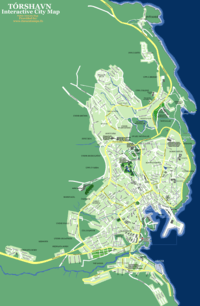
Tórshavn
| Tórshavn | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Tinganes, Tórshavn old town | ||
| ||
| Nickname(s): Havn | ||
 Tórshavn Location in Faroe Islands | ||
| Coordinates: 62°0′42″N 6°46′3″W / 62.01167°N 6.76750°WCoordinates: 62°0′42″N 6°46′3″W / 62.01167°N 6.76750°W | ||
| State |
| |
| Constituent Country |
| |
| Municipality |
| |
| Founded | 10th century | |
| Town rights | 1909 | |
| Government | ||
| • Mayor | Annika Olsen (Fólkaflokkurin) | |
| Area | ||
| • Land | 172.9 km2 (66.8 sq mi) | |
| Elevation | 24 m (79 ft) | |
| Population (2015-01-01) | ||
| • City | 12,648 | |
| • Density | 78/km2 (200/sq mi) | |
| • Metro | 20,015[1] | |
| • Metro density | 125/km2 (320/sq mi) | |
| population-ranking: 1st | ||
| Postal code | FO-100, FO-110 | |
| Climate | Cfc | |
| Website |
www | |
Tórshavn (Faroese pronunciation: [ˈtʰɔuʂhaun]; literally, "Thor's harbour"; Danish: Thorshavn [ˈtoɐ̯ˀshɑwˀn]) is the capital and largest town of the Faroe Islands. Tórshavn is in the southern part on the east coast of Streymoy. To the northwest of the city lies the 347-meter-high (1,138 ft) mountain Húsareyn, and to the southwest, the 350-meter-high (1,150 ft) Kirkjubøreyn. They are separated by the Sandá River. The town proper has a population of 13,000 (2008), and the greater urban area a population of 19,000.
The Norse established their parliament on the Tinganes peninsula in AD 850.[2] Tórshavn thus became the capital of the Faroe Islands and has remained so ever since. All through the Middle Ages the narrow peninsula jutting out into the sea made up the main part of Tórshavn. Early on, Tórshavn became the centre of the islands' trade monopoly, thereby being the only legal place for the islanders to sell and buy goods. In 1856, the trade monopoly was abolished and the islands were left open to free trade.
History
Early history
It is not known whether the site of Tórshavn was of interest to the Celtic monks who were probably the first settlers in the Faroes. The Viking settlers in the 9th century established their own parliaments, called tings, in different parts of the islands, it being the tradition in each case to hold the ting at a neutral and thus uninhabited place, so no one location gave anyone an advantage. The main ting for the islands was convoked in Tórshavn in 825, on Tinganes, the peninsula that divides the harbour into two parts: Eystaravág and Vestaravág. The Vikings would thus meet on the flat rocks of Tinganes every summer, as the most central place on the islands, although there was no settlement at Tinganes at that time. The Færeyinga Saga says: "the place of the ting of the Faroese was on Streymoy, and there is the harbour that is called Tórshavn". The Viking age ended in 1035. The ting was followed by a market which gradually grew into a permanent trading area.
All through the Middle Ages, the narrow peninsula jutting out into the sea made up the main part of Tórshavn. It belonged to the outfield of two farmers. Unlike other Faroese villages, Tórshavn was never a distinct farming community. During the 12th century, all trade between Norway and the Faroes, along with other tributary islands to the west, became centralised in Bergen. In 1271, a royal trade monopoly was established in Tórshavn by the Norwegian Crown. According to a document from 1271, two ships would sail regularly to Tórshavn from Bergen with cargoes of salt, timber and cereal. Tórshavn therefore had more contact with the outside world than did the other villages. Under the Norwegian, and then Danish rule, government officials made Tórshavn their home. All of these things, combined with the fact that Tórshavn was the seat of the ting of the islands, influenced the town’s development.
