Dropped ceiling

A dropped ceiling is a secondary ceiling, hung below the main (structural) ceiling. It may also be referred to as a drop ceiling, T-bar ceiling, false ceiling, suspended ceiling, grid ceiling, drop in ceiling, drop out ceiling, or ceiling tiles and is a staple of modern construction and architecture in both residential and commercial applications.
History
Dropped ceilings and ceiling tiles were being used in Japan for aesthetic reasons as early as the Muromachi Period (1337 to 1573).[1] Blackfriars Theater in London, England, built in 1596, had dropped ceilings to aid acoustics.[2]
U. S. Patent No. 1,470,728 for modern dropped ceilings was applied for by E. E. Hall on May 28, 1919 and granted on October 16, 1923.[3] Initially modern dropped ceilings were built using interlocking tiles and the only way to provide access for repair or inspection of the area above the tiles was by starting at the edge of the ceiling, or at a designated "key tile", and then removing contiguous tiles one at a time until the desired place of access was reached. Once the repair or inspection was completed, the tiles had to be reinstalled. This process could be very time-consuming and expensive. On September 8, 1958 Donald A. Brown of Westlake, Ohio filed for a patent for Accessible Suspended Ceiling Construction. This invention provided suspended ceiling construction in which access may readily be obtained at any desired location. Patent Number US 2,984,946 A was granted on May 23, 1961.[4] Brown has sometimes been credited as being the inventor of the dropped ceiling [5] even though other patents preceded his as shown in the table below.
| U. S. Dropped Ceiling Patents to September 8, 1958 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date Filed | Patent No. | Applicant | Title | Comments |
| 05/28/1919 | 1,470,728 | Hall | Suspended Ceiling | |
| 09/03/1931 | 1,931,574 | Danielson | Suspended Ceiling Hanger | |
| 10/24/1950 | 2,710,679 | Bibb, Remmen, Bibb | Suspended Ceiling Construction | First fully developed grid system concept |
| 12/13/1955 | 2,816,623 | Wong | Modular Ceiling | First integration of tiles and grid. Wong founded Cepco Manufacturing, a company now absorbed into Ceilume, a division of Empire West, Inc. |
| 05/11/1956 | 2,896,752 | Wilde | Suspended Ceiling Grid Construction | |
| 07/31/1956 | 2,894,291 | Sorenson | Suspended Ceiling System | |
| 10/25/1956 | 2,895,180 | Byssing | Suspended Ceiling | |
| 02/07/1958 | 2,963,251 | Fuss | Supporting Electric Lighting Fixture from Suspended Ceiling Framework | |
| 09/08/1958 | 2,984,946 | Brown | Accessible Suspended Ceiling | |
(To search for U.S. patent images, go to https://www.google.com/?tbm=pts and enter the patent number in the search box.)
Design objectives
Effective building design requires balancing multiple objectives: aesthetics, acoustics, environmental factors, and integration with the building's infrastructure—not to mention cost of construction as well as long-term operation costs.[6]
Aesthetics
Modern dropped ceilings were initially created to hide the building infrastructure, including piping, wiring, and/or ductwork,[3] by creating a plenum space above the dropped ceiling, while allowing access for repairs and inspections. Drop ceilings may also be used to hide problems, such as structural damage. Further, drop out ceilings can also conceal the sprinkler systems while still providing full fire suppression functionality.
For many years, dropped ceilings were made of basic white tiles, but modern innovations now offer a plethora of options in sizes, colors, materials (including retro designs and faux leather, wood, or metal), visual effects and shapes, patterns, and textures as well as support systems and ways to access the plenum.[7] Custom runs of specialty ceiling tiles can be done at relatively low cost compared with the past.
Acoustics
Acoustic balance and control was another early objective of dropped ceilings.[8] A noisy room can overstimulate occupants, while a too quiet interior may seem dull and uninviting.
The acoustic performance of suspended ceilings has improved dramatically over the years, with enhanced sound absorption and attenuation. This is sometimes achieved by adding insulation known as Sound Attenuation Batts (SABs), more commonly referred to as "sound batts", above the panels to help deaden sounds and keep adjacent rooms quieter.[9]
Environmental factors
Indoor environmental quality
Indoor environmental quality includes ventilation, VOC emissions, lighting and thermal system control, thermal comfort, use of daylight for natural illumination, acoustics, and optimization of outdoor view availability.
