Tai–Kadai languages
| Tai–Kadai | |
|---|---|
| Kra–Dai, Daic, Kadai | |
| Geographic distribution |
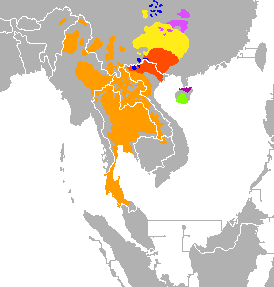
parts of Southern China, Hainan Island, Indochina and Northeast India |
| Linguistic classification | One of the world's primary language families |
| Subdivisions | |
| ISO 639-2 / 5 | tai |
| Glottolog | taik1256[1] |
|
Distribution of the Tai–Kadai language family. | |
The Tai–Kadai languages, also known as Kra–Dai, Daic, and Kadai, are a language family of highly tonal languages found in southern China, northeast India and Southeast Asia. They include Thai and Lao, the national languages of Thailand and Laos respectively. There are nearly 100 million speakers of these languages in the world.[2] Ethnologue lists 95 languages in this family, with 62 of these being in the Tai branch.[3]
The diversity of the Tai–Kadai languages in southern China, especially in Guizhou and Hainan, suggests that this is close to their homeland. The Tai branch moved south into Southeast Asia only about a thousand years ago, founding the nations that later became Thailand and Laos in what had been Austroasiatic territory.
The name "Tai–Kadai" is controversial, and arguments have been made that it should be replaced.[4] The name comes from an obsolete bifurcation of the family into two branches, Tai and Kadai (all else). Yet the name Kadai suggests that it includes Tai, and as such is sometimes used to refer to the entire family.[5] On the other hand, some references restrict the usage of "Kadai" to the Kra branch of the family, for which the name Kra suffices. The replacement name Kra–Dai has been suggested, as Kra and Dai are two large and well-established subgroups that are on different sides of a major historical split.[4] The name Kra–Dai has since been adopted in several major scholarly works on the family.[6][7][8]
Internal classification
Tai–Kadai consists of five well established branches, Hlai, Kra, Kam–Sui, Tai, and the Ong Be language:
- Ong Be (Hainan)
- Kra (southern China, northern Vietnam; called Kadai in Ethnologue)
- Kam–Sui (mainland China)
- Hlai (Hainan)
- Tai (southern China and Southeast Asia)
In 1942, Paul K. Benedict placed three Kra languages (Gelao, Laqua and Lachi) together with Hlai in a group for which he coined the name "Kadai", from ka meaning "person" in Gelao and Laqua, and Dai, a form of a Hlai autonym. He further proposed a genetic grouping of Tai, Kadai and Malayo-Polynesian.[9]
Edmondson and Solnit
An early but influential classification, with the traditional Kam–Tai clade, was Edmondson and Solnit's classification from 1988:[5][10]
| Tai–Kadai |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This classification is used by Ethnologue, though by 2009 Lakkja was made a third branch of Kam–Tai and Biao was moved into Kam–Sui.
Ostapirat
Based on the large amount of vocabulary they share, the Kam–Sui, Be, and Tai branches are often classified together. (See Kam–Tai.) However, Weera Ostapirat believes this is negative evidence, possibly due to lexical replacement in the other branches. He also claims that morphological similarities suggest instead that Kra and Kam–Sui be grouped together as Northern Kra–Dai on the one hand, and Hlai with Tai as Southern Kra–Dai on the other.[11] The position of Ong Be in Ostapirat's proposal is undetermined. Note that Ostapirat prefers to use the name Kra–Dai to Tai–Kadai, which he argues to be obsolete.
| Kra–Dai |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Norquest
Norquest (2007) accepts this distinction, and adds the difficult Lakkja and Ong Be in his classification. However, he states that Lakkja may turn out to be Kam–Sui, and Be may be Tai, specifically one of the Northern Tai languages but divergent due to contact with other languages on Hainan.[6] Following Ostapirat, Norquest adopts the name Kra–Dai for the family as a whole.
| Kra–Dai |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
External relationships
The Tai–Kadai languages were formerly considered to be part of the Sino-Tibetan family, but outside China they are now classified as an independent family. They contain large numbers of words that are similar in Sino-Tibetan languages. However, these are seldom found in all branches of the family, and do not include basic vocabulary, indicating that they are old loan words.[11]
Several Western scholars have presented suggestive evidence that Tai–Kadai is related to or a branch of the Austronesian language family.[12] There are a number of possible cognates in the core vocabulary. Among proponents, there is yet no agreement as to whether they are a sister group to Austronesian in a family called Austro-Tai, a backmigration from Taiwan to the mainland, or a later migration from the Philippines to Hainan during the Austronesian expansion.
The Austric proposal suggests a link between Austronesian and the Austroasiatic languages. Echoing part of Benedict's conception of Austric, who added Tai–Kadai and Hmong–Mien to the proposal, Kosaka (2002) argued specifically for a Miao–Dai family.[13]
In China, they are called Zhuang–Dong languages and are generally considered to be related to Sino-Tibetan languages along with the Miao–Yao languages. It is still a matter of discussion among Chinese scholars whether Kra languages such as Gelao, Qabiao, and Lachi can be included in Zhuang–Dong, since they lack the Sino-Tibetan similarities that are used to include other Zhuang–Dong languages in Sino-Tibetan.
