Timeline of Cambridge, Massachusetts
This is a timeline of the history of the city of Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA.
17th century
- 1630 - English settlers arrive.
- 1632 - First Parish meeting house built.
- 1636 - The "New College" founded.
- 1638
- Newe Towne renamed "Cambridge."[1]
- John Harvard, a Puritan minister, bequeaths his library and half his monetary estate to the college.
- 1639 - New College renamed Harvard College for benefactor John Harvard.
- 1640 - Bay Psalm Book printed.[2]
- 1642 - Harvard holds its first commencement.
- 1662 - Great Bridge built.
- 1663 - Algonquin-language Mamusse Wunneetupanatamwe Up-Biblum God published.[3]
- 1682 - Cooper-Frost-Austin House built (date approximate).
- 1685 - Hooper-Lee-Nichols House built.
- 1688 - Cambridge Village, later renamed Newton, separated from Cambridge.[4]
18th century
- 1713 - Town of Lexington separated from Cambridge.[1]
- 1720 - Harvard's Massachusetts Hall built.
- 1727 - William Brattle House built.
- 1759
- Christ Church congregation founded.
- Vassall House built.[1]
- 1760 - Apthorp House built.[1]
- 1767 - Elmwood (residence) built.
- 1775
- April 18: William Dawes traverses the town en route to sounding warnings on eve of Battles of Lexington and Concord.[5]
- April 19: Skirmishes between retreating British troops and American patriots at Watson's Corner and elsewhere in North Cambridge.[6]
- May 12: The New-England Chronicle in publication.[7]
- July 3: George Washington takes command of American army.[8]
- 1780 - May 19: New England's Dark Day.
- 1782 - Harvard Medical School founded.[9]
- 1793 - West Boston Bridge built.[10]
- 1796 - Fresh Pond Hotel built.[11]
19th century
1800s–1840s
- 1800 - Printer William Hilliard in business.[12]
- 1805 - Harvard Botanic Garden founded.[13]
- 1807
- Cambridge and Concord Turnpike opens.
- Little Cambridge separates from Cambridge and is renamed Brighton.[14]
- West Cambridge, later renamed Arlington, separated from Cambridge.[15]
- 1809 - Craigie's Bridge opens.
- 1814 - Cambridge Humane Society[16] and Female Humane Society founded.[17]
- 1815 - Harvard's University Hall built.
- 1816 - Middlesex County Courthouse (Massachusetts) built.
- 1817 - Harvard Law School founded.
- 1818 - New England Glass Company established.
- 1824 - East Cambridge Charitable Society formed.[16]
- 1826 - Frederic Tudor and Nathaniel Wyeth begin harvesting ice at Fresh Pond.[18]
- 1827 - First Evangelical Congregational church[19] and Second Baptist Church[20] established.
- 1830 - Population: 6,072.[21]
- 1831
- Mount Auburn Cemetery founded.[22]
- Cambridge Market Hotel (later Porter's Hotel) built.[23]
- 1832 - Cambridge Fire Department established.
- 1833
- Hunt & Co's Circulating Library in business.[24]
- First Parish meeting house built, corner Church St. and Mass. Ave.
- 1835 - West Cambridge Social Library active.[24]
- 1837
- August 31: Emerson gives "American Scholar" speech.[25]
- East Cambridge Anti-Slavery Society formed.[17]
- Henry Wadsworth Longfellow moves to Craigie House.[8]
- 1839
- Hopkins Classical School established.
- Harvard College Observatory founded.
- 1840
- 1841 - Cambridge Lyceum organized.
- 1846
- Cambridge Chronicle begins publication.
- Stickney-Shepard House built.
- Lexington and West Cambridge Railroad begins operating.[27]
- Alvan Clark & Sons telescope maker in business.
- City chartered.[1]
- James D. Green becomes mayor.[28]
- Population: 12,500.[29]
- 1847 - Great Refractor telescope installed.[30]
- 1848 - Franklin Library Association founded.[24]
- 1849 - Cambridge Athenaeum incorporated.[31]
1850s–1890s
- 1850 - Howard Benevolent Society organized.[16]
- 1852
- Cambridge Water Works Corporation chartered.[28]
- Riverside Press established.
- 1854 - Cambridge Cemetery consecrated.[19]
- 1856 - Population: 20,473.[29]
- 1857
- Cambridge Circulating Library in business.[24]
- Walden Street Cattle Pass built.
- 1858 - Harvard Glee Club founded.[32]
- 1859 - Museum of Comparative Zoology founded.
- 1860 - Cambridge Horticultural Society organized.[16]
- 1861 - Veterans' Services established.[33]
- 1862 - Sanitary Society active (approximate date).[17]
- 1865 - Old Cambridge Mutual Relief Society organized.[16]
- 1866
- Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology and New Church Theological School[1] founded.
- Cambridge Press newspaper begins publication.[26][34]
- 1867 - Episcopal Theological School founded.[1]
- 1868 - Cambridge Mechanics Literary Association organized.[16]
- 1869
- Old Cambridge Baptist Church built on Harvard Street.
- North Cambridge Choral Society organized.[16]
- 1870 - Soldiers' Monument dedicated on Cambridge Common[35]
- 1871
- 1872 - Cambridge Choral Society formed.[16]
- 1873
- The Harvard Crimson newspaper begins publication.[36]
- Basket Club formed.[17]
- 1875
- Church of the Ascension organized.[19]
- Kennedy Steam Bakery built.
