Tilmicosin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
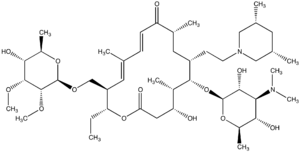
| IUPAC name
[(2R,3R,4E,6E,9R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-12-{[3,6-Dideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-β-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy}-11-{2-[(3R,5S)-3,5-dimethylpiperidin-1-yl]ethyl}-2-ethyl-14-hydroxy-5,9,13-trimethyl-8,16-dioxooxacyclohexadeca-4,6-dien-3-yl]methyl 6-deoxy-2,3-di-O-methyl-β-D-allopyranoside | |
| Other names
Micotil; 20-Deoxy-20-(3,5-dimethylpiperidin-1-yl)-desmycosin[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.167.324 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C46H80N2O13 | |
| Molar mass | 869.15 g·mol−1 |
| 566 mg/mL[1] | |
| Pharmacology | |
| QJ01FA91 (WHO) | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tilmicosin is a macrolide antibiotic. It is used in veterinary medicine for the treatment of bovine respiratory disease and enzootic pneumonia caused by Mannheimia (Pasteurella) haemolytica in sheep.[2] In humans, Tilmicosin causes fatal cardiotoxic effects at amounts greater than 1 milliliter when injected, something most commonly seen in veterinary personnel and farmers. [3]
References
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.