1500–1800

.jpg)
Sources do not mention a built-up area in Tórshavn until after the Protestant reformation in 1539. In ca. 1580 a small fort, Skansin, was built by the Faroese naval hero and trader Magnus Heinason at the north end of the harbour. Later small fortifications were built at Tinganes.
In 1584 Tórshavn had 101 inhabitants. The population was divided into three equally large groups made up of farmers, their families and servants, trade and government officials and people who owned no land and therefore not much else; this included the landless proletariat from the villages that during this period came to Tórshavn in search of work. They were set to guard duty on Skansin without pay, and for clothing and food they depended on the bounty of the farmers.
In 1655 king Frederick III of Denmark granted the Faroe Islands to his favourite statesman Kristoffer Gabel, the rule of the von Gabel Family, 1655–1709, is known as Gablatíðin. It is the darkest chapter in the history of Tórshavn. Gabel's administration suppressed the islanders in various ways. The trade monopoly was in the family’s hands and it was not designed for the needs of the Faroese people. People across the country brought products into town and had to be satisfied with whatever price they were given. At the same time imported goods were limited and expensive. There came considerable complaints from the islands' inhabitants of unjust treatment by the civil administration in Tórshavn. These not only included the persons in charge of the monopoly trade, but also the bailiff and others. It was during this period, in 1673, that Tinganes was ravaged by a fire after a store of gunpowder kept at Tinganes had blown up. Many old houses burnt to the ground and old Faroese records were lost as were Gabel's documents.
Conditions improved in Tórshavn when the trade monopoly became a royal monopoly in 1709. The royal monopoly was supplied with goods from Copenhagen three times a year. However, in 1709 Tórshavn was hit by a plague of smallpox, killing nearly the entire population. The town had by this time reached a population of 300 and 250 of the inhabitants died. Still, it was during the latter half of the 18th century that Tórshavn started to develop into a small town. This was while Niels Ryberg was in charge of the trade monopoly. From 1768 and during the next 20 years onwards Ryberg was allowed to carry on an entrepot trade which was mainly based on smuggling to England. Because of the French-British conflict there was room for this kind of operation. In Tórshavn his warehouses filled up with goods. Ryberg was the first person who thought of making a financial profit from fishing, which later became the most important economic factor to the islands. He experimented with salted cod and herring but at this point in time nothing much beyond this happened.
Tórshavn Cathedral was first built in 1788 and partly rebuilt in 1865. Since 1990, it has been the seat of the Bishop of the Faroe Islands (in the Church of the Faroe Islands).
1800–present

On 30 March 1808, during the Gunboat War, the Cruizer class brig-sloop HMS Clio entered Tórshavn and briefly captured the fort at Skansin. The fort surrendered without firing a shot as the landing party approached. Clio spiked the fort's eight 18-pounder guns and took all the smaller guns and weapons before leaving. Shortly after 6 May a German privateer who had assumed the name "Baron von Hompesch" plundered the defenseless city and seized the property of the Danish Crown Monopoly. The Admiralty Prize Court, however, refused to condemn it as a lawful prize.

In 1856, free trade came to the Faroe Islands. By opening the islands to the world, it transformed the economy, with Tórshavn at its centre. The farming land was rented to townspeople who could later buy it if they wished. These small plots of land enabled people to keep cows and sheep.
In 1866, Tórshavn's town council was founded. The town has been the capital of the Faroe Islands ever since. Later, in 1909, Tórshavn became a market town with the same municipal charter as Danish market towns.
In 1927, Tórshavn had a modern harbour built. This made it possible for larger ships to berth.[3]
During the British occupation of the Faroe Islands in World War II, Skansin was used as the headquarters of the Royal Navy Command and two 5.5-inch guns used aboard HMS Furious before World War II were deployed.[4]
In 1974, the neighboring villages Hoyvík and Hvítanes were made part of the town area. Later, even more municipalities joined the Tórshavn municipality. In 1978 Kaldbak, in 1997 Argir, in 2001 Kollafjørður, and finally in 2005, Kirkjubøur, Hestur, and Nólsoy.
