ceratopogonids), rudist bivalves, and cheilostome bryozoans. Archaeopteryx, a possible ancestor to the birds, appears in the fossil record, along with triconodontid and symmetrodont mammals. Diversity in stegosaurian and theropod dinosaurs. |
| 130 Ma | The rise of the angiosperms: Some of these flowering plants bear structures that attract insects and other animals to spread pollen;other angiosperms were pollinated by wind or water. This innovation causes a major burst of animal evolution through coevolution. First freshwater pelomedusid turtles. |
| 120 Ma | Oldest fossils of heterokonts, including both marine diatoms and silicoflagellates |
| 115 Ma | First monotreme mammals |
| 110 Ma | First hesperornithes, toothed diving birds. Earliest limopsid, verticordiid, and thyasirid bivalves. |
| 106 Ma | Spinosaurus, the largest theropod dinosaur, appears in the fossil record |
| 100 Ma | Earliest bees |
| 90 Ma | Extinction of ichthyosaurs. Earliest snakes and nuculanid bivalves. Large diversification in angiosperms: magnoliids, rosids, hamamelidids, monocots, and ginger. Earliest examples of ticks. Probable origins of placental mammals (earliest undisputed fossil evidence is 66 Ma). |
| 80 Ma | First ants |
| 70 Ma | Multituberculate mammals increase in diversity. First yoldiid bivalves. |
| 68 Ma | Tyrannosaurus, the largest terrestrial predator of what is now western North America appears in the fossil record. First species of Triceratops. |
Cenozoic Era
66 Ma – present



| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 66 Ma | The Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event eradicates about half of all animal species, including mosasaurs, pterosaurs, plesiosaurs, ammonites, belemnites, rudist and inoceramid bivalves, most planktic foraminifers, and all of the dinosaurs excluding the birds.[64] |
| From 66 Ma | Rapid dominance of conifers and ginkgos in high latitudes, along with mammals becoming the dominant species. First psammobiid bivalves. Earliest rodents. Rapid diversification in ants. |
| 63 Ma | Evolution of the creodonts, an important group of meat-eating (carnivorous) mammals |
| 60 Ma | Diversification of large, flightless birds. Earliest true primates, along with the first semelid bivalves, edentate, carnivoran and lipotyphlan mammals, and owls. The ancestors of the carnivorous mammals (miacids) were alive. |
| 56 Ma | Gastornis, a large flightless bird, appears in the fossil record |
| 55 Ma | Modern bird groups diversify (first song birds, parrots, loons, swifts, woodpeckers), first whale (Himalayacetus), earliest lagomorphs, armadillos, appearance of sirenian, proboscidean, perissodactyl and artiodactyl mammals in the fossil record. Angiosperms diversify. The ancestor (according to theory) of the species in the genus Carcharodon, the early mako shark Isurus hastalis, is alive. |
| 52 Ma | First bats appear (Onychonycteris) |
| 50 Ma | Peak diversity of dinoflagellates and nannofossils, increase in diversity of anomalodesmatan and heteroconch bivalves, brontotheres, tapirs, rhinoceroses, and camels appear in the fossil record, diversification of primates |
| 40 Ma | Modern-type butterflies and moths appear. Extinction of Gastornis. Basilosaurus, one of the first of the giant whales, appeared in the fossil record. |
| 37 Ma | First nimravid ("false saber-toothed cats") carnivores — these species are unrelated to modern-type felines |
| 35 Ma | Grasses diversify from among the monocot angiosperms; grasslands begin to expand. Slight increase in diversity of cold-tolerant ostracods and foraminifers, along with major extinctions of gastropods, reptiles, amphibians, and multituberculate mammals. Many modern mammal groups begin to appear: first glyptodonts, ground sloths, canids, peccaries, and the first eagles and hawks. Diversity in toothed and baleen whales. |
| 33 Ma | Evolution of the thylacinid marsupials (Badjcinus) |
| 30 Ma | First balanids and eucalypts, extinction of embrithopod and brontothere mammals, earliest pigs and cats |
| 28 Ma | Paraceratherium appears in the fossil record, the largest terrestrial mammal that ever lived |
| 25 Ma | Pelagornis sandersi appears in the fossil record, the largest flying bird that ever lived |
| 25 Ma | First deer |