- Population: 47,838.[29]
- 1876 - Harvard Lampoon begins publication.
- 1877 - Harvard's Memorial Hall built.
- 1878
- The Cambridge Tribune newspaper begins publication.[26]
- Harvard's Sever Hall built.
- 1879 - Cambridge Public Library established.[31]
- 1880 - Population: 52,669.[1]
- 1881 - Cambridge Club active.[17]
- 1882
- Society for the Collegiate Instruction of Women incorporated.
- Harvard Cooperative founded.
- 1883
- 1884 - Odd Fellows Hall built.
- 1886 - Cambridge Hospital, Cambridge English High School (Broadway & Fayette St.),[39] Cambridge Latin School (Lee St.),[39] and Cambridge School for Girls established.
- 1887 - Cambridgeport Cycle Club organized.[37]
- 1889
- City Hall, Brattle Hall, and William James' house[40] built.
- Buckingham School founded.[38]
- Cambridge Plant Club established.[39][41]
- 1890 - Population: 70,028.[1]
- 1891 - Harvard Bridge built.
- 1892 - Old Cambridge Photographic Club formed.[17]
- 1893 - Road built around Fresh Pond.[11]
- 1894
- Radcliffe College chartered.
- Cambridge Walking Club founded.[17]
- 1895
- Lechmere Canal built.
- Keezer's clothier in business.[42]
- W. E. B. Du Bois earns PhD from Harvard University.[43]
- 1896 - Cambridge Political Equality Association established.[44]
- 1897 - Cambridge Skating Club founded.[45]
20th century
1900s–1940s
- 1900 - Population: 91,886.[1]
- 1901 - Swedenborg Chapel built.[40]
- 1903
- Cambridge Sentinel newspaper begins publication.[26]
- Busch–Reisinger Museum opens.
- 1904 - Harvard's Phillips Brooks House Association established.
- 1905 - Cambridge Historical Society founded.[46][47]
- 1906 - Longfellow Bridge opens.[1]
- 1908
- Andover Theological Seminary relocates to city.[1]
- Harvard's Business School established.
- 1909 - Lesley School founded.[48]
- 1910 - Harvard Square Business Association founded.[49]
- 1911 - Cambridge Housing Association formed.[50]
- 1912 - Kendall/MIT (MBTA station), Central (MBTA station), and Harvard (MBTA station) open.
- 1913
- Harvard University Press and Harvard Legal Aid Bureau established.
- Cohen harness maker in business.[51]
- 1914 - Cambridge Planning Board established.[52]
- 1915
- Anderson Memorial Bridge and Harvard's Widener Library built.
- Cooperative Open Air School founded.
- 1916
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology moves to Cambridge[53]
- Tasty Sandwich Shop in business.[54]
- 1917
- Wursthaus restaurant in business.[54]
- Arthur D. Little Inc., Building constructed.
- 1923 - Washington Elm dies on Cambridge Common.
- 1924 - The Church of St. Paul (Harvard Square) built.
- 1926 - Harvard Square Theater opens.[55]
- 1927
- John W. Weeks Bridge built.
- Necco factory opens on Massachusetts Avenue.
- Grolier Poetry Bookshop and Mac-Gray Corp.[56] in business.
- 1928 - Boston University Bridge built.
- 1929 - Cambridge Community Center founded.[57]
- 1930
- First Church of Christ, Scientist built.
- Longy School of Music moves to Cambridge.
- Russian bells installed in Harvard's Lowell House.
- 1932
- Harvard Book Store and MIT's Technology Press and School of Architecture established.
- Harvard's Memorial Church built.
- 1936 - Harvard's Graduate School of Public Administration and Graduate School of Design established.
- 1938
- Hayes-Bickford Cafeteria in business (approximate date).[54]
- Harvard's Nieman Foundation for Journalism established.
- 1940 - National Research Corporation in business.[58]
- 1941
- Magazine of Cambridge begins publication.[59]
- Harvard's Houghton Library built.
- 1942 - John B. Atkinson becomes city manager.
- 1945 - Cambridge Civic Unity Committee established.[60]
- 1945 - Irving House established.[61]
- 1946 - WMIT begins broadcasting.
- 1947
- September 9: Computer bug found at the Harvard Computation Lab.
- Demise of the Harvard Botanic Garden.[13]
- Edgerton, Germeshausen, and Grier in business.[62]
1950s–1970s
- 1950
- Cardullo's Gourmet Shop in business.[54]
- Joseph DeGuglielmo becomes mayor.
- 1951
- 1952
- John J. Curry becomes city manager.
- MIT School of Industrial Management and MIT Center for International Studies[63] established.
- 1953
- Brattle Theatre begins screening movies.
- Harvard Model United Nations conference begins.
- 1954 - Wang Laboratories, Cheapo Records,[64] and Hong Kong restaurant[65] in business.
- 1955
- Out of Town News, Casablanca bar,[54] Elsie's eatery[66] and Ferranti-Dege camera store[67] in business.
- Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory relocated to Cambridge.
- 1957
- Cambridge Buddhist Association established.[68]
- Pangloss Bookstore in business.[69]
- 1958
- Club 47 (music venue) opens.[70]
- Joyce Chen restaurant[71] and Chez Jean restaurant[54] in business.
- Lisp (programming language) invented at MIT.[72]
- Smoot measurement established.
- 1959
- Café Pamplona in business.
- Harvard/MIT Center for Urban Studies and MIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory[72] established.