Politics and government

Tórshavn is the capital of the Faroe Islands, and as such is the seat of the Faroes’ self rule government. The government holds the executive power in local government affairs. Today a part of the government is located on the Tinganes peninsula of Tórshavn, the Prime Minister's office is here and the Ministry of Internal Affairs was here until it was closed in 2013. The other ministries are located in other office buildings in various places in Tórshavn, i.e. the Ministry of Health[5] and the Ministry of Social Affairs[6] are located near the Hospital of the Faroes in Eirargarður, and the Ministry of Finance is located in Argir in a building called Albert Hall on the street Kvíggjartún.[7] The parliament, the Løgting, which was originally located on Tinganes, was relocated to the town square, Vaglið, in 1856.
Climate
Tórshavn features a subpolar oceanic climate (Cfc) with average summer highs around 12 °C (54 °F) and average winter highs around 6 °C (43 °F), and with winter temperatures rarely dropping below freezing, and frequent cloudy skies. Average monthly precipitation is highest in fall and winter, peaking in January, owing to frequent, intense storms crossing the area from the North Atlantic Ocean, while May and June are markedly drier months. Tórshavn is among the cloudiest places in the world, with significant sunshine records at only about 2.4 hours of sunshine per day; however no data exists for places such as the Aleutian Islands or parts of southern Chile, which may have even less sun. Because of the cloudy weather and the ice-free water surrounding Torshavn, its winter temperatures are exceptionally mild for such a northerly location. Summer temperatures are much lower than those found in continental Scandinavia on similar parallels. The temperature amplitude in the period from 1961 to 2010 is a mere 33 °C (59 °F) between the absolute warmest and coldest temperatures.
| Climate data for Tórshavn (1981–2010, extremes 1961–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 11.6 (52.9) |
12.0 (53.6) |
12.3 (54.1) |
18.3 (64.9) |
19.7 (67.5) |
20.0 (68) |
20.2 (68.4) |
22.0 (71.6) |
19.5 (67.1) |
15.2 (59.4) |
14.7 (58.5) |
13.2 (55.8) |
22.0 (71.6) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 5.8 (42.4) |
5.6 (42.1) |
6.0 (42.8) |
7.3 (45.1) |
9.2 (48.6) |
11.1 (52) |
12.8 (55) |
13.1 (55.6) |
11.5 (52.7) |
9.3 (48.7) |
7.2 (45) |
6.2 (43.2) |
8.8 (47.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.0 (39.2) |
3.6 (38.5) |
4.0 (39.2) |
5.2 (41.4) |
7.0 (44.6) |
9.0 (48.2) |
10.7 (51.3) |
11.0 (51.8) |
9.6 (49.3) |
7.5 (45.5) |
5.5 (41.9) |
4.3 (39.7) |
6.8 (44.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 1.7 (35.1) |
1.3 (34.3) |
1.7 (35.1) |
3.0 (37.4) |
5.1 (41.2) |
7.1 (44.8) |
9.0 (48.2) |
9.2 (48.6) |
7.6 (45.7) |
5.4 (41.7) |
3.4 (38.1) |
2.1 (35.8) |
4.7 (40.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −8.8 (16.2) |
−11.0 (12.2) |
−9.2 (15.4) |
−9.9 (14.2) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
0.0 (32) |
1.5 (34.7) |
1.5 (34.7) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
−7.2 (19) |
−10.5 (13.1) |
−11.0 (12.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 157.7 (6.209) |
115.2 (4.535) |
131.6 (5.181) |
89.5 (3.524) |
63.3 (2.492) |
57.5 (2.264) |
74.3 (2.925) |
96.0 (3.78) |
119.5 (4.705) |
147.4 (5.803) |
139.3 (5.484) |
135.3 (5.327) |
1,321.3 (52.02) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 22 | 17 | 21 | 16 | 13 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 18 | 22 | 21 | 22 | 210 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 90 | 89 | 89 | 87 | 88 | 88 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 89 | 90 | 89 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 14 | 36 | 71 | 106 | 124 | 125 | 111 | 98 | 80 | 49 | 20 | 6 | 840 |
| Source #1: Danish Meteorological Institute[8] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: NOAA (sun, humidity and precipitation days 1961–1990)[9][10] | |||||||||||||
Sport

Tórshavn, as the capital city, is the centre of sport in the islands; the largest sports centre is located in the Gundadalur district of Tórshavn. Also, the largest football stadium, Tórsvøllur, is located here, seating 6,000 spectators. The stadium serves as home to the Faroe Islands national football team. Around the city there are also two other football pitches, indoor tennis courts, badminton courts and a swimming pool.