Sustainability
Many manufacturers of modern dropped ceilings include sustainability as an objective. Sustainable features may include:
- Energy efficiency, including daylight efficacy and thermal insulating qualities. This uses the ceiling plane to reflect daylight as well as electrical illumination to maximize lumen efficacy, which also improves the comfort and usability of interior spaces. A common measure of the light reflectance of a ceiling material is ASTM E 1477 for Light Reflectance (LR-1). A level of about 75% is considered good, although higher levels are possible.[7]
- Reduced resources needed for construction of the tiles
- Recyclable/reused/renewable materials
Integration with infrastructure
Integration with mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) is important with dropped ceilings, since most of these systems are by definition above the ceiling. Fortunately, most ceiling system products are now designed with this integration in mind. Decisions here can also affect aesthetics as well as access and maintenance.[6]
Cost
Dropped ceilings may have an improved return on investment (ROI) over open ceilings[10]
Suspension grids
A typical dropped ceiling consists of a grid-work of metal channels in the shape of an upside-down "T", suspended on wires from the overhead structure. These channels snap together in a regularly spaced pattern of cells. Each cell is then filled with lightweight ceiling tiles or "panels" which simply drop into the grid. The primary grid types are "Standard 1" (15/16 face), Slimline (9/16" grid), and concealed grid.
In the United States the cell size in the suspension grids is typically either 2 ft × 2 ft or 2 ft × 4 ft and the ceiling tiles are the same size. In Europe the cell size in the suspension grids is 600×600 mm, while the ceiling tiles are slightly smaller at 595mm x 595mm or 595mm x 1195mm.
Concealed grid
An older, less common type of dropped ceiling is the concealed grid system. This type of dropped ceiling employs a method of interlocking panels into each other and the grid with the use of small strips of metal called 'splines', thus making it difficult to remove panels to gain access above the ceiling without damaging the installation or the panels. Normally, these type of ceilings will have a "key panel" (usually in the corner) which can be removed, allowing for the other panels to be slid out of the grid (a series of metal channels called 'z bars') one by one, until eventually removing the desired panel. This type of ceiling is more commonly found in older installations or installations where access to above the ceiling is generally considered unnecessary.
This system has some major disadvantages compared to the more common "drop panel" system, most notably the difficulty in removing and reattaching panels from the grid, which in some cases can cause irreparable damage to the panels removed. Finding replacement panels for this type of dropped ceiling is becoming increasingly more difficult as demand for them is slowing, as is production of the parts. Small clips are still available which allow tiles to be inserted into gaps in the ceiling where a tile is missing, they work by being placed on the edge of a concealed tile, then being slid along as the tile is placed to 'lock' it in place.
Stretch Ceiling

With similar advantages to a dropped ceiling, a stretch ceiling is often used to conceal pipework, wires or the existing ceiling. On top of this there is usually a broad choice of colour or texture and the membrane can be manipulated into a variety of shapes.[11]

A stretch ceiling is a suspended ceiling system and it is made of three main components
- Perimeter Track - Aluminium or Plastic PVC.
- Membrane - Typically a PVC or Nylon material, lightweight sheets are made to size/shape from roll material. Can be printed or painted to achieve the desired effect.
- Harpoon or Catch - This is ultrasonically welded to the edge of the membrane or sheet in the factory, the edging slots into the perimeter track to keep the ceiling in place.
When installing a stretch ceiling, semi-concealed plastic/aluminum track, the preferred choice for most architects and designers, is cut to size and fixed to the perimeter of the ceiling area. The membrane is stretched and the harpoon or catch edge is clipped into the track.[12] Stretching is aided by heating up the membrane or sheet prior to fitting.
Drop out ceilings
Approved Drop out (or drop-out) ceilings allow the installation of a dropped ceiling beneath existing fire sprinklers because the tiles, sometimes called melt-out ceiling tiles, are heat sensitive and designed to fall from the dropped ceiling suspension grid in the event of a fire, allowing the sprinklers to do their job.[13]
Drop out ceiling tiles can add to the aesthetic appeal of a ceiling since the fire sprinklers are hidden by the tiles. Commonly made from vinyl or expanded polystyrene, drop out ceiling tiles are available in multiple sizes and finishes from a variety of manufacturers.
Installation is subject to the local Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ) and, in the U. S., must meet the standards listed in the section below at a minimum.
Drop out ceiling standards (U.S.)
The standards listed below are in addition to those for ceiling tiles in general. No clips, fasteners, or impediments of any kind can be used to limit the ceiling tile's ability to drop from the suspension system without restraint in the event of a fire unless these have been used in the testing process. Painting can void an approval. Note that additional local requirements may exist.
- FM Global - Approval Standards for Plastic Suspended Ceilings[14]
- UL - Ceiling Panels for Use Beneath Sprinklers[15]
- ICC-ES - AC-12 Section 4.4 - Foam Plastic Drop-Out Ceiling Panels and Tiles[16]
- NFPA 13 - Standard for the Installation of Sprinkler Systems[17]
Safety issues
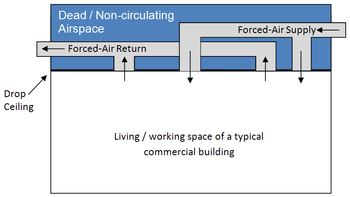

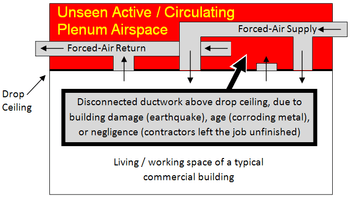
In older buildings the space above the dropped ceiling was often used as a plenum space for ventilation systems, requiring only enclosed ducts that deliver fresh air into the room below, with return air entering the ceiling space through open grilles across the ceiling. This practice is now used less frequently in new construction.
In the event that the dropped ceiling is used as a plenum, low-voltage cables and wiring not installed inside conduit need to use a special low-smoke and low-toxicity wire insulation which will tend to char and stop burning on its own. This helps to protect building occupants so that they are not poisoned with toxic chemicals sucked through the ventilation system in the event of a fire, and helps to prevent fires from spreading inside the hidden plenum space. This special low-smoke cable is typically referred to as plenum cable or Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH or LS0H) cable. While twisted pair cable for networking and telephone service is the most common form of plenum cable, coaxial cable also needs to be plenum-rated for safety.
High-voltage electrical equipment (generally regarded as being over 50 volts) is not permitted to be exposed in the plenum space above a drop ceiling. High voltage wiring must be enclosed in conduit or raceways, and must be physically isolated from low-voltage wiring. High voltage electrical devices similarly must be enclosed in a plenum space, inside a metallic container. Similarly, electrical outlets for domestic powered devices are not permitted inside the plenum space, though outlets can be installed on ceiling tiles inside electrical boxes, with the sockets exposed on the exterior bottom face of the drop ceiling. The purpose of these restrictions is to limit flame spread inside the unseen plenum space, in the event of high voltage equipment or wiring failure. Low voltage cabling is permitted because current flow is typically negligible so the risk of overheating and fire is limited.
In earthquake prone areas (e.g., California) diagonal wire stays are often required by building codes in order to ensure the ceiling grid won't sway laterally during an earthquake, which can lead to partial or total collapse of the ceiling grid on the occupants below during a severe tremor. Compression posts may also be added to keep the ceiling from bouncing vertically during an earthquake.
Lighting fixtures and other devices installed in a dropped ceiling are required to be firmly secured to the dropped ceiling framework. In the event of a fire above a dropped ceiling it is often necessary for firemen to have to pull down the ceiling in a hurry to quickly gain access to the conflagration. Loose fixtures merely resting in the framework by force of gravity can become unseated and swing down on their armorflex power cables to hit the firemen below. Binding the fixtures to the framework assures that if the framework must be pulled down the fixture will come down with it and not become a pendulous swinging hazard to the firemen.
Advantages
Fire safety
To address fire safety, ceiling tiles made from mineral fibres, plastic, tin, composite, or fire-rated wood panels can be used within the construction to meet acceptable standards/ratings. Some tiles, in specific situations, can provide the needed additional resistance to meet the "time rating" required for various fire code, city ordinance, commercial, or other similar building construction regulations. Fire ratings for ceiling panels vary based on the materials used, the preparation of each panel, and the safety testing and third party evaluation done to determine where and how they can be safely installed. In the UK it can be required for the tiles from certain manufacturers to be clipped into the grid with special ceiling clips in order to provide a fire rating; there are special tiles designed for the underside of mezzanine floors however that can give a fire rating without being clipped.
Drop out ceilings have a further advantage in that they can be mounted underneath fire sprinklers, thus hiding the sprinklers for a more attractive appearance. When installed underneath fire sprinklers, certain requirements for materials, applications, installation, and maintenance of drop out ceilings must be met in order to comply with fire safety regulations.[18] (The white paper Drop-out Ceiling Panels–A Discussion on Their Use With Fire Sprinklers, referenced by the article, is available here)
Ease of modification
Another advantage of a dropped ceiling is that the easily removed ceiling panels offer instant access to the plenum, greatly simplifying repairs or alterations.
Wiring and piping installed behind traditional plaster or wallboard ceilings is extremely difficult to modify once the finished ceiling is in place. Wires must either be fished through hollow spaces in the walls behind the finished ceiling, or the ceiling must be demolished in order for wiring or piping changes to be made.
In contrast, the tiles and other parts of a dropped or stretch ceiling are easily removed to allow access to the area above the grid to do any necessary wiring or plumbing modifications. In the event of remodelling, nearly all components of the grid can be dismantled and reassembled somewhere else.
