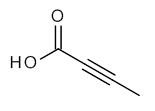
Tetrolic acid
 | |
_crystals.jpg) | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
But-2-ynoic acid | |
| Other names
2-Butynoic acid But-2-ynoic acid Butynoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 84.07 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.9641 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 78 °C (172 °F; 351 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 203 °C (397 °F; 476 K)[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tetrolic acid (2-butynoic acid) is a short-chain unsaturated carboxylic acid, described by the formula CH3-C≡C-CO2H. Salts and esters of tetrolic acid are known as tetrolates.
History
The first reported synthesis[2] of tetrolic acid is believed to be by German chemist Johann Georg Anton Geuther in 1871 as part of his work investigating the derivatives of ethyl acetoacetate.
Production
Tetrolic acid is manufactured[3] on a commercial scale by treatment of propyne with a strong base (to form an acetylide), followed by carbon dioxide:

Strong bases such as n-BuLi[4] and NaNH2[5] can be used.
Properties
Tetrolic acid is highly soluble in polar solvents (water, ethanol) and may be recrystallized from non polar solvents (such as heptane, toluene). The compound is a white crystalline solid which can exist in two polymorphous crystalline forms.[6]
The proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) spectrum in deuterated dimethyl sulfoxide shows a characteristic singlet peak at 1.99 ppm corresponding to the -CH3 protons.
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tetrolic acid. |
- 1 2 3 Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. 3.88. ISBN 1439855110.
- ↑ Geuther, A. (1871). "Ethyldiacetic Acid and some of its Derivatives". J. Chem. Soc. 24: 812–837. doi:10.1039/JS8712400808.
- ↑ Smith, W. (1973) "Preparation of tetrolic acid" U.S. Patent 3,752,848A
- ↑ Hartzoulakis, Basil; Gani, David (1994). "Synthesis of (2S, 3R)- and (2S, 3S)-3-methylglutamic acid". J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1. 1994 (18): 2525–2531. doi:10.1039/P19940002525.
- ↑ Kauer, J. C.; Brown, M. (1962). "Tetrolic Acid (2-Butynoic Acid)". Org. Synth. 42: 97. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.042.0097.; Coll. Vol., 5, p. 1043
- ↑ Flakus, Henryk T.; Hachuła, Barbara (2008). "Effects of "excessive" exciton interactions in polarized IR spectra of the hydrogen bond in 2-butynoic acid crystals: Proton transfer induced by dynamical co-operative interactions involving hydrogen bonds". Chemical Physics. 345 (1): 49–64. doi:10.1016/j.chemphys.2008.01.035.