- 1960
- 1961
- Julia Child moves to Cambridge.[73]
- October 14: Fire destroys the original WGBH television and radio studios, at MIT.
- 1962
- Temple Beth Shalom founded.[74]
- Fresh Pond Shopping Center built.[11]
- Cambridge Electron Accelerator in operation.[75]
- Harvard's Carpenter Center for the Visual Arts built.
- Cambridge Seven Associates in business.
- Cambridge Sports Union founded.[76]
- 1963 - Cambridge Historical Commission established.[77]
- 1964 - NASA Electronics Research Center established.[78]
- 1965 - Head of the Charles Regatta established.
- 1966 - Cambridge School Volunteers founded.
- 1967
- Joseph DeGuglielmo becomes city manager.
- Cambridge Forum,[79] MIT's Center for Advanced Visual Studies established.
- 1968
- 1969
- Student antiwar protest.[81]
- Union of Concerned Scientists,[82] and Harvard's Institute for African and African-American Research founded.
- Passim[70] and Plough and Stars in business.
- 1970
- The Middle East restaurant opens.
- Rent control[83] and Massachusetts Department of Transportation Volpe Center[78] established.
- Alfred Vellucci becomes mayor.
- 1971
- Cambridge and Somerville Legal Services established.[84]
- Grendel's Den pub in business.
- Revels performance series begins.
- 1972
- 1973
- Harvard–Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics established.
- Draper Laboratory active.
- T.T. the Bear's Place and Hacker's Haven car repair shop in business.
- 1974
- Cambridge Food Co-op,[88] city Arts Council,[89] city Community Development Department,[52][90] and Buckingham Browne & Nichols school established.
- James Sullivan becomes city manager.
- Cambridge Naturals in business.[91]
- 1975 - Coffee Connection in business.
- 1977
- Cambridge Rindge and Latin School formed.
- River Festival begins.[92]
- Changsho restaurant in business.[93]
- 1978
- National Bureau of Economic Research active.[82]
- Formaggio Kitchen in business.[94]
- 1979 - Harvard's Film Archive opens.
1980s–1990s
- 1980
- American Repertory Theater and MIT's PiKa housing cooperative[95] established.
- MIT Museum active.
- 1981
- American Academy of Arts and Sciences moves to Cambridge.[96]
- Cambridge College active.[97]
- Robert W. Healy becomes city manager.[98]
- Cambridge Center complex construction begins.[78]
- 1982
- Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research founded.
- Biogen,[99] Toscanini's, and Upstairs at the Pudding restaurant in business.[54]
- Sister city relationships established with Coimbra, Portugal, and Gaeta, Italy.[100]
- 1983
- Harvard Square Homeless Shelter and Albert Einstein Institution established.
- Monitor Group and Cambridge Energy Research Associates headquartered in Cambridge.
- Sister city relationships established with Tsukuba Science City, Ibaraki, Japan; and Dublin, Ireland.[100]
- Pegasystems Inc. and Forrester Research in business.
- Premiere of Marsha Norman's play Night, Mother.
- 1984
- MIT Media Lab,[101] Institute for Resource and Security Studies,[102] and city Police Review & Advisory Board[103] established.
- Sister city relationship established with Ischia, Italy.[100]
- Porter MBTA Red Line station opens.
- Conflict Management Group headquartered in city.
- Thinking Machines Corporation and Charles Hotel in business.
- 1985
- Alewife (MBTA station) opens.
- Harvard's Arthur M. Sackler Museum built.
- Dante Alighieri Society building inaugurated.[104]
- Memorial Drive partially pedestrianized along Riverbend Park.
- 1986
- Garment District (clothing retailer) in business.
- Thinking Machines' Connection Machine invented.[72]
- MIT flea market begins.[105]
- 1987
- Sister city relationships established with Yerevan, Armenia;[106] San José Las Flores, Chalatenango, El Salvador; and Catania, Italy.[100]
- Cambridge becomes a Peace Messenger City.[107]
- Catch a Rising Star in business.
- Joseph P. Kennedy II becomes U.S. representative for Massachusetts's 8th congressional district.
- 1988 - Cambridge Community Television[108] and Cambridge Eviction Free Zone established.
- 1989
- 1990
- CambridgeSide Galleria built.
- Sapient Corporation in business.
- 1991
- City Bicycle Committee[103] and Ig Nobel Prize established.
- MÄK Technologies in business.
- 1992
- Boston Dynamics (robotics firm)[109] and Dewey, Cheetham & Howe[110] in business.
- Kenneth Reeves becomes mayor.
- Sister city relationship established with Florence, Italy.[100]
- 1993
- City master plan published.[111]
- MIT's The Tech newspaper web edition begins publication.
- Timothy J. Toomey, Jr. becomes state representative for 29th Middlesex district.[112]
- 1994
- 1995
- 1996
- Cambridge Health Alliance and On The Rise nonprofit established.[116]
- City Dance Party begins.[117][118]
- Sheila Russell becomes mayor.
- 1997
- City website online.[119]
- Cambridge Civic Journal begins publication.[120]
- Sister city relationship established with Galway, Ireland.[100]
- French-American International School active.
- 1998
- Akamai Technologies in business.
- MIT's Center for Reflective Community Practice active.[121]
- Francis Duehay becomes mayor.
- Harvard's Berkman Center for Internet & Society founded.
- 1999
- Cambridge Innovation Center in business.
- Mike Capuano becomes U.S. representative for Massachusetts's 8th congressional district.[122]
21st century
- 2000
- Zipcar in business.