The city has several football clubs, including three Premier League teams: HB Tórshavn, B36 Tórshavn and Argja Bóltfelag. Other football clubs with connections to the city are FF Giza (Nólsoy), FC Hoyvík and Undrið FF. Handball is the second most popular sport in Tórshavn. The city's handball teams are Kyndil, Neistin and Ítróttafelagið H71 and the Faroe Island's national handball team practice in the city. Tórshavn city has several popular rowing clubs, including, Havnar Róðrarfelag and Róðrarfelagið Knørrur.[11]
Every year in July the Tour of Faroe Islands, which is a road bicycle race, is held around the islands. The race is called Kring Føroyar (Tour de Faroe / Around the Faroes), it starts in Klaksvík and ends in Tórshavn.[12]
Music
The Tórshavn Jazz Festival has been held annually since 1983. It attracts musicians from all over North America and Europe and has become a popular tourist event.
Transport
The harbour is served by the Smyril Line international ferry service to Denmark and Iceland. The harbour is also used by domestic ferry services of Strandfaraskip Landsins within the Faroe Islands, chiefly on the route to Tvøroyri.
The town is served by Bussleiðin - a network of local buses. Buses also depart to villages throughout the islands.
There is a helipad in Tórshavn; the nearest airport is Vágar Airport.
Sites of interest

- Tinganes, the old part of town, it is still made up of small wooden houses covered with turf roofs. The oldest one dates back 500 years.
- Tórshavn Cathedral, the second oldest church in the country.
- Tórshavn harbour.
- Fort Skansin, a historic site dating back to the sixteenth century
- Listasavn Føroya, the Faroese art museum.
- The main church, Vesturkirkjan, with outside art work by Hans Pauli Olsen.
- The Nordic House in the Faroe Islands, the most important cultural institution in the Faroes.
- The historical museum in Hoyvík, with all its treasures.
- The museum of Natural History, with a small botanical garden with 150 Faroese plants.
- Niels Finsens gøta, Tórshavn's only pedestrianised street.
Institutions in Tórshavn
- Løgtingið and Landstýrið, is the Faroese parliament and government with all its national institutions.
- Kringvarp Føroya (Faroese national television and radio) which is publicly owned.
- University of the Faroe Islands, situated next to the national archives, a navigational college, a teachers college, etc.
- Postverk Føroya is the postal service of the Faroe Islands.
- A number of countries have a Consulate-General in Tórshavn, including all Nordic countries and several EU countries.[13]
- Føroya Studentaskúli og HF-Skeið is the largest and oldest high school in the country. It is located just outside Tórshavn.
Notable natives and inhabitants

- Niels Ryberg Finsen (1860–1904), winner of the Nobel Prize in Medicine and Physiology 1903.
- Daniel Jacob Danielsen (1871–1916), a missionary and humanitarian who helped Roger Casement to expose the horror of Belgian rule in Congo.[14]
- Petur Alberg (1885–1940), composer, most famous for composing the national anthem.
- William Heinesen (1900–1991), writer, poet, composer and painter.
- Jørgen-Frantz Jacobsen (1900–1938), writer.
- Høgni Reistrup (1984), musician, singer and songwriter.
- Ingálvur av Reyni (1920–2005), painter.
- Janus Kamban (1913–2009), sculptor.
- Zacharias Heinesen (1936), painter.
- Lisbeth L. Petersen (1939), politician.
- Katrin Ottarsdóttir (1957), filmmaker.
- Carl Jóhan Jensen (1957), writer.
- Týr, folk metal band.
- Óli Jógvansson (1969), songwriter and composer.
