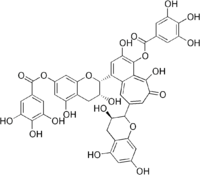
Theaflavin digallate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[1-[(2R,3R)-3,5-Dihydroxy-7-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)oxychroman-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-6-oxo-8-[(3R)-3,5,7-trihydroxychroman-2-yl]benzo[7]annulen-4-yl] 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate | |
| Other names
TFDG TF-3 Theaflavin-3,3'-digallate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C43H32O20 | |
| Molar mass | 868.71 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Theaflavin digallate (TFDG) is an antioxidant natural phenol found in black tea, and a theaflavin derivative.
Health
- TFDG is a scavenger of superoxide in vitro, even more so than EGCG.[1]
- Tea polyphenols including TFDG reduce angiogenesis, which is implicated in non-liquid cancers, an area of intense current research, by decreasing vascular endothelial growth factor production and receptor phosphorylation.
- TFDG inhibits activity of the enzyme 3CLPro in vitro.[2]
References
- ↑ Lin, Jen-Kun; Chen, Ping-Chung; Ho, Chi-Tang; Lin-Shiau, Shoei-Yn (2000). "Inhibition of Xanthine Oxidase and Suppression of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species in HL-60 Cells by Theaflavin-3,3'-digallate, (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, and Propyl Gallate". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 48 (7): 2736. PMID 10898615. doi:10.1021/jf000066d.
- ↑ Chia-Nan Chen1, Coney P. C. Lin, Kuo-Kuei Huang, Wei-Cheng Chen, Hsin-Pang Hsieh, Po-Huang Liang and John T.-A. Hsu (2005). "Inhibition of SARS-CoV 3C-like Protease Activity by Theaflavin-3,3'-digallate (TF3)". Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2 (2): 209–215. PMC 1142193
 . PMID 15937562. doi:10.1093/ecam/neh081.
. PMID 15937562. doi:10.1093/ecam/neh081.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.