- Anthony Galluccio becomes mayor.
- MIT's Kismet (robot) introduced.[72]
- 2001
- 2002 - Michael A. Sullivan becomes mayor.[125]
- 2003
- Novartis research division headquartered in city.[126]
- Longwood Players (theatre group) active.[127][128]
- MIT's Poverty Action Lab and Harvard's Ash Institute for Democratic Governance and Innovation[63] founded.
- Sister city relationship established with Santo Domingo Oeste, Dominican Republic.[100]
- 2004
- Broad Institute, Community Charter School of Cambridge,[129] and ActBlue (nonprofit)[130] established.
- MIT's Stata Center built.
- Lorem Ipsum bookshop in business.
- Sister city relationship established with Southwark, London, England.[100]
- Cambridge Somerville Resource Guide begins publication.[131]
- February 4: Facebook launched at Harvard College.[132]
- 2005
- Papercut Zine Library opens.
- Cambridge Local First network organized.[133]
- Sister city relationships established with Cienfuegos, Cuba;[106] Yuseong, Daejeon, Korea; and Haidian, Beijing, China.[100]
- Cambridge Day begins publication.
- Patricia D. Jehlen becomes state senator for 2nd Middlesex district.[134][135]
- 2006
- Green Decade Cambridge incorporated.[136]
- Kenneth Reeves becomes mayor again.
- Harvard's Rappaport Institute for Greater Boston established.
- HubSpot in business.
- 2007
- Microsoft New England Research & Development Center opens.[137]
- Cambridge Science Festival begins.[101]
- MIT's Center for Future Civic Media established.
- Unitarian Universalist Service Committee headquartered in Cambridge.
- Anthony Petruccelli becomes state senator for 1st Suffolk and Middlesex district.[138]
- 2008
- Alliance of Cambridge Tenants,[139] and Google Inc. branch established.
- ImprovBoston moves to Cambridge.
- Sofra bakery[123] and Hungry Mother restaurant[140] in business.
- Harvard Square Library incorporated.[79]
- E. Denise Simmons becomes mayor.
- ROFLCon meme convention begins.
- Central Square Theater built.[141]
- Jon Hecht elected state representative for 29th Middlesex district.
- 2009
- July: Henry Louis Gates arrest controversy
- West Cambridge Youth and Community Center opens.[142]
- Kendall Square Association established.[78]
- Cambridge Open Studios active.
- Trader Joe's grocery in business at Fresh Pond.[143]
- 2010
- David Maher becomes mayor.
- Population: 105,162;[144] metro 4,552,402.[145]
- Sal DiDomenico becomes state senator for Middlesex, Suffolk and Essex district.[146]
- 2011
- January 6: Aaron Swartz arrested.
- Area Four restaurant, Veggie Galaxy restaurant[147][148] and Danger!awesome in business.
- 2012
- MIT/Harvard edX launched.
- Henrietta Davis becomes mayor.
- Hack/reduce nonprofit founded.
- Sinclair[149] and Amazon office[150] in business.
- 2013
- Richard Rossi becomes city manager.
- Cambridge Open Data Ordinance drafted.[151]
- Cambridge Happenings in publication.[152]
- April 18–19: MIT officer killed; Boston Marathon bombings suspects manhunt takes place.[153]
- November: Municipal election.
- December: Katherine Clark becomes U.S. representative for Massachusetts's 5th congressional district.[154]
- Marjorie Decker becomes state representative for 25th Middlesex district, Dave Rogers becomes state representative for 24th Middlesex district,[155] and Jay Livingstone becomes state representative for 8th Suffolk district.
- Kensho Technologies in business.
- 2014
- 2015
- January 2015 North American blizzard.
- September 6: Lawrence Lessig presidential campaign, 2016 headquartered in city.
- December 3: Fire.[158]
See also
- Cambridge, Massachusetts history section
- List of mayors of Cambridge, Massachusetts
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Cambridge, Massachusetts
- List of National Historic Landmarks in Massachusetts, Cambridge section
- History of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- History of Harvard University
- Timelines of other municipalities in Middlesex County, Massachusetts: Lowell, Somerville, Waltham
- Timeline of Massachusetts
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Britannica 1910.
- ↑ Roden 1905.
- ↑ Alden Bradford (1843). New England Chronology. Boston: S.G. Simpkins.
- ↑ Ritter, Priscilla R.; Thelma Fleishman (1982). Newton, Massachusetts 1679–1779: A Biographical Directory. New England Historic Genealogical Society.
- ↑ "The American Revolution Comes to Cambridge, Part II (Note 3) Retrieved 2 November 2013 Archived June 17, 2013, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "The American Revolution Comes to Cambridge, Part III: Retreat: Deadly Skirmishes in North Cambridge" Access date 7 December 2013 Archived June 17, 2013, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Eighteenth-Century American Newspapers in the Library of Congress: Massachusetts". Library of Congress. Retrieved August 16, 2011.
- 1 2 Baedeker 1909.
- ↑ "Harvard Medical School history". Retrieved August 15, 2011.
- ↑ "Boston", Appleton's Handbook of American Travel: Northern and Eastern Tour, New York: D. Appleton and Company, 1870
- 1 2 3 "Brief Chronology of Fresh Pond". Friends of Fresh Pond Reservation. Retrieved April 30, 2014.
- ↑ White 1931.
- 1 2 Aloian, John (November 5, 2012). "The Harvard Botanic Garden". Harvard Community Garden.
