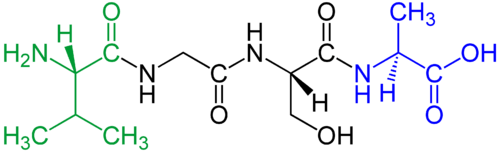
Tetrapeptide
A tetrapeptide is a peptide, classified as an oligopeptide, since it only consists of four amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Many tetrapeptides are pharmacologically active, often showing affinity and specificity for a variety of receptors in protein-protein signaling. Present in nature are both linear and cyclic tetrapeptides, tetrapeptides may be cyclized by a fourth peptide bond or other covalent bonds.
Examples of tetrapeptides are:
- Tuftsin (L-threonyl-L-lysyl-L-prolyl-L-arginine) is a peptide related primarily to the immune system function.
- Rigin (glycyl-L-glutaminyl-L-prolyl-L-arginine) is a tetrapeptide with functions similar to those of tuftsin.
- Postin (Lys-Pro-Pro-Arg) is the N-terminal tetrapeptide of cystatin C and an antagonist of tuftsin.
- Endomorphin-1 (H-Tyr-Pro-Trp-Phe-NH2) and endomorphin-2 (H-Tyr-Pro-Phe-Phe-NH2) are peptide amides with the highest known affinity and specificity for the μ opioid receptor.
- Morphiceptin (H-Tyr-Pro-Phe-Pro-NH2) is a casomorphin peptide isolated from β-casein.
- Gluten exorphines A4 (H-Gly-Tyr-Tyr-Pro-OH) and B4 (H-Tyr-Gly-Gly-Trp-OH) are peptides isolated from gluten.
- Tyrosine-MIF-1 (H-Tyr-Pro-Leu-Gly-NH2) is an endogenous opioid modulator.
- Tetragastrin (N-((phenylmethoxy)carbonyl)-L-tryptophyl-L-methionyl-L-aspartyl-L-phenylalaninamide) is the C-terminal tetrapeptide of gastrin. It is the smallest peptide fragment of gastrin which has the same physiological and pharmacological activity as gastrin.
- Kentsin (H-Thr-Pro-Arg-Lys-OH) is a contraceptive peptide first isolated from female hamsters.
- Achatin-I (glycyl-phenylalanyl-alanyl-aspartic acid) is a neuroexcitatory tetrapeptide from giant African snail (Achatina fulica).
- Tentoxin (cyclo(N-methyl-L-alanyl-L-leucyl-N-methyl-trans-dehydrophenyl-alanyl-glycyl)) is a natural cyclic tetrapeptide produced by phytopathogenic fungi from genus Alternaria.
- Rapastinel (H-Thr-Pro-Pro-Thr-NH2) is a partial agonist of the NMDA receptor.
- HC-toxin, cyclo(D-Pro-L-Ala-D-Ala-L-Aeo), where Aeo is 2-amino-8-oxo-9,10-epoxy decanoic acid, is a virulence factor for the fungus Cochliobolus carbonum on its host, maize.
- Elamipretide, (D-Arg-dimethylTyr-Lys-Phe-NH2) a drug candidate that targets mitochondria.[1][2]
See also
References
- ↑ "Elamipretide". AdisInsight. Retrieved 24 April 2017.
- ↑ Kloner, RA; Shi, J; Dai, W (February 2015). "New therapies for reducing post-myocardial left ventricular remodeling.". Annals of translational medicine. 3 (2): 20. PMC 4322169
 . PMID 25738140.
. PMID 25738140.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.