Ticlopidine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ticlid |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a695036 |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | >80% |
| Protein binding | 98% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life |
12 hours (single dose) 4–5 days (repeated dosing) |
| Excretion | Renal and fecal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.054.071 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
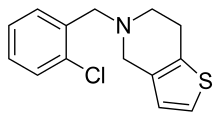
| Formula | C14H14ClNS |
| Molar mass | 263.786 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Ticlopidine (trade name Ticlid) is an antiplatelet drug in the thienopyridine family which is an adenosine diphosphate (ADP) receptor inhibitor. Research initially showed that it was useful for preventing strokes and coronary stent occlusions. However, because of its rare but serious side effects of neutropenia and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura it was primarily used in patients in whom aspirin was not tolerated, or in whom dual antiplatelet therapy was desirable. With the advent of newer and safer antiplatelet drugs such as clopidogrel and ticagrelor, its use remained limited.
History
Ticlopidine was discovered incidentally in the 1970s while trying to develop a new anti-inflammatory medication. Pharmacology developers noted that this new compound had strong anti-platelet properties. In 1978 it began to be marketed in France for patients at high risk for thrombotic events: postoperative cardiac patients, patients undergoing hemodialysis, peripheral vascular disease, and the prevention of strokes and ischemic heart disease.[1]
Ticlopidine was introduced to the United States under the trade name Ticlid by Roche after it was FDA approved in 1991.[2] The first generic ticlopidine hydrochloride was FDA approved in 1999.[3] As of April 2015, Roche, Caraco, Sandoz, Par, Major, Apotex, and Teva had discontinued generic ticlopidine and no ticlopidine preparations were available in the US.[4]
Medical uses
Ticlopidine is FDA approved for the prevention of strokes and, when combined with aspirin, for patients with a new coronary stent to prevent closure. There are also several off-label uses, including acute treatment of myocardial infarction and unstable angina, peripheral vascular disease, prevention of myocardial infarctions, diabetic retinopathy, and sickle cell disease.
Stroke
Ticlopidine is considered a second-line option for the prevention of thrombotic strokes among patients who have previously had a stroke or TIA. Studies have shown that it is superior to aspirin in the prevention of death or future strokes. However, it also has more frequent and serious side effects compared to aspirin, so it is reserved for those patients that cannot take aspirin.[5]
Heart disease
When a patient needs to have a stent placed in one of the vessels around their heart, it is important that that stent stay open to keep blood flowing to the heart. Therefore, patients with stents must take medications after the procedure to help maintain that blood flow. Ticlopidine, taken together with aspirin, is FDA approved for this purpose, and in studies it has been shown to work better than aspirin alone or aspirin with an anticoagulant.[6][7] However, ticlopidine’s serious side effects make it less useful than its cousin, clopidogrel. Current recommendations no longer recommend ticlopidine’s use.[8]
Research
Soon after its release, studies regarding ticlopidine found it had the potential to be helpful for other diseases including peripheral vascular disease,[9] diabetic retinopathy,[10] and sickle cell disease.[11] However none had enough evidence for FDA approval. Due to the blood cell side effects associated with ticlopidine, researchers for treatments for these conditions have turned to other avenues.
Adverse effects
The most serious side effects associated with ticlopidine are those that affect the blood cells, although these life-threatening complications are relatively rare. The most common side effects include:[12]
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Dyspepsia
- Rash
- Abdominal pain
Ticlopidine may also cause an increase in cholesterol, triglycerides, liver enzymes, and bleeding.[12]
Hematological
Use of ticlopidine has been associated with neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), and aplastic anemia. Because of this risk, patients who are started on ticlopidine are typically monitored with blood tests to test their cell counts every two weeks for the first three months.[12]
Contraindications
The use of ticlopidine is contraindicated in anyone with:
- Increased risk of bleeding (i.e. frequent falls, gastrointestinal bleeds)
- History of hematological disease
- Severe liver disease
- History of allergic reaction to ticlopidine or any thienopyridine drug such as clopidogrel
Because of the increased risk of bleeding, patients taking ticlopidine should discontinue the medication 10–14 days before surgery.[12]
Pregnancy and lactation
Ticlopidine is a FDA pregnancy risk category B. There have been no studies done in humans. Studies in rats show that high drug levels could cause toxicity in both mother and fetus, but there are no known birth defects associated with its use.[12]
There have been no studies to test whether ticlopidine goes into breast milk. Studies in rats have shown that it is passed in rats’ milk.[12]
Mechanism of action
Ticlopidine is a thienopyridine which, when metabolized by the body, irreversibly blocks the ADP receptor on the surface of platelets. Without ADP, fibrinogen does not bind to the platelet surface, preventing platelets from sticking to each other.[12] By interfering with platelet function, ticlopidine prevents clots from forming on the inside of blood vessels.[13] Anti-platelet effects start within 2 days and reach their maximum by 6 days of therapy. Ticlopidine’s effects persist for 3 days after discontinuing ticlopidine although it may take 1–2 weeks for platelet function to return to normal, as the medication affects platelets irreversibly. Therefore, new platelets must be formed before platelet function normalizes.[12]
Pharmacokinetics
Ticlopidine is ingested orally with 80% bioavailability with rapid absorption. Even higher absorption can occur if ticlopidine is taken with food. It is metabolized by the liver with both renal and fecal elimination. Clearance is nonlinear and varies with repeated dosing. After the first dose the half life is 12.6 hours, but with repeated dosing the maximum half life is 4–5 days. Clearance is also slower in the elderly. The drug is 98% reversibly bound to proteins.[12]
Drug-drug interactions
Ticlopidine interacts with several classes of medications. It increases the antiplatelet effects of aspirin and other NSAIDs.[12] Taking ticlopidine at the same time as antacids decreases the absorption of ticlopidine.[12] Ticlopidine inhibits liver CYP2C19[14] and CYP2B6[15] and thus can affect blood levels of medications metabolized by these systems.
Chemical properties
Ticlopidine's systemic name is 5-[(2-chlorophenyl)methyl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine. Its molecular weight is 263.786 g/mol. It is a white crystalline solid. It is soluble in water and methanol and somewhat soluble in methylene chloride, ethanol, and acetone. It self buffers in water to a pH of 3.6.[12]
References
- ↑ Maffrand, JP (2012). "The story of clopidogrel and its predecessor, ticlopidine: Could these major antiplatelet and antithrombotic drugs be discovered and developed today?". Comptes Rendus Chimie. 15 (8): 737–743. doi:10.1016/j.crci.2012.05.006.
- ↑ "Ticlid". Drugs@FDA. US Food & Drug Administration. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ↑ "Press release: Apotex First To Market Generic Version Of Ticlid®". July 6, 1999.
- ↑ "Ticlopidine Tablets". Resolved Shortages Bulletin. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. April 1, 2015. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ↑ Hass WK, Easton JD, Adams HP Jr, Pryse-Phillips W, Molony BA, Anderson S, Kamm B (24 August 1989). "A randomized trial comparing ticlopidine hydrochloride with aspirin for the prevention of stroke in high-risk patients. Ticlopidine Aspirin Stroke Study Group". N Engl J Med. 321: 501–507. PMID 2761587. doi:10.1056/nejm198908243210804.
- ↑ Schomig L, Neumann FJ, Kastrati A, et al. (1996). "A randomized comparison of antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapy after the placement of coronary-artery stents". N Engl J Med. 334: 1084–1089. PMID 8598866. doi:10.1056/nejm199604253341702.
- ↑ Leon MB1, Baim DS, Popma JJ, Gordon PC, Cutlip DE, Ho KK, Giambartolomei A, Diver DJ, Lasorda DM, Williams DO, Pocock SJ, Kuntz RE (3 December 1993). "A clinical trial comparing three antithrombotic-drug regimens after coronary-artery stenting. Stent Anticoagulation Restenosis Study Investigators". N Engl J Med. 339: 1665–1671. PMID 9834303. doi:10.1056/nejm199812033392303.
- ↑ American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (2014). "2014 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Management of Patients With Non–ST-Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes". Circulation. 130 (25): e344–426. PMID 25249585. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000134.
- ↑ Kirstein P, Jogestrand T, Johnsson H, et al. (1980). "Antiaggregatory, physiological and clinical effects of ticlopidine in subjects with peripheral atherosclerosis". Atherosclerosis. 36: 471–480. doi:10.1016/0021-9150(80)90240-3.
- ↑ The TIMAD Study Group (1990). "Ticlopidine treatment reduces the progression of nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy". Arch Ophthalmol. 108: 1577. doi:10.1001/archopht.1990.01070130079035.
- ↑ Cabannes R, Lonsdorfer J, Castaigne JP, et al. (1984). "Clinical and biological double-blind study of ticlopidine in preventive treatment of sickle cell disease crises". Agents Actions.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Roche Laboratories, Inc. (2001). "Ticlid (ticlopidine) package insert" (PDF). US Food & Drug Administration.
- ↑ Katzung B, Masters S, Trevor A (2012). Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, 12th ed. pp. Chapter 34: Drugs Used in Disorders of Coagulation.
- ↑ Ha-Duong NT, Dijols S, Macherey, AC (2001). "Ticlopidine as selective mechanism-based inhibitor of human cytochrome P450 2C19". Biochemistry. 40: 12112–12122. doi:10.1021/bi010254c.
- ↑ Turpeinen M, Tolonen A, Uusitalo J, et al. (2005). "Effect of clopidogrel and ticlopidine on cytochrome P450 2B6 activity as measured by bupropion hydroxylation". Clin Pharmacol Ther. 77: 553–559. doi:10.1016/j.clpt.2005.02.010.