Thioflavin
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-(3,6-dimethyl-1,3-benzothiazol-3 | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.482 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H19ClN2S | |
| Molar mass | 318.86 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Thioflavins are dyes used for histology staining and biophysical studies of protein aggregation.[1] They are also used in biophysical studies of the electrophysiology of bacteria.[2]
Thioflavin T
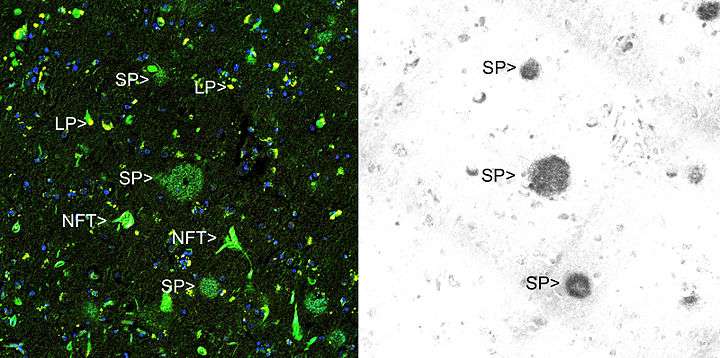
Thioflavin T (Basic Yellow 1 or CI 49005) is a benzothiazole salt obtained by the methylation of dehydrothiotoluidine with methanol in the presence of hydrochloric acid. The dye is widely used to visualize and quantify the presence of misfolded protein aggregates called amyloid, both in vitro and in vivo (e.g., plaques composed of amyloid beta found in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients).[1]
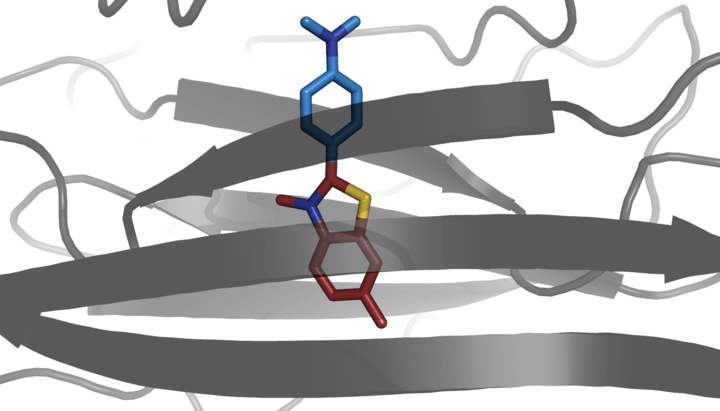
When it binds to beta sheet-rich structures, such as those in amyloid aggregates, the dye displays enhanced fluorescence and a characteristic red shift of its emission spectrum.[3][4] Additional studies also consider fluorescence changes as result of the interaction with double stranded DNA.[5] This change in fluorescent behavior can be caused by many factors that affect the excited state charge distribution of thioflavin T, including binding to a rigid, highly-ordered nanopocket, and specific chemical interactions between ThT and the nanopocket.[6][7]
Thioflavin T fluorescence is often used as a diagnostic of amyloid structure, but it is not perfectly specific for amyloid. Depending on the particular protein and experimental conditions, thioflavin T may[6] or may not[8][9] undergo a spectroscopic change upon binding to precursor monomers, small oligomers, unaggregated material with a high beta sheet content, or even alpha helix-rich proteins. Conversely, some amyloid fibers do not affect thioflavin T fluorescence,[10] raising the prospect of false negative results.
In adult C. elegans, exposure to thioflavin T results "in a profoundly extended lifespan and slowed aging" at some levels, but decreased lifespan at higher levels.[11]
Thioflavin S
Thioflavin S is a homogenous mixture of compounds that results from the methylation of dehydrothiotoluidine with sulfonic acid. It is also used to stain amyloid plaques. Like thioflavin T it binds to amyloid fibrils but not monomers and gives a distinct increase in fluorescence emission. However unlike thioflavin T, it does not produce a characteristic shift in the excitation or emission spectra.[3] This latter characteristic of thioflavin S results in high background fluorescence, making it unable to be used in quantitative measurements of fibril solutions.[3] Another dye that is used to identify amyloid structure is Congo Red.
References
- 1 2 M. Biancalana; S. Koide (July 2010). "Molecular mechanism of Thioflavin-T binding to amyloid fibrils". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1804 (7): 1405–1412. PMC 2880406
 . PMID 20399286. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.04.001.
. PMID 20399286. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.04.001. - ↑ Prindle; et al. (2015). "Ion channels enable electrical communication in bacterial communities". Nature. 527 (7576): 59–63. PMC 4890463
 . PMID 26503040. doi:10.1038/nature15709.
. PMID 26503040. doi:10.1038/nature15709. - 1 2 3 H. LeVine III, Methods in Enzymology. 309, 274 (1999)
- ↑ Groenning, M.; et al. (2010). "Binding mode of Thioflavin T and other molecular probes in the context of amyloid fibrils—current status.". J. Chem. Bio. 3 (1): 1–18. doi:10.1007/s12154-009-0027-5.
- ↑ Ilanchelian, M.; et al. (2004). "Emission of thioflavin T and its control in the presence of DNA". Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry. 162 (1): 129–137. doi:10.1016/s1010-6030(03)00320-4.
- 1 2 3 Wolfe, L.S.; et al. (2010). "Protein-induced photophysical changes to the amyloid indicator dye thioflavin T". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107 (39): 16863–8. PMC 2947910
 . PMID 20826442. doi:10.1073/pnas.1002867107.
. PMID 20826442. doi:10.1073/pnas.1002867107. - ↑ Biancardi, A.; et al. (2017). "Fluorescent dyes in the context of DNA-binding: The case of Thioflavin T". Int. J. Q. Chem. 117 (8): e25349. doi:10.1002/qua.25349.
- ↑ H. LeVine III (1993) Prot. Sci. 2, 404
- ↑ H. LeVine III, (1995) Amyloid Int. J. Exp. Clin. Invest. 2, 1
- ↑ Cloe, A.L.; et al. (2011). "The Japanese Mutant Aβ (ΔE22-Aβ1-39) Forms Fibrils Instantaneously, with Low-Thioflavin T Fluorescence: Seeding of Wild-Type Aβ1-40 into Atypical Fibrils by ΔE22-Aβ1-39". Biochemistry. 50 (12): 2026–2039. doi:10.1021/bi1016217.
- ↑ Alavez S. et al, (2011). Amyloid-binding compounds maintain protein homeostasis during ageing and extend lifespan Nature