Fluvalinate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATCvet code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.233.047 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
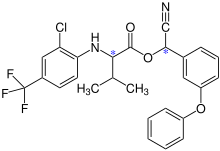
| Formula | C26H22ClF3N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 502.913 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Fluvalinate is a synthetic pyrethroid chemical compound contained as an active agent in the products Apistan, Klartan, and Minadox, that is an acaricide (specifically, a miticide), that is commonly used to control varroa mites in honey bee colonies, infestations that constitute a significant disease of such insects.
Fluvalinate is a stable, non-volatile[1], viscous heavy oil (technical) soluble in organic solvents.[2] Its effectiveness was first demonstrated in France and Israel.
Although the compound may be found in drones, a study has found honey samples virtually absent of fluvalinate, on account of its affinity to beeswax.[3]
Stereoisomerism
Fluvalinate is synthesized from racemic valine [(RS)-valine], the synthesis is not diastereoselective. Thus, fluvinate is a mixture of four stereoisomers, each approx. 25 %.[4]
| Fluvalinate (4 stereoisomers) |
|---|
-Fluvalinat_Structural_Formula_V1.svg.png) (R,R)-configuration |
-Fluvalinat_Structural_Formula_V1.svg.png) (S,S)-configuration |
-Fluvalinat_Structural_Formula_V1.svg.png) (S,R)-configuration |
-Fluvalinat_Structural_Formula_V1.svg.png) (R,S)-configuration |
Tau-fluvalinate (τ-fluvalinate) is the trivial name for (2R)-fluvalinate. The C atom in the valinate structure is in (R)-absolute configuration, while the second chiral atom is a mixture of (R)- and (S)-configurations:[2]
| τ-Fluvalinate (2 diastereomers) |
|---|
-Fluvalinat_Structural_Formula_V1.svg.png) (R,R)-configuration |
-Fluvalinat_Structural_Formula_V1.svg.png) (R,S)-configuration |
See also
References
- ↑ "tau-fluvalinate", Pesticide Properties DataBase, University of Hertfordshire, retrieved June 24, 2017
- 1 2 "Tau-fluvalinate", PubChem. The Open Chemistry Database, National Institutes of Health, retrieved June 24, 2017
- ↑ MAF Biosecurity New Zealand (2001). "A Review of Treatment Options for Control of Varroa Mite in New Zealand [HortResearch Client Report No. 2001/249]" (PDF). Retrieved 28 August 2016.
This report was commissioned by MAF to aid in internal decision making only. This report in no way constitutes MAF's advice to beekeepers and is useful only as background information.
- ↑ David M. Whitacre (2012) (in German), [, p. 125, at Google Books Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology], Springer, p. 125, ISBN 978-1-4614-3280-7, , p. 125, at Google Books
Further reading
- Bessin, Ric (2016). "Varroa Mites Infesting Honey Bee Colonies [Insect & Pest Info, Home & Health Pests, ENTFACT-608, April 2016 revision]". North Lexington, KY: University of Kentucky, Department of Entomology. Retrieved 28 August 2016.
Apistan is a product available that will kill the mites and cause the mites to drop from the bees. … Apistan strips, which contain the miticide fluvalinate, are available from most large beekeeping suppliers and can be used both for detection and treatment of varroa infestations.
External links
- EPA: Tau-fluvalinate; Reregistration Eligibility Decision for Low Risk Pesticide; Notice of Availability
- Tau-fluvalinate in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
- Fluvalinate in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)