- Bárður Oskarsson (1972), writer and illustrator.
- Guðrið Hansdóttir (1980), singer, songwriter.
- Teitur Lassen (1977), singer, songwriter.
- Bárður Háberg (1979), songwriter and composer.
- Christian Mouritsen (1988), footballer.
- Gunnar Nielsen (1986), footballer.
- Rógvi Baldvinsson (1989), footballer.
- Súni Olsen (1981), footballer.
- Greta Svabo Bech (1987), singer.
- Helgi Dam Ziska (1990), chess player.
- Magnus Jákupsson (1994), swimmer.
Gallery
 Eystaravág
Eystaravág.jpg) City bus on the Norðari Ringvegur
City bus on the Norðari Ringvegur.jpg) View over central Tórshavn
View over central Tórshavn Vestaravág
Vestaravág- Niels Finsens Gøta
.jpg) The British cannon at Skansin
The British cannon at Skansin- Tórshavn cathedral
%2C_Bryggjubakki_street_at_night.jpg) Bryggjubakki street at night
Bryggjubakki street at night The municipal park
The municipal park%2C_Tinganes.jpg) Alleys of Tinganes
Alleys of Tinganes
Twin cities
Tórshavn is twinned with:
 Asker, Norway
Asker, Norway Garðabær, Iceland
Garðabær, Iceland Reykjavík, Iceland[15]
Reykjavík, Iceland[15] Jakobstad, Finland
Jakobstad, Finland Mariehamn, Åland[16]
Mariehamn, Åland[16] Eslöv, Sweden
Eslöv, Sweden Birkerød, Denmark
Birkerød, Denmark Riolunato, Italy
Riolunato, Italy
See also
References
- ↑ "Fólkatalið í Sandoynni veksur aftur". Kringvarp Føroya (in Faroese).
- ↑ "Tórshavn Municipality". Tórshavn Municipality.
- ↑ Gregoriussen, Jákup Pauli (2000). Tórshavn, vár miðstøð og borg II. Tekningar úr Havn (in Faroese). Velbastaður: Forlagið í Støplum. pp. 11–15. ISBN 99918-914-4-7.
- ↑ British 5.5"/50 (14 cm) BL Mark I
- ↑ "Ministry of Health Affairs". The government of the Faroe Islands. Archived from the original on 2015-07-11.
- ↑ "Ministry of Social Affairs". The government of the Faroe Islands.
- ↑ "Ministry of Finance". The government of the Faroe Islands.
- ↑ "Monthly means and extremes 1961–1990 and 1981–2010 for air temperature, atmospheric pressure, hours of bright sunshine and precipitation–Denmark, The Faroe Islands and Greenland" (PDF). Danish Meteorological Institute. pp. 16–19. Retrieved January 18, 2015.
- ↑ "TORSHAVN Climate Normals 1961-1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved November 15, 2012.
- ↑ "Sunshine data for Tórshavn 1961-1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved November 15, 2012.
- ↑ "ISF.fo Faroese confederation of sports and Olympic committee". Ítróttasamband Føroya.
- ↑ "Effo Kring Føroyar (Tour de Faroe)". Tórshavnar súkklufelag (Bycycle club of Tórshavn) (in Faroese).
- ↑
- ↑ Maye, Brian (14 December 2014). "Daniel J Danielsen – a pioneering humanitarian who helped Roger Casement expose the horror of Belgian rule in the Congo". The Irish Times. Retrieved 27 December 2015.
- ↑ "Torshavn.fo, Vina- og samstarvsbýir". Tórshavn Municipality (in Faroese).
- ↑ "Mariehamns stads vänorter". Archived from the original on December 1, 2008.
Other sources
- Havsteen-Mikkelsen, Sven (1995) Føroyinga søga (Bjarni Niclasen, týddi; Jørgen Haugan, skrivaði eftirmæli. Tórshavn: Føroya skúlabókagrunnur)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tórshavn. |
- Tórshavn Municipality website
 Tórshavn travel guide from Wikivoyage
Tórshavn travel guide from Wikivoyage