Cognate comparison[14]
| English | Tai | Gelao | Hla |
|---|---|---|---|
| dog | maa A1 | mpau33 | paa4 |
| fire | fai A2 | pai33 | fei1 |
| thick | naa A1 | ntau44 | naa1 |
| cloud | faa B1 | pau44 | faa3 |
| snow | nai A2 (Shan) | ntai44 | N/A |
| frost | miai A1 (Lao) | mplai44 | N/A |
References
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian, eds. (2016). "Tai–Kadai". Glottolog 2.7. Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Diller, Anthony, Jerry Edmondson, Yongxian Luo. (2008). The Tai–Kadai Languages. London [etc.]: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-7007-1457-5
- ↑ Ethnologue Tai–Kadai family tree
- 1 2 Ostapirat, Weera. (2000). "Proto-Kra." Linguistics of the Tibeto-Burman Area 23 (1): 1-251.
- 1 2 Edmondson, Jerold A. and David B. Solnit, editors. 1988. Comparative Kadai: Linguistic studies beyond Tai. Summer Institute of Linguistics and the University of Texas at Arlington Publications in Linguistics, 86. Dallas: Summer Institute of Linguistics and the University of Texas at Arlington. vii, 374 p.
- 1 2 Norquest, Peter K. 2007. A Phonological Reconstruction of Proto-Hlai. Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Anthropology, University of Arizona.
- ↑ Pittayaporn, Pittayawat. 2009. The phonology of Proto-Tai. Ph.D. Thesis, Cornell University
- ↑ Peter Jenks and Pittayawat Pittayaporn. Kra-Dai Languages. Oxford Bibliographies in “Linguistics”, Ed. Mark Aranoff. New York: Oxford University Press.
- ↑ Benedict, Paul K. (1942). "Thai, Kadai, and Indonesian: A New Alignment in Southeastern Asia". American Anthropologist. 44 (4): 576–601. JSTOR 663309. doi:10.1525/aa.1942.44.4.02a00040.
- ↑ Edmondson, Jerold A. and David B. Solnit, editors. 1997. Comparative Kadai: the Tai branch. Summer Institute of Linguistics and the University of Texas at Arlington Publications in Linguistics, 124. Dallas: Summer Institute of Linguistics and the University of Texas at Arlington. vi, 382 p.
- 1 2 Ostapirat, Weera. (2005). "Kra–Dai and Austronesian: Notes on phonological correspondences and vocabulary distribution", pp. 107–131 in Sagart, Laurent, Blench, Roger & Sanchez-Mazas, Alicia (eds.), The Peopling of East Asia: Putting Together Archaeology, Linguistics and Genetics. London/New York: Routledge-Curzon.
- ↑ Sagart, Laurent. 2004. The higher phylogeny of Austronesian and the position of Tai–Kadai. Oceanic Linguistics 43. 411–440
- ↑ Kosaka, Ryuichi. 2002. "On the affiliation of Miao-Yao and Kadai: Can we posit the Miao-Dai family." Mon-Khmer Studies 32:71-100.
- ↑ Ostapirat, W. E. E. R. A. Kadai dummy*-m.
- Edmondson, J.A. and D.B. Solnit eds. 1997. Comparative Kadai: the Tai branch. Dallas: Summer Institute of Linguistics and the University of Texas at Arlington. ISBN 0-88312-066-6
- Blench, Roger. 2004. Stratification in the peopling of China: how far does the linguistic evidence match genetics and archaeology? Paper for the Symposium "Human migrations in continental East Asia and Taiwan: genetic, linguistic and archaeological evidence". Geneva June 10–13, 2004. Université de Genève.
Further reading
- Diller, A., J. Edmondson, & Yongxian Luo, ed., (2005). The Tai–Kadai languages. London [etc.]: Routledge. ISBN 0-7007-1457-X
- Edmondson, J. A. (1986). Kam tone splits and the variation of breathiness.
- Edmondson, J. A., & Solnit, D. B. (1988). Comparative Kadai: linguistic studies beyond Tai. Summer Institute of Linguistics publications in linguistics, no. 86. [Arlington, Tex.]: Summer Institute of Linguistics. ISBN 0-88312-066-6
- Ostapirat, Weera. (2000). "Proto-Kra." Linguistics of the Tibeto-Burman Area 23 (1): 1-251.
- Somsonge Burusphat, & Sinnott, M. (1998). Kam–Tai oral literatures: collaborative research project between. Salaya Nakhon Pathom, Thailand: Institute of Language and Culture for Rural Development, Mahidol University. ISBN 974-661-450-9
- Tai–Kadai Languages. (2007). Curzon Pr. ISBN 978-0-7007-1457-5
- Mann, Noel, Wendy Smith and Eva Ujlakyova. 2009. Linguistic clusters of Mainland Southeast Asia: an overview of the language families. Chiang Mai: Payap University.
External links
- Word lists of Tai–Kadai languages from the Austronesian Basic Vocabulary Database
- StarLing: Tai–Kadai 100-word lists and etymology
- Comparative Tai–Kadai Swadesh vocabulary lists (from Wiktionary's Swadesh list appendix)