| 20 Ma | First giraffes, hyenas, bears and giant anteaters, increase in bird diversity |
| 15 Ma | Genus Mammut appears in the fossil record, first bovids and kangaroos, diversity in Australian megafauna |
| 10 Ma | Grasslands and savannas are established, diversity in insects, especially ants and termites, horses increase in body size and develop high-crowned teeth, major diversification in grassland mammals and snakes |
| 9.5 Ma | The Great American Interchange, where various land and freshwater faunas migrated between North and South America. Armadillos, opossums, hummingbirds Phorusrhacids, Ground Sloths, Glyptodonts, and Meridiungulates traveled to North America, while horses, tapirs, saber-toothed cats, Jaguars, Bears, Coaties, Ferrets, Otters, Skunks and deer entered South America. |
| 6.5 Ma | First hominins (Sahelanthropus) |
| 6 Ma | Australopithecines diversify (Orrorin, Ardipithecus) |
| 5 Ma | First tree sloths and hippopotami, diversification of grazing herbivores like zebras and elephants, large carnivorous mammals like lions and the genus Canis, burrowing rodents, kangaroos, birds, and small carnivores, vultures increase in size, decrease in the number of perissodactyl mammals. Extinction of nimravid carnivores. |
| 4.8 Ma | Mammoths appear in the fossil record |
| 4 Ma | Evolution of Australopithecus, Stupendemys appears in the fossil record as the largest freshwater turtle, first modern elephants, giraffes, zebras, lions, rhinoceros and gazelles appear in the fossil record |
| 2.7 Ma | Evolution of Paranthropus |
| 2.5 Ma | The earliest species of Smilodon evolve |
| 2 Ma | First members of the genus Homo appear, Homo Habilis in the fossil record. Diversification of conifers in high latitudes. The eventual ancestor of cattle, aurochs (Bos primigenus), evolves in India. |
| 1.7 Ma | Extinction of australopithecines |
| 1.2 Ma | Evolution of Homo antecessor. The last members of Paranthropus die out. |
| 800 Ka | Short-faced bears (Arctodus simus) become abundant in North America |
| 600 ka | Evolution of Homo heidelbergensis |
| 350 ka | Evolution of Neanderthals |
| 300 ka | Gigantopithecus, a giant relative of the orangutan from Asia dies out |
| 250 ka | Anatomically modern humans appear in Africa.[65][66][67] Around 50,000 years before present they start colonising the other continents, replacing the Neanderthals in Europe and other hominins in Asia. |
| 40 ka | The last of the giant monitor lizards (Varanus priscus) die out |
| 30 ka | Extinction of Neanderthals, first domestic dogs |
| 15 ka | The last woolly rhinoceros (Coelodonta antiquitatis) are believed to have gone extinct |
| 11 ka | Short-faced bears vanish from North America, with the last giant ground sloths dying out. All Equidae become extinct in North America. |
| 10 ka | The Holocene epoch starts 10,000[68] years ago after the Late Glacial Maximum. The last mainland species of woolly mammoth (Mammuthus primigenus) die out, as does the last Smilodon species. |
| 8 ka | The Giant Lemur died out |
Historical extinctions



| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 6000 ya (c. 4000 BC) | Small populations of American mastodon die off in places like Utah and Michigan |
| 4500 ya (c. 2500 BC) | The last members of a dwarf race of woolly mammoths vanish from Wrangel Island near Alaska |
| c. 600 ya (c. 1400) | The moa and its predator, Haast's eagle, die out in New Zealand |
| 390 ya (1627) | The last recorded wild aurochs die out |
| 329 ya (1688) | The dodo goes extinct |
| 249 ya (1768) | The Steller's sea cow goes extinct |
| 134 ya (1883) | The quagga, a subspecies of zebra, goes extinct |
| 103 ya (1914) | Martha, last known passenger pigeon, dies |
| 81 ya (1936) | The thylacine goes extinct in a Tasmanian zoo, the last member of the family Thylacinidae |
| 65 ya (1952) | The Caribbean monk seal goes extinct[71] |
| 9 ya (2008) | The baiji, the Yangtze river dolphin, becomes functionally extinct, according to the IUCN Red List[72] |
| 6 ya (2011) | The western black rhinoceros is declared extinct |
See also
References
- ↑ McKinney 1997, p. 110
- ↑ Stearns, Beverly Peterson; Stearns, S. C.; Stearns, Stephen C. (2000). Watching, from the Edge of Extinction. Yale University Press. p. preface x. ISBN 978-0-300-08469-6. Retrieved 30 May 2017.