- ↑ "History of Brighton-Allston". Retrieved 2013-11-26.
- ↑ "Town of Arlington, Massachusetts: History". Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Greenough 1873.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Library Special Collections, Cambridge Historical Society, retrieved June 30, 2014
- ↑ Weightman, Gavin (2003). The Frozen-Water Trade: A True Story. New York: Hyperion. p. 110
- 1 2 3 Greenough 1910.
- 1 2 3 Cambridge Historical Commission. "Finding Aids to Archival Collections". City of Cambridge. Retrieved April 30, 2014.
- 1 2 Population of the 100 Largest Cities and Other Urban Places in the United States: 1790 to 1990, U.S. Census Bureau, 1998
- ↑ "United States and Canada, 1800–1900 A.D.: Key Events". Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. New York: Metropolitan Museum of Art. Retrieved June 30, 2014.
- ↑ Cambridge Historical Commission 1977, pp. 134-35.
- 1 2 3 4 Davies Project. "American Libraries before 1876". Princeton University. Retrieved August 14, 2013.
- ↑ Louis Menand (2001). The Metaphysical Club: A Story of Ideas in America. Farrar, Straus and Giroux. ISBN 978-0-374-19963-0.
- 1 2 3 4 "US Newspaper Directory". Chronicling America. Washington DC: Library of Congress. Retrieved November 4, 2012.
- ↑ Henry Varnum Poor (1860), History of the railroads and canals of the United States, New York: J.H. Schultz
- 1 2 Gilman 1896.
- 1 2 3 City Council 1875.
- ↑ "The Great Refractor". Harvard College Observatory. Retrieved August 15, 2011.
- 1 2 Report of the Free Public Library Commission of Massachusetts. 1891.
- ↑ Donna M. Di Grazia, ed. (2013). Nineteenth-Century Choral Music. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-98852-0.
- ↑ Department of Veterans' Services. "Our History". City of Cambridge. Retrieved April 30, 2014.
- ↑ "Massachusetts: Cambridge". American Newspaper Directory. George P. Rowell. 1884.
- ↑ Soldiers' Monument in Cambridge, Cambridge, MA: J. Wilson and Son, 1870, OCLC 6322068
- 1 2 Harvard Crimson 2001.
- 1 2 Cambridge Historical Society. Proceedings, 1980-1985.
- 1 2 "BB&N – A Brief History". Buckingham Browne & Nichols School. Retrieved August 15, 2011.
- 1 2 3 Cambridge Historical Society Proceedings for the years 1953-54.
- 1 2 Moravek 2010.
- ↑ Schlesinger Library, Radcliffe Institute. "Cambridge Plant and Garden Club. Records, 1889-1991: A Finding Aid".
- ↑ "Keezer's". Retrieved June 30, 2014.
- ↑ Robin D. G. Kelley and Earl Lewis, ed. (2005). "Chronology". To Make Our World Anew: a History of African Americans. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-983893-6.
- ↑ J. Leonard, ed. (1914). Woman's Who's Who of America. NY: American Commonwealth Co.
- ↑ "Cambridge Skating Club".
- ↑ Proceedings, 1, Cambridge Historical Society, 1906
- ↑ "Who We Are". Cambridge Historical Society.
- ↑ "Lesley University History". Lesley University. Retrieved August 15, 2011.
- ↑ "Harvard Square Business Association Archives". Harvard Square Business Association. Retrieved August 14, 2013.
- ↑ Report of the Cambridge Housing Association, 1913
- ↑ "Big Bang at Lechmere", Boston Globe, June 2, 1989
- 1 2 Stephen Kaiser (February 10, 2014), Creation of the Community Development Department: A Brief History, Cambridge Community Television
- ↑ "MIT facts". MIT. Retrieved August 15, 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Robertson 2012.
- 1 2 3 "Movie Theaters in Cambridge, MA". CinemaTreasures.org. Los Angeles: Cinema Treasures LLC. Retrieved August 11, 2013.
- ↑ "Mac-Gray is Cleaning Up in World of Wash and Dry", Boston Globe, May 16, 2006
- ↑ "History". Cambridge Community Center.
- ↑ Sloan School. "Timeline". MIT Course XV Centennial. MIT. Retrieved June 30, 2014.
- ↑ "Magazine of Cambridge, Cambridge, Mass.: Cambridge Chamber of Commerce, 1941-1973". WorldCat.
- ↑ "Civic Unity Committee", Cambridge Civic Journal, Robert Winters, 2011
- ↑ Irving House at Harvard
- ↑ Karl L. Wildes; Nilo A. Lindgren (1985). A Century of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at MIT, 1882-1982. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-23119-0.
- 1 2 "Organizations". International Relations and Security Network. Switzerland: Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule Zürich. Retrieved March 10, 2014.
- ↑ Cheapo Records
- ↑ "Hong Kong Restaurant Celebrates 60th Anniversary", Harvard Crimson, February 24, 2014
- ↑ "Elsie's Tradition Endures in Falmouth", The Crimson, October 18, 1983
- ↑ Mincer, Shifra B. (October 6, 2006). "Camera Shop Shutters, Its Long Kodak Moment Over". The Harvard Crimson.
- ↑ Pluralism Project. "Buddhism in America". America's Many Religions: Timelines. Harvard University. Retrieved October 4, 2013.
- ↑ "Pangloss Bookstore". Harvard Crimson. December 13, 1957. Retrieved August 14, 2013.
