Television transmitter
A television transmitter is a device which broadcasts an electromagnetic signal to the television receivers. Television transmitters may be analog or digital.
The principals of primarily analog systems are summarized as they are typically more complex than digital transmitters due to the multiplexing of VSB and FM modulation stages.
Types of transmitters
There are many types of transmitters depending on
- The system standard
- Output power
- Back up facility, usually the Modulator, Multiplexer and Power Amplifier
- Stereophonic (or dual sound) facility, for analogue TV systems
- Aural and visual power combining principal, for analogue TV systems
- Active circuit element in the final amplifier stage
The system standard
An international plan by ITU (International Telecommunication Union) on broadcast standards which is usually known as Stockholm plan (1961) defines standards used in broadcasting. In this plan, most important figures for transmitters are radio frequency, frequency separation between aural and visual carriers and band width. [1]
Input stage of a transmitter
The audio (AF) input (or inputs in case of stereophonic broadcasting) is usually a signal with 15 kHz maximum bandwidth and 0 dBm maximum level. Preemphasis time constant is 50 µs. The signal after passing buffer stages is applied to a modulator where it modulates an intermediate frequency carrier (IF). The modulation technique is usually frequency modulation (FM) with a typical maximum deviation of 50 kHz (for 1 kHz. input at 0 dBm level).
The video (VF) input is a composite video signal (video information with sync) of maximum 1 volt on 75 Ω impedance. (1 V limit is for luminance signal. Some operators may accept superimposed color signals slightly over 1 V.) After buffer and 1 V clipping circuits the signal is applied to the modulator where it modulates an intermediate frequency signal (which is different from the one used for aural signal.) The modulator is an amplitude modulator which modulates the IF signal in a manner where 1 V VF corresponds to low level IF and 0 volt VF corresponds to high level IF. AM modulator produces two symmetrical side bands in the modulated signals. Thus IF band width is two times the video band width. (i.e. if the VF bandwidth is 4.2 MHz, the IF bandwidth is 8.4 MHz.) However, the modulator is followed by a special filter known as Vestigal sideband (VSB) filter. This filter is used to suppress a portion of one side band, thus bandwidth is reduced. (Since both side bands contain identical information, this suppression doesn't cause a loss in information.) Although the suppression causes phase delay problems the VSB stage also includes correction circuits to equalise the phase.
Output stages
The modulated signal is applied to a mixer (also known as frequency converter). Another input to the mixer which is usually produced in a crystal oven oscillator is known as subcarrier. The two outputs of the mixer are the sum and difference of two signals. Unwanted signal (usually the sum) is filtered out and the remaining signal is the radio frequency (RF) signal. Then the signal is applied to the amplifier stages. The number of series amplifiers depends on the required output power. The final stage is usually an amplifier consisting of many parallel power transistors. But in older transmitters tetrodes or klystrons are also utilized.
In modern solid-state VHF and UHF transmitters, LDMOS power transistors are the device of choice for the output stage, with the latest products employing 50V LDMOS devices for higher efficiency and power density. Even higher energy efficiency is possible using Envelope Tracking, which in the broadcast industry is often referred to as 'drain modulation'.
Combining aural and visual signals
There are two methods:
- Split sound system: Actually there are two parallel transmitters one for aural and one for visual signal. The two signals are combined at the output via a high power combiner. In addition to a combiner, this system requires separate mixer and amplifiers for aural and visual signals. This is the system used in most high power applications.
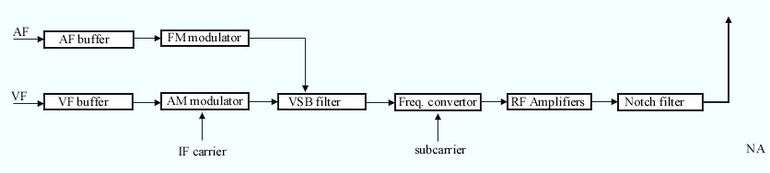
- Intercarrier system : There are two input stages one for AF and one for VF. But the two signals are combined in low power IF circuits (i.e., after modulators) The mixer and the amplifiers are common to both signals and the system needs no high power combiners. So both the price of the transmitter and the power consumption is considerably lower than that of split sound system of the same power level. But two signals passing through amplifiers produce some intermodulation products. So intercarrier system is not suitable for high power applications and even at lower power transmitters a notch filter to reject the cross modulation products must be used at the output.
The output power
The output power of the transmitter is defined as the power during sync pulse. (Real output power is variable depending on the content.) But the output power of the transmitting equipment and the output power of the antenna are two different quantities. The output power of the antenna is known as ERP which is actually the transmitter power times the antenna gain.
See also
- Amplitude modulation
- Broadcast relay station
- Broadcast television systems
- Differential gain
- Differential phase
- Intercarrier method
- Studio/transmitter link (STL)
- Transmitter
- Transmitter/studio link (TSL)
- Transmitter station
- Transposer
References
- ↑ Analogue TV Broadcast Systems by Paul Schlyter
Further reading
- Bernard Grob,Charles E.Herndon: Television and video systems, Glencoe McGraw-Hill
- Reference data for Radio Engineers, Chapter 30, Howard W.Sams Co Inc., Indianapolis,1977, ISBN 0-672-21218-8
- FARWAY IRFC, TV and Radio Transmission , Radio Data System Encoders , Broadcasting Technologies
