System anatomy
A system anatomy is simple visual description of a system, focusing on the dependencies between system capabilities. The system anatomy was first used in a project at Ericsson, and Jack Järkvik, is considered the inventor of the concept. After that, the system anatomy and the similar project anatomy (also integration anatomies) have been used widely in different Ericsson projects and now they are being spread to other major companies with complex system development as well.
Anatomies can be said to be a human centric way of describing a system, since they are used as a means to obtain a common view of the system under development.
The anatomies are especially useful in development of large complex systems in incremental and integration driven development, and as a means to coordinate agile development teams.
Advantages and limitations
The system anatomy, unlike its siblings (project anatomy, integration anatomy), is actually just another view of the system, different from product structures, UML-models and flow charts. By focusing on the system’s capabilities – both internal and money making ones – and the dependencies between those, the development team gets a common picture of the system to be developed, that is easier to grasp than many other models. One of the key features of the system anatomy is its simplicity. That, of course, means that the anatomy cannot replace other models or design tools. It is only another way of describing the design, in SW tools, on paper or in the heads of the system engineers. The system anatomy can be used as a starting point when creating an integration anatomy (aka project anatomy) that has more use as a project management tool.
Example
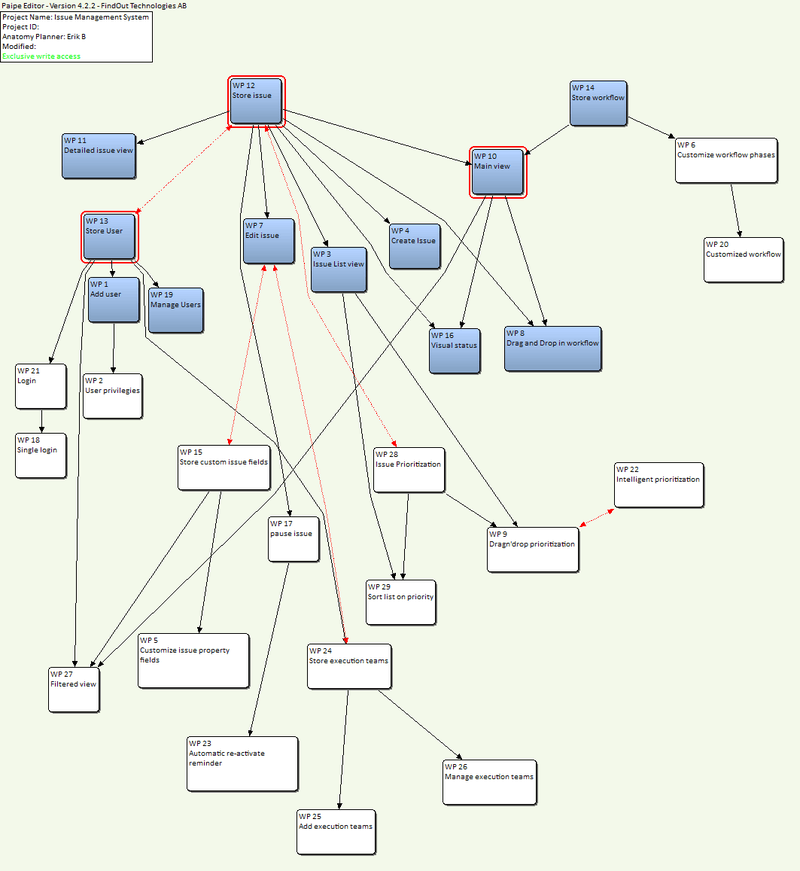
The following example is a simplified example of a system anatomy for an issue management system.
This anatomy is drawn with the most basic capabilities at the top. The notation is that the capability at the end of the arrow is a dependant of the capability at the beginning. In this example the anatomy also shows development progress (blue boxes).
See also
Further reading
- Taxén L et al., The System Anatomy: Enabling Agile Project Management, Studentlitteratur, ISBN 978-91-44-07074-2
- Adler, N. (1999). Managing Complex Product Development – Three approaches. EFI, Stockholm School of Economics. ISBN 91-7258-524-2
- Berggren, C., Järkvik, J., & Söderlund, J. (2008). Lagomizing, organic integration, and systems emergency wards: Innovative practices in managing complex systems development projects. Project Management Journal, Supplement, 39, 111–122
- Lilliesköld, J., Taxén, L., Karlsson, M., & Klasson, M. (2005). Managing complex development projects – using the system anatomy. In Proceedings Portland International Conference on Management of Technology and Engineering, PICMET ’05, July 31 – Aug 4th, 2005, Portland, Oregon – USA.
- Taxén L, Lilliesköld J (2005) Manifesting Shared Affordances in System Development – the System Anatomy, ALOIS*2005, The 3rd International Conference on Action in Language, Organisations and Information Systems, 15–16 March 2005, Limerick, Ireland, pp. 28–47. Retrieved from http://www.alois2005.ul.ie/ (Feb 2006).
- Järkvik, J., Berggren, C., & Söderlund, J. (2007). Innovation in project management: A neo-realistic approach to time-critical complex systems development. IRNOP VIII Conference, Brighton, UK, September 19–21, 2007
- Jönsson, P. (2006). The Anatomy-An Instrument for Managing Software Evolution and Evolvability. Second International IEEE Workshop on Software Evolvability (SE'06) (pp. 31–37). Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA. September 24, 2006.
- Taxén, L., & Lilliesköld, J. (2008). Images as action instruments in complex projects, International Journal of Project Management, 26(5), 527–536
- Taxén, L., & Petterson, U. (2010). Agile and Incremental Development of Large Systems. In The 7th European Systems Engineering Conference, EuSEC 2010. Stockholm, Sweden, May 23–26, 2010
- Söderlund, J. (2002). Managing complex development projects: arenas, knowledge processes and time. R&D Management, 32(5), 419–430.