- 1 2 Club Passim: 50 Years Of Folk Legends, USA: National Public Radio, August 2008
- ↑ "Cambridge dumpling festival a tribute to Joyce Chen", Boston Globe, September 29, 2014
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Timeline: Building Smarter Machines", New York Times, June 24, 2010
- ↑ "Julia Child". Britannica.com. Retrieved August 15, 2011.
- 1 2 Pluralism Project. "Cambridge, Massachusetts". Directory of Religious Centers. Harvard University. Retrieved August 14, 2013.
- ↑ Harvard University Archives. "Records of the Cambridge Electron Accelerator: an inventory". Harvard University. Retrieved August 14, 2013.
- ↑ "About CSU: Club History". Cambridge Sports Union. Retrieved January 18, 2016.
- ↑ "About the Historical Commission". City of Cambridge. Retrieved August 15, 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 Boston Globe 2014.
- 1 2 "Affiliated Organizations". First Parish in Cambridge.
- ↑ Harvard Crimson, December 2, 1968
- ↑ Mitchell K. Hall (2008). "Chronology". Historical Dictionary of the Nixon-Ford Era. Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-0-8108-6410-8.
- 1 2 Mike Tigas; Sisi Wei (eds.). "Cambridge, Massachusetts". Nonprofit Explorer. New York: ProPublica. Retrieved March 10, 2014.
- ↑ Harvard Crimson, October 7, 1970
- ↑ "About Us: History". Greater Boston Legal Services.
- ↑ "About". Broadway Bicycle School. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- ↑ "A Woman Without A Bicycle Is Like A Fish Without A Man?", The Crimson, 1991,
Bicycle Repair Collective
- ↑ Flora Davis (1991), Moving the mountain: the women's movement in America since 1960, Simon & Schuster, ISBN 0671602071
- ↑ "Harvest Co-op Market (Cambridge)". Iowa: National Cooperative Grocers Association.
- ↑ "Cambridge City Arts Council".
- ↑ Community Development Department, City of Cambridge
- ↑ "Cambridge Naturals".
- ↑ "Cambridge Arts". City of Cambridge.
- ↑ "Stylish New Home for Cambridge Favorite", Boston Globe, January 29, 1987
- ↑ "Formaggio Kitchen". Archived from the original on August 18, 2007.
- ↑ "About pika". Cambridge: pika. Retrieved October 25, 2013.
- ↑ American Academy of Arts and Sciences. "Historical notes". Retrieved August 15, 2011.
- ↑ "About Cambridge College". Archived from the original on June 18, 2003.
- ↑ "The Most Powerful Man in Cambridge", Harvard Crimson, May 24, 2012, retrieved April 30, 2014
- ↑ "How Cambridge became the life sciences capital", Boston Globe, March 17, 2016
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Cambridge Peace Commission (2008). "Information on Cambridge's Sister Cities". City of Cambridge. Archived from the original on February 2, 2015. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- 1 2 MIT 2011.
- ↑ "Think Tank Directory". Philadelphia, USA: Foreign Policy Research Institute. Retrieved March 10, 2014.
- 1 2 "Boards and Commissions Directory". City of Cambridge. Retrieved August 14, 2013.
- ↑ "Cultural Center: a Slice of Italy", Boston Globe, June 17, 1985
- ↑ Associated Press (September 25, 2016), "MIT's Flea Market Specializes in Rare, Obscure Electronics", New York Times
- 1 2 "Looking to strengthen family ties with `sister cities'", Boston Globe, October 12, 2008, (Subscription required (help))
- ↑ "Member Cities". International Association of Peace Messenger Cities. Retrieved July 23, 2013.
- ↑ "CCTV newsletter". January 2002.
- ↑ Boston Dynamics Inc., archived from the original on December 2, 1998
- ↑ "Motor Mouths", Boston Globe, January 12, 2005
- ↑ Community Development Department, Master Plan and Growth Policy, City of Cambridge
- ↑ "House of Representatives of the General Court of Massachusetts". Public Officers of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. 1993.
- ↑ "50 Best Restaurants", Boston Magazine, October 2014
- ↑ "Tech Speak", Boston Globe, February 10, 1995
- ↑ "New club in Central Square", Boston Globe, November 23, 1995
- ↑ On the Rise, archived from the original on May 1, 2001
- ↑ "City Dance Party". News. City of Cambridge. Retrieved June 30, 2014.
- ↑ "Dance party to take over Cambridge street", Boston Globe, May 29, 2015
- ↑ "Cambridge, MA - Official Web Site". Archived from the original on February 1997 – via Internet Archive, Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Issues". Cambridge Civic Journal. Robert Winters. Retrieved July 23, 2013.
- ↑ Center for Reflective Community Practice, MIT, archived from the original on June 9, 2004
- ↑ "Massachusetts". Official Congressional Directory. Washington DC: Government Printing Office. 1999–2000.
- 1 2 "Boston Turkish Festival". 2010.
- ↑ https://www.cambridgema.gov/Water/wateroperationsdivision/watertreatment.aspx
- ↑ Harvard Crimson 2002.
- ↑ Ross, Casey (2010-10-27). "Novartis doubles plan for Cambridge". Boston Globe.
- ↑ "About Us". Cambridge: Longwood Players, Inc. Retrieved October 26, 2013.
- ↑ "Member Directory". Eastern Massachusetts Association of Community Theatres. Retrieved October 26, 2013.
- ↑ "About CCSC". Retrieved August 15, 2011.