In office buildings, the drop ceiling is often used in conjunction with hollow steel studs to construct small office spaces out of a much larger cavernous space. Wiring and other services are run through the open ceiling, down through the hollow stud walls, and to outlets in the work areas. If business needs change, the office spaces are easily dismantled and the overall cavernous space reconfigured with a different floor plan.
In older buildings that have seen multiple renovations over time, it is not uncommon for a dropped ceiling to have been installed in one renovation and then subsequently removed in another, its installation having been an inexpensive fix to prolong the time between major renovations.
Disadvantages
One disadvantage with this ceiling system is reduced headroom. Clearance is required between the grid and any pipes or ductwork above to install the ceiling tiles and light fixtures. In general, a minimum clearance of 100 to 200 millimetres (4 to 8 in) is often needed between the lowest obstruction and the level of the ceiling grid. A direct-mount grid may work for those who want the convenience of a dropped ceiling, but have limited headroom. Stretch ceiling supports require less than one inch of vertical space, and no space is required for tiles to be lifted out with a stretch ceiling, but a greater clearance space may be chosen to allow room for MEC or for aesthetic reasons.
Dropped ceilings generally conceal many of the functional and structural elements of a building, creating an aesthetic paradigm that discourages the use of functional building systems as aesthetic design elements. Concealing these elements makes the complexity of today's advanced building technologies more difficult to appreciate. It is also more difficult to perform maintenance on or diagnose problems with the concealed systems.
As a renovation tool, dropped ceilings are a quick and inexpensive way to repair a ceiling or reduce HVAC costs. Some materials may show their age quickly— for example, mineral fiber sags, is damaged easily when handled, and stains easily, but stretch ceiling, tin and vinyl do not have these characteristics.
See also
Further reading
- Drop‐Out Ceiling Panels – A Discussion on Their Use with Fire Sprinklers by Gary G. Piermattei of Rolf Jensen & Associates, Inc., 2014
- Thermoformed Ceiling Panels and Tiles: Drop-out Ceiling Panels Installed Beneath Fire Sprinklers, The Construction Specifier Magazine, 2014 (especially the Maintenance section)
- Specifying Drop-Out Ceilings beneath Fire Sprinklers by Ed Davis and Michael Chusid, Consulting-Specifying Engineer Magazine, 2016
- Safety, Code Issues of Drop-Out Ceilings by Ed Davis and Michael Chusid, Consulting-Specifying Engineer Magazine, 2016
References
- ↑ Interview with Matthew Welch, Curator of Japanese and Korean Art, Minneapolis Institute of Arts, retrieved January 12, 2014
- ↑ The Acoustic World of Early Modern England by Bruce R. Smith, page 216, retrieved January 14, 2014
- 1 2 Suspended Ceiling Patent, retrieved January 14, 2014
- ↑ Patent US 2,984,946 A - Accessible Suspended Ceiling Construction, retrieved January 12, 2014
- ↑ "Don Brown remembered as a man with lots of ideas". The Morning Journal. 2010-01-19. Retrieved January 14, 2014.
- 1 2 New Trends in Ceiling Designs and Materials, retrieved January 15, 2014
- 1 2 Ceiling Technology and Aesthetics, retrieved January 15, 2014
- ↑ Suspended Ceiling Construction, retrieved January 15, 2014
- ↑ Let us Talk about Dropped Ceilings, retrieved January 15, 2014
- ↑ Life Cycle Analysis: Wall-to-Wall Ceilings and the Open Plenum--Energy Savings and Other Benefits of Suspended Ceilings vs. Open Plenum, retrieved January 15, 2014
- ↑ "HOME DZINE Home Improvement - What is a stretch ceiling?". home-dzine.co.za.
- ↑ "Stretch Ceilings Technical Downloads". stretchceilings.co.uk.
- ↑ "Drop‐Out Ceiling Panels – A Discussion on Their Use with Fire Sprinklers" by Gary G. Piermattei of Rolf Jensen & Associates, Inc., retrieved December 29, 2016
- ↑ FM Global. "Approval Standard for Plastic Suspended Ceiling Panels" (PDF). FM Global., retrieved January 15, 2014
- ↑ Underwriter's Laboratory. "Ceiling Panels for Use Beneath Sprinklers"., retrieved January 15, 2014
- ↑ ICC-ES (2012). AC12 Foam Plastic Insulation. ICC. p. 5., retrieved January 15, 2014
- ↑ NFPA 13: Standard for the Installation of Sprinkler Systems, retrieved January 15, 2014
- ↑ The Construction Specifier. "Thermoformed Ceiling Panels and Tiles: Drop-out Ceiling Panels Installed Beