Tholeiitic magma series
The tholeiitic magma series, named after the German municipality of Tholey, is one of two main magma series in igneous rocks, the other magma series being the calc-alkaline. A magma series is a series of compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic magma, which is high in magnesium and iron and produces basalt or gabbro. The International Union of Geological Sciences recommends that tholeiitic basalt be used in preference to the term "tholeiite" (Le Maitre and others, 2002).
Geochemical characterization
Rocks in the tholeiitic magma series are classified as subalkaline (they contain less sodium than some other basalts) and are distinguished from rocks in the calc-alkaline magma series by the redox state of the magma they crystallized from (tholeiitic magmas are reduced; calc-alkaline magmas are oxidized). When the parent magmas of basalts crystallize, they preferentially crystallize the more magnesium-rich and iron-poor forms of the silicate minerals olivine and pyroxene, causing the iron content of tholeiitic magmas to increase as the melt is depleted of iron-poor crystals. However, a calc-alkaline magma is oxidized enough to precipitate significant amounts of the iron oxide magnetite, causing the iron content of the magma to remain more steady as it cools than with a tholeiitic magma.
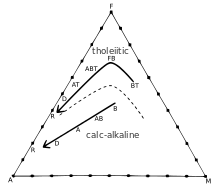
The difference between these two magma series can be seen on an AFM diagram, a ternary diagram showing the relative proportions of the oxides Na2O + K2O (A), FeO + Fe2O3 (F), and MgO (M). As magmas cool, they precipitate out significantly more iron and magnesium than alkali, causing the magmas to move towards the alkali corner as they cool. In the tholeiitic magma, as it cools and preferentially produces magnesium-rich crystals, the magnesium content of the magma plummets, causing the magma to move away from the magnesium corner until it runs low on magnesium and simply moves towards the alkali corner as it loses iron and any remaining magnesium. With the calc-alkaline series, however, the precipitation of magnetite causes the iron-magnesium ratio to remain relatively constant, so the magma moves in a straight line towards the alkali corner on the AFM diagram.
Petrography


Like all basalt, the rock type is dominated by clinopyroxene plus plagioclase, with minor iron-titanium oxides.[1] Orthopyroxene or pigeonite may also be present in tholeiitic basalt, and olivine, if present, may be rimmed by either of these calcium-poor pyroxenes. Tridymite or quartz may be present in the fine-grained groundmass of tholeiitic basalt, and feldspathoids are absent. Tholeiitic rocks may have a fine, glassy groundmass, as may other types of basalt.
Geologic context
Basalt magmas are partial melts of peridotite (olivine and pyroxene) produced by decompression melting in the Earth's mantle, a process described for igneous rocks. Tholeiitic basalts are the most common volcanic rocks on Earth, as they are produced by submarine volcanism at mid-ocean ridges and make up much of the ocean crust. MORB, the acronym for typical mid-ocean-ridge basalt, is a type of tholeiitic basalt particularly low in incompatible elements. In contrast, alkali basalt is not typical at ocean ridges, but is erupted on some oceanic islands and on continents, as also is tholeiitic basalt.[1] Because the Moon is extremely reduced, all of its basalt is tholeiitic.
See also
References
- R. W. Le Maitre (editor), A. Streckeisen, B. Zanettin, M. J. Le Bas, B. Bonin, P. Bateman, G. Bellieni, A. Dudek, S. Efremova, J. Keller, J. Lamere, P. A. Sabine, R. Schmid, H. Sorensen, and A. R. Woolley, Igneous Rocks: A Classification and Glossary of Terms, Recommendations of the International Union of Geological Sciences, Subcommission of the Systematics of Igneous Rocks. Cambridge University Press, 2002. ISBN 0-521-66215-X
- American Geological Institute. Dictionary of Geological Terms. New York: Dolphin Books, 1962.