- ↑ Novacek, Michael J. (November 8, 2014). "Prehistory’s Brilliant Future". The New York Times. New York: The New York Times Company. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2014-12-25.
- ↑ Miller & Spoolman 2012, p. 62
- ↑ Mora, Camilo; Tittensor, Derek P.; Adl, Sina; et al. (August 23, 2011). "How Many Species Are There on Earth and in the Ocean?". PLOS Biology. San Francisco, CA: Public Library of Science. 9 (8): e1001127. ISSN 1545-7885. PMC 3160336
 . PMID 21886479. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001127.
. PMID 21886479. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001127. - ↑ Hickman, Crystal; Starn, Autumn. "The Burgess Shale & Models of Evolution". Reconstructions of the Burgess Shale and What They Mean... Morgantown, WV: West Virginia University. Retrieved 2015-10-18.
- ↑ Barton et al. 2007, Figure 10.20 Four diagrams of evolutionary models
- ↑ https://cosmosmagazine.com/palaeontology/measuring-sixth-mass-extinction
- 1 2 http://www.bbc.co.uk/nature/history_of_the_earth
- ↑ https://cosmosmagazine.com/palaeontology/big-five-extinctions
- ↑ Myers, Norman; Knoll, Andrew H. (May 8, 2001). "The biotic crisis and the future of evolution". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. Washington, D.C.: National Academy of Sciences. 98 (1): 5389–5392. Bibcode:2001PNAS...98.5389M. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 33223
 . PMID 11344283. doi:10.1073/pnas.091092498.
. PMID 11344283. doi:10.1073/pnas.091092498. - ↑ Moskowitz, Clara (March 29, 2012). "Life's Building Blocks May Have Formed in Dust Around Young Sun". Space.com. Salt Lake City, UT: Purch. Retrieved 2012-03-30.
- ↑ Herres, Gregg; Hartmann, William K. "The Origin of the Moon". Planetary Science Institute. Tucson, AZ. Retrieved 2015-03-04.
- ↑ Astrobio (September 24, 2001). "Making the Moon". Astrobiology Magazine ("Based on a Southwest Research Institute press release"). New York: NASA. ISSN 2152-1239. Retrieved 2015-03-04.
Because the Moon helps stabilize the tilt of the Earth's rotation, it prevents the Earth from wobbling between climatic extremes. Without the Moon, seasonal shifts would likely outpace even the most adaptable forms of life.
- ↑ Dodd, Matthew S.; Papineau, Dominic; Grenne, Tor; Slack, John F.; Rittner, Martin; Pirajno, Franco; O'Neil, Jonathan; Little, Crispin T. S. (1 March 2017). "Evidence for early life in Earth’s oldest hydrothermal vent precipitates". Nature. 543: 60–64. doi:10.1038/nature21377. Retrieved 2 March 2017.