- ↑ "How to Pump Young Democrats’ Energy and Money into the Political Process", Boston Phoenix, 2004-06-28
- ↑ Cambridge Somerville Resource Guide
- ↑ "Happy Tenth Birthday, Facebook", Boston Magazine, February 4, 2014
- ↑ Cambridge Local First
- ↑ "Senate of the General Court of Massachusetts". Public Officers of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. 2007.
- ↑ "Massachusetts Senatorial Districts — 2002". Secretary of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Retrieved July 30, 2014.
- ↑ Green Decade Cambridge
- ↑ "About". Microsoft New England Research & Development Center. Microsoft Corporation.
- ↑ "General Court Senatorial Districts, with Senators for 2007-2008". Massachusetts General Court. Archived from the original on August 1, 2008.
- ↑ "History". Alliance of Cambridge Tenants.
- ↑ "Business Directory". Cambridge Local First. Retrieved May 30, 2015.
- ↑ "Central Square Theater". Retrieved April 30, 2014.
- ↑ City Manager. "Annual Report 2009/2010". City of Cambridge. Retrieved August 14, 2013.
- ↑ Cambridge Day, November 13, 2009
- ↑ "Cambridge (city), Massachusetts". State & County QuickFacts. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved April 30, 2014.
- ↑ "Largest Urbanized Areas With Selected Cities and Metro Areas (2010)". US Census Bureau. 2012.
- ↑ "General Court Massachusetts Senatorial Districts, with Senators for 2009-2010". Massachusetts General Court. Archived from the original on August 6, 2010.
- ↑ Harris, Patricia; Lyon, David (2012). Food Lovers' Guide to Boston: The Best Restaurants, Markets & Local Culinary Offerings. Globe Pequot Press. p. 279. ISBN 978-0762788880. Retrieved 2013-09-12.
- ↑ Chen, Jialu (October 12, 2011). "Vegetarian diner food reaches for the stars". The Boston Globe. NY Times Co. Retrieved 2013-01-21.
- ↑ "The Sinclair", Harvard Crimson, February 7, 2013
- ↑ Scott Kirsner (May 24, 2015), "What’s next for Kendall Square?", Boston Globe
- ↑ "Open Data Policies at Work". Washington DC: Sunlight Foundation. Archived from the original on October 22, 2013.
- ↑ Saul Tannenbaum, ed. (March 7, 2013), Cambridge Happenings, retrieved April 30, 2014 – via Paper.li
- ↑ "Manhunt Underway, Boston Under Lockdown", The Atlantic, April 19, 2013
- ↑ Civic Impulse, LLC. "Members of Congress". GovTrack. Washington, D.C. Archived from the original on April 12, 2014.
- ↑ "Ballotpedia". Lucy Burns Institute. Retrieved July 30, 2014.
- ↑ Saul Tannenbaum (June 8, 2014). "City Launches Portal Providing Access to City Datasets". Cambridge Community Television.
Socrata
- ↑ "Munch Madness 2015", Boston Globe, retrieved 26 March 2015
- ↑ Firefighters battle major fire in Cambridge, Massachusetts, Reuters, December 3, 2016
Bibliography
Published in the 19th century
- 1800s-1840s
- Abiel Holmes (1801), History of Cambridge, Boston: Samuel Hall
- "Cambridge". Edinburgh Gazetteer. Edinburgh. 1822.
- Jedidiah Morse; Richard C. Morse (1823), "Cambridge", A New Universal Gazetteer (4th ed.), New Haven: S. Converse
- William Darby; Theodore Dwight Jr. (1834), "Cambridge", New gazetteer of the United States of America (2nd ed.), Hartford: E. Hopkins
- City of Cambridge, Annual Report
- Cambridge Directory ... for 1848.
- 1850s-1870s
- John Hayward (1857), "Cambridge, Ms.", New England Gazetteer (2nd ed.), Boston: Otis Clapp, OCLC 3441657
- Charter and Ordinances of the City of Cambridge. Riverside Press. 1871.
- Revised Ordinances of 1889 of the City of Cambridge. Cashman, Keating & Co. 1890.
- Dean Dudley (1872). Cambridge Directory. Cambridge.
- Cambridge Directory for 1873. Boston: Greenough, Jones & Co.
- Griffith Morgan Hopkins (1873). Atlas of the City of Cambridge. Philadelphia: G.M. Hopkins & Co. – via Harvard University. 1886 ed.
- Annual Report of the City Engineer, City of Cambridge. 1875-
- Cambridge in the 'Centennial': Proceedings, July 3, 1875, in Celebration of the Centennial Anniversary of Washington's Taking Command of the Continental Army. City Council. 1875.
- Greenough's Cambridge Directory. Boston: Greenough & Co.
- Lucius R. Paige (1877), History of Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1630-1877, Boston: H.O. Houghton and Company, OCLC 1305589
- 1880s-1890s
- Samuel Adams Drake (1880), History of Middlesex County, Massachusetts, Boston: Estes and Lauriat
- Exercises in celebrating the two hundred and fiftieth anniversary of the settlement of Cambridge, held December 28, 1880, Cambridge, Mass.: University Press, John Wilson & Son, 1881
- (Cambridge and parts of Somerville). Boston, Massachusetts. 6. New York: Sanborn Map and Publishing Co. 1888 – via Harvard University.
- George F. Crook, ed. Cambridge annual for 1886-1888.
- Blue Book of Cambridge for 1892.
- Gossiping Guide to Harvard and Places of Interest in Cambridge, Cambridge, Mass.: Cambridge Tribune, 1892, OCLC 4571172
- Park Commission, Annual Report, City of Cambridge 1894- . 1890s
- Atlas of the City of Cambridge. Philadelphia: G.W. Bromley and Co. – via Harvard University.. 1894?
- Blue Book of Cambridge for 1895.
- Arthur Gilman (1896), Cambridge of Eighteen Hundred and Ninety-Six, Cambridge: Riverside Press
- Walter Gee Davis, ed. (1897), Cambridge Fifty Years a City, 1846-1896, Cambridge: Riverside Press, OCLC 911131
- John Wesley Freese (1897), Historic Houses and Spots in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and Near-By Towns, Boston: Ginn & Company, OCLC 1821792
- Thomas Wentworth Higginson (1899), Old Cambridge, New York: Macmillan Company, OCLC 2220162
Published in the 20th century
- Insurance Maps of Cambridge, Mass. New York: Sanborn-Perris Map Company. 1900 – via Harvard University.
- Records of the Town of Cambridge (Formerly New-Towne) Massachusetts, 1630-1703, Cambridge, 1901
- Atlas of the City of Cambridge. Philadelphia: G.W. Bromley and Co. 1903 – via Harvard University. 1916 ed.
- Robert F. Roden (1905), The Cambridge Press, 1638-1692, NY: Dodd, Mead, and Company
- Massachusetts Daughters of the American Revolution, Hannah Winthrop Chapter, Cambridge (1907), An Historic Guide to Cambridge, Cambridge, Mass., OCLC 3292475
- "Cambridge", United States (4th ed.), Leipzig: K. Baedeker, 1909, OCLC 02338437
- "Cambridge", Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.), New York, 1910, OCLC 14782424 – via Internet Archive
- Cambridge Directory. Boston: Greenough & Co. 1910.
- Samuel A. Eliot (1913), A History of Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1630-1913, Cambridge, Mass.: Cambridge Tribune, OCLC 6876563
- Atlas of the City of Cambridge. G.W. Bromley & Co. 1930 – via State Library of Massachusetts.
- Norman Hill White Jr. (1931), Proceedings for the Years 1920 and 1921, Publications, 15, Cambridge Historical Society,
Printing in Cambridge Since 1800
- Federal Writers' Project (1937), "Cambridge", Massachusetts: a Guide to its Places and People, American Guide Series, Boston: Houghton Mifflin + Chronology
- Survey of Architectural History in Cambridge: Northwest Cambridge, Cambridge Historical Commission, 1977, ISBN 0-262-53032-5
- Police Department, Annual Crime Report, City of Cambridge 1995- 2004-present
- "Cambridge". Historical Data Relating to Counties, Cities and Towns in Massachusetts. Boston: New England Historic Genealogical Society. 1997. pp. 28–29. (Timeline of boundary changes)
- "Commonwealth Communities: City of Cambridge". Commonwealth of Massachusetts Official Website. Archived from the original on 1998.
- Anthony Mitchell Sammarco (1999), Cambridge, Arcadia Publishing, OL 7981887M
Published in the 21st century
- "Timeline: 1972-1976", Harvard Crimson, June 5, 2001
- "Timeline 2001-2002", Harvard Crimson, June 6, 2002
- Natalie Moravek (2010), "Walking Tour", William James' Cambridge, Cambridge Historical Society
- "MIT Timeline". MIT 150. Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 2011.
- Rain Robertson (2012). "Cambridge's Culinary Culture". Cambridge Historical Society.
- "A Kendall Square Timeline", Boston Globe, February 2, 2014
- Saul Tannenbaum (February 21, 2014), The Case for Municipal Broadband in Cambridge, NeighborMedia, Cambridge Community Television
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to History of Cambridge, Massachusetts. |
- "Cambridge (Mass.)". Boston TV News Digital Library. WBGH. 1960s-2000
- "Local Media Map". Cambridge Community Television.
Local stories mapped right down to the street corner where they take place
- MIT Media Lab (2014). "Cambridge Biking Accidents". You Are Here.
2010-2013
(map) - "Cambridge Room (blog)". Cambridge Public Library.
- Items related to Cambridge, various dates (via Digital Public Library of America).
- "Town Guides: Massachusetts: Cambridge". New England Historic Genealogical Society.
Images
 George Washington in Cambridge, 1775
George Washington in Cambridge, 1775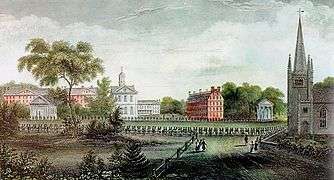 Harvard alumni procession, Harvard Square, 1836
Harvard alumni procession, Harvard Square, 1836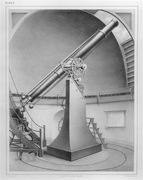 Cambridge Observatory, 1849
Cambridge Observatory, 1849 Harvard Square, ca.1880s-1900s
Harvard Square, ca.1880s-1900s Washington Elm, Cambridge Common, ca.1880s-1900s
Washington Elm, Cambridge Common, ca.1880s-1900s Cambridge Public Library, 1891
Cambridge Public Library, 1891 Central Square and Mass. Ave., 1910s
Central Square and Mass. Ave., 1910s Overview of Harvard Square area, 1919
Overview of Harvard Square area, 1919 Harvard Bridge and MIT, ca.1920
Harvard Bridge and MIT, ca.1920
Coordinates: 42°22′25″N 71°06′38″W / 42.373611°N 71.110556°W
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.