- ↑ Zimmer, Carl (1 March 2017). "Scientists Say Canadian Bacteria Fossils May Be Earth’s Oldest". New York Times. Retrieved 2 March 2017.
- ↑ Ghosh, Pallab (1 March 2017). "Earliest evidence of life on Earth 'found'". BBC News. Retrieved 2 March 2017.
- ↑ Dunham, Will (1 March 2017). "Canadian bacteria-like fossils called oldest evidence of life". Reuters. Retrieved 1 March 2017.
- 1 2 3 Bjornerud 2005
- ↑ Abramov, Oleg; Mojzsis, Stephen J. (May 21, 2009). "Microbial habitability of the Hadean Earth during the late heavy bombardment" (PDF). Nature. London: Nature Publishing Group. 459 (7245): 419–422. Bibcode:2009Natur.459..419A. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 19458721. doi:10.1038/nature08015. Retrieved 2015-03-04.
- 1 2 Borenstein, Seth (October 19, 2015). "Hints of life on what was thought to be desolate early Earth". Excite. Yonkers, NY: Mindspark Interactive Network. Associated Press. Retrieved 2015-10-20.
- ↑ Bell, Elizabeth A.; Boehnike, Patrick; Harrison, T. Mark; et al. (November 24, 2015). "Potentially biogenic carbon preserved in a 4.1 billion-year-old zircon" (PDF). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. Washington, D.C.: National Academy of Sciences. 112 (47): 14518–14521. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 4664351
 . PMID 26483481. doi:10.1073/pnas.1517557112. Retrieved 2015-12-30.
. PMID 26483481. doi:10.1073/pnas.1517557112. Retrieved 2015-12-30. - ↑ Woese, Carl; Gogarten, J. Peter (October 21, 1999). "When did eukaryotic cells (cells with nuclei and other internal organelles) first evolve? What do we know about how they evolved from earlier life-forms?". Scientific American. Stuttgart: Georg von Holtzbrinck Publishing Group. ISSN 0036-8733. Retrieved 2015-03-04.
- ↑ Romano, Antonio H.; Conway, Tyrrell (July–September 1996). "Evolution of carbohydrate metabolic pathways". Research in Microbiology. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier for the Pasteur Institute. 147 (6–7): 448–455. ISSN 0923-2508. PMID 9084754. doi:10.1016/0923-2508(96)83998-2.
- ↑ Knowles, Jeremy R. (July 1980). "Enzyme-Catalyzed Phosphoryl Transfer Reactions". Annual Review of Biochemistry. Palo Alto, CA: Annual Reviews. 49: 877–919. ISSN 0066-4154. PMID 6250450. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004305.
- ↑ "Oldest traces of life on Earth found in Quebec, dating back roughly 3.8 billion years", by Nicole Mortilanno, CBC News
- ↑ Ohtomo, Yoko; Kakegawa, Takeshi; Ishida, Akizumi; et al. (January 2014). "Evidence for biogenic graphite in early Archaean Isua metasedimentary rocks". Nature Geoscience. London: Nature Publishing Group. 7 (1): 25–28. Bibcode:2014NatGe...7...25O. ISSN 1752-0894. doi:10.1038/ngeo2025. Retrieved 2015-03-04.
- ↑ Borenstein, Seth (November 13, 2013). "Oldest fossil found: Meet your microbial mom". Excite. Yonkers, NY: Mindspark Interactive Network. Associated Press. Retrieved 2013-11-15.
- ↑ Noffke, Nora; Christian, Daniel; Wacey, David; Hazen, Robert M. (November 8, 2013). "Microbially Induced Sedimentary Structures Recording an Ancient Ecosystem in the ca. 3.48 Billion-Year-Old Dresser Formation, Pilbara, Western Australia". Astrobiology. New York: Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. 13 (12): 1103–1124. ISSN 1531-1074. PMC 3870916
 . PMID 24205812. doi:10.1089/ast.2013.1030. Retrieved 2013-11-15.
. PMID 24205812. doi:10.1089/ast.2013.1030. Retrieved 2013-11-15. - ↑ Doolittle, W. Ford (February 2000). "Uprooting the Tree of Life" (PDF). Scientific American. Stuttgart: Georg von Holtzbrinck Publishing Group. 282 (2): 90–95. ISSN 0036-8733. PMID 10710791. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0200-90. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-09-07. Retrieved 2015-04-05.
- ↑ Glansdorff, Nicolas; Ying Xu; Labedan, Bernard (July 9, 2008). "The Last Universal Common Ancestor: emergence, constitution and genetic legacy of an elusive forerunner". Biology Direct. London: BioMed Central. 3: 29. ISSN 1745-6150. PMC 2478661
 . PMID 18613974. doi:10.1186/1745-6150-3-29.
. PMID 18613974. doi:10.1186/1745-6150-3-29. - ↑ Hahn, Jürgen; Haug, Pat (May 1986). "Traces of Archaebacteria in ancient sediments". Systematic and Applied Microbiology. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier. 7 (2–3): 178–183. ISSN 0723-2020. doi:10.1016/S0723-2020(86)80002-9.
- ↑ Olson, John M. (May 2006). "Photosynthesis in the Archean era". Photosynthesis Research. Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Springer Science+Business Media. 88 (2): 109–117. ISSN 0166-8595. PMID 16453059. doi:10.1007/s11120-006-9040-5.
- ↑ http://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/why-are-cells-powered-by-proton-gradients-14373960
- 1 2 Buick, Roger (August 27, 2008). "When did oxygenic photosynthesis evolve?". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. London: Royal Society. 363 (1504): 2731–2743. ISSN 0962-8436. PMC 2606769
 . PMID 18468984. doi:10.1098/rstb.2008.0041.
. PMID 18468984. doi:10.1098/rstb.2008.0041. - 1 2 Beraldi-Campesi, Hugo (February 23, 2013). "Early life on land and the first terrestrial ecosystems" (PDF). Ecological Processes. Heidelberg: SpringerOpen. 2 (1): 1–17. ISSN 2192-1709. doi:10.1186/2192-1709-2-1.
- ↑ Javaux, Emmanuelle J.; Marshall, Craig P.; Bekker, Andrey (February 18, 2010). "Organic-walled microfossils in 3.2-billion-year-old shallow-marine siliciclastic deposits". Nature. London: Nature Publishing Group. 463 (7283): 934–938. Bibcode:2010Natur.463..934J. ISSN 1744-7933. PMID 20139963. doi:10.1038/nature08793.
- ↑ Bernstein, Harris; Bernstein, Carol (May 1989). "Bacteriophage T4 genetic homologies with bacteria and eucaryotes". Journal of Bacteriology. Washington, D.C.: American Society for Microbiology. 171 (5): 2265–2270. ISSN 0021-9193. PMC 209897
 . PMID 2651395.
. PMID 2651395. - ↑ Bjornerud 2005, p. 151
- ↑ Knoll, Andrew H.; Javaux, Emmanuelle J.; Hewitt, David; et al. (June 29, 2006). "Eukaryotic organisms in Proterozoic oceans". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. London: Royal Society. 361 (1470): 1023–1038. ISSN 0962-8436. PMC 1578724
 . PMID 16754612. doi:10.1098/rstb.2006.1843.
. PMID 16754612. doi:10.1098/rstb.2006.1843. - ↑ Fedonkin, Mikhail A. (March 31, 2003). "The origin of the Metazoa in the light of the Proterozoic fossil record" (PDF). Paleontological Research. Tokyo: Palaeontological Society of Japan. 7 (1): 9–41. ISSN 1342-8144. doi:10.2517/prpsj.7.9. Retrieved 2015-03-08.
- ↑ Bernstein, Bernstein & Michod 2012, pp. 1–50
- ↑ Bernstein, Harris; Byerly, Henry C.; Hopf, Frederic A.; Michod, Richard E. (October 7, 1984). "Origin of sex". Journal of Theoretical Biology. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier. 110 (3): 323–351. ISSN 0022-5193. PMID 6209512. doi:10.1016/S0022-5193(84)80178-2.
- ↑ Butterfield, Nicholas J. (Summer 2000). "Bangiomorpha pubescens n. gen., n. sp.: implications for the evolution of sex, multicellularity, and the Mesoproterozoic/Neoproterozoic radiation of eukaryotes". Paleobiology. Boulder, CO: Paleontological Society. 26 (3): 386–404. ISSN 0094-8373. doi:10.1666/0094-8373(2000)026<0386:BPNGNS>2.0.CO;2.
- ↑ Erwin, Douglas H. (9 November 2015). "Early metazoan life: divergence, environment and ecology". Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B. 370 (20150036). doi:10.1098/rstb.2015.0036. Retrieved 7 January 2016.
- ↑ Hoffman, Paul F.; Kaufman, Alan J.; Halverson, Galen P.; Schrag, Daniel P. (August 28, 1998). "A Neoproterozoic Snowball Earth" (PDF). Science. Washington, D.C.: American Association for the Advancement of Science. 281 (5381): 1342–1346. Bibcode:1998Sci...281.1342H. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 9721097. doi:10.1126/science.281.5381.1342. Retrieved 2007-05-04.
- ↑ Kirschvink 1992, pp. 51–52
- ↑ Boyle, Richard A.; Lenton, Timothy M.; Williams, Hywel T. P. (December 2007). "Neoproterozoic 'snowball Earth' glaciations and the evolution of altruism" (PDF). Geobiology. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell. 5 (4): 337–349. ISSN 1472-4677. doi:10.1111/j.1472-4669.2007.00115.x. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-09-10. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
- ↑ Corsetti, Frank A.; Awramik, Stanley M.; Pierce, David (April 15, 2003). "A complex microbiota from snowball Earth times: Microfossils from the Neoproterozoic Kingston Peak Formation, Death Valley, USA". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. Washington, D.C.: National Academy of Sciences. 100 (8): 4399–4404. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.4399C. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 153566
 . PMID 12682298. doi:10.1073/pnas.0730560100.
. PMID 12682298. doi:10.1073/pnas.0730560100. - ↑ Corsetti, Frank A.; Olcott, Alison N.; Bakermans, Corien (March 22, 2006). "The biotic response to Neoproterozoic snowball Earth". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier. 232 (2–4): 114–130. ISSN 0031-0182. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.10.030.
- ↑ "Formation of the Ozone Layer". Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center. NASA. September 9, 2009. Retrieved 2013-05-26.
- ↑ Narbonne, Guy (January 2008). "The Origin and Early Evolution of Animals". Kingston, Ontario, Canada: Queen's University. Retrieved 2007-03-10.
- ↑ Waggoner, Ben M.; Collins, Allen G.; et al. (November 22, 1994). Rieboldt, Sarah; Smith, Dave, eds. "The Cambrian Period". Tour of geologic time (Online exhibit). Berkeley, CA: University of California Museum of Paleontology. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
- ↑ Lane, Abby (January 20, 1999). "Timing". The Cambrian Explosion. Bristol, England: University of Bristol. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
- ↑ Clarke, Tom (April 30, 2002). "Oldest fossil footprints on land". Nature. London: Nature Publishing Group. ISSN 1744-7933. doi:10.1038/news020429-2. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
The oldest fossils of footprints ever found on land hint that animals may have beaten plants out of the primordial seas. Lobster-sized, centipede-like animals made the prints wading out of the ocean and scuttling over sand dunes about 530 million years ago. Previous fossils indicated that animals didn't take this step until 40 million years later.
- ↑ "Ciesielski, Paul F. "Transition of plants to land". Gainesville, FL: University of Florida. Archived from the original on 1999-10-09. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
The oldest fossils reveal evolution of non-vascular plants by the middle to late Ordovician Period (~450-440 m.y.a.) on the basis of fossil spores.
- ↑ Carrington, Sean. "The Conquest of the Land". BIOL1020 Diversity of Life I: The Plant Kingdom. Cave Hill, Saint Michael, Barbados: University of the West Indies. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
The land plants evolved from the algae, more specifically green algae, as suggested by certain common biochemical traits
- ↑ Garwood, Russell J.; Edgecombe, Gregory D. (September 2011). "Early Terrestrial Animals, Evolution, and Uncertainty". Evolution: Education and Outreach. New York: Springer Science+Business Media. 4 (3): 489–501. ISSN 1936-6426. doi:10.1007/s12052-011-0357-y. Retrieved 2015-07-21.
- ↑ Martin, R. Aidan. "Evolution of a Super Predator". Biology of Sharks and Rays. North Vancouver, BC, Canada: ReefQuest Centre for Shark Research. Retrieved 2015-03-10.
The ancestry of sharks dates back more than 200 million years before the earliest known dinosaur.
- ↑ "Amniota". Palaeos. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
- ↑ Sahney, Sarda; Benton, Michael J. (April 7, 2008). "Recovery from the most profound mass extinction of all time" (PDF). Proceedings of the Royal Society B. London: Royal Society. 275 (1636): 759–765. ISSN 0962-8452. PMC 2596898
 . PMID 18198148. doi:10.1098/rspb.2007.1370.
. PMID 18198148. doi:10.1098/rspb.2007.1370. - ↑ Rybicki, Ed (April 2008). "Origins of Viruses". Introduction of Molecular Virology (Lecture). Cape Town, Western Cape, South Africa: University of Cape Town. Retrieved 2015-03-10.
Viruses of nearly all the major classes of organisms - animals, plants, fungi and bacteria / archaea - probably evolved with their hosts in the seas, given that most of the evolution of life on this planet has occurred there. This means that viruses also probably emerged from the waters with their different hosts, during the successive waves of colonisation of the terrestrial environment.
- ↑ Dell'Amore, Christine (April 24, 2014). "Meet Kryptodrakon: Oldest Known Pterodactyl Found in China". National Geographic News. Washington, D.C.: National Geographic Society. Retrieved 2014-04-25.
- ↑ Chiappe, Luis M.; Dyke, Gareth J. (November 2002). "The Mesozoic Radiation of Birds". Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics. Palo Alto, CA: Annual Reviews. 33: 91–124. ISSN 1545-2069. doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.33.010802.150517.
- ↑ Karmin M, Saag L, Vicente M, et al. (April 2015). "A recent bottleneck of Y chromosome diversity coincides with a global change in culture". Genome Research. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. 25 (4): 459–466. ISSN 1088-9051. PMC 4381518
 . PMID 25770088. doi:10.1101/gr.186684.114.
. PMID 25770088. doi:10.1101/gr.186684.114. - ↑ Brown, Frank; Fleagle, John; McDougall, Ian (February 16, 2005). "The Oldest Homo sapiens" (Press release). Salt Lake City, UT: University of Utah. Retrieved 2015-03-10.
- ↑ Alemseged, Zeresenay; Coppens, Yves; Geraads, Denis (February 2002). "Hominid cranium from Homo: Description and taxonomy of Homo-323-1976-896". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons for the American Association of Physical Anthropologists. 117 (2): 103–112. ISSN 0002-9483. PMID 11815945. doi:10.1002/ajpa.10032.
- ↑ "International Stratigraphic Chart (v 2014/10)" (PDF). Beijing, China: International Commission on Stratigraphy. Retrieved 2015-03-11.
- ↑ Blanchard, Ben (December 13, 2006). "INTERVIEW-Chinese river dolphin almost certainly extinct". Reuters. Retrieved 2015-10-19.
- ↑ Lovgren, Stefan (December 14, 2006). "China's Rare River Dolphin Now Extinct, Experts Announce". National Geographic News. Washington, D.C.: National Geographic Society. Retrieved 2015-10-18.
- ↑ "It's official: Caribbean monk seal is extinct". msnbc.com. June 6, 2008. Retrieved 2015-03-11.
- ↑ Smith, B.D.; Zhou, K.; Wang, D.; Reeves, R.R.; Barlow, J.; Taylor, B.L. & Pitman, R. (2008). "Lipotes vexillifer". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 2015-10-19.
Bibliography
- Barton, Nicholas H.; Briggs, Derek E.G.; Eisen, Jonathan A.; Goldstein, David B.; Patel, Nipam H. (2007). Evolution. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. ISBN 978-0-87969-684-9. LCCN 2007010767. OCLC 86090399.
- Bernstein, Harris; Bernstein, Carol; Michod, Richard E. (2012). "DNA Repair as the Primary Adaptive Function of Sex in Bacteria and Eukaryotes". In Kimura, Sakura; Shimizu, Sora. DNA Repair: New Research. Hauppauge, NY: Nova Science Publishers. ISBN 978-1-62100-808-8. LCCN 2011038504. OCLC 828424701.
- Bjornerud, Marcia (2005). Reading the Rocks: The Autobiography of the Earth. Cambridge, MA: Westview Press. ISBN 0-8133-4249X. LCCN 2004022738. OCLC 56672295.
- Kirschvink, Joseph L. (1992). "Late Proterozoic Low-Latitude Global Glaciation: the Snowball Earth" (PDF). In Schopf, J. William; Klein, Cornelis. The Proterozoic Biosphere: A Multidisciplinary Study (PDF). Cambridge; New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-36615-1. LCCN 91015085. OCLC 23583672.
- McKinney, Michael L. (1997). "How do rare species avoid extinction? A paleontological view". In Kunin, William E.; Gaston, Kevin J. The Biology of Rarity: Causes and consequences of rare—common differences (1st ed.). London; New York: Chapman & Hall. ISBN 0-412-63380-9. LCCN 96071014. OCLC 36442106.
- Miller, G. Tyler; Spoolman, Scott E. (2012). Environmental Science (14th ed.). Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole. ISBN 978-1-111-98893-7. LCCN 2011934330. OCLC 741539226.
|ref=harv}}
Further reading
- Dawkins, Richard (2004). The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of Life. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company. ISBN 0-618-00583-8. LCCN 2004059864. OCLC 56617123.
External links
- "Understanding Evolution: your one-stop resource for information on evolution". University of California, Berkeley. Retrieved 2015-03-18.
- "Life on Earth". Tree of Life Web Project. University of Arizona. January 1, 1997. Retrieved 2015-03-18. Explore complete phylogenetic tree interactively
- Brandt, Niel. "Evolutionary and Geological Timelines". TalkOrigins Archive. Houston, TX: The TalkOrigins Foundation, Inc. Retrieved 2015-03-18.
- "Palaeos: Life Through Deep Time". Palaeos. Retrieved 2015-03-18.
- Kyrk, John. "Evolution" (SWF). Cell Biology Animation. Retrieved 2015-03-18. Interactive timeline from Big Bang to present
- "Plant Evolution". Plant and Animal Evolution. University of Waikato. Retrieved 2015-03-18. Sequence of Plant Evolution
- "The History of Animal Evolution". Plant and Animal Evolution. University of Waikato. Retrieved 2015-03-18. Sequence of Animal Evolution
- Yeo, Dannel; Drage, Thomas (2006). "History of Life on Earth". Retrieved 2015-03-19.
- Exploring Time. The Science Channel. 2007. Retrieved 2015-03-19.
- Roberts, Ben. "Plant evolution timeline". University of Cambridge. Retrieved 2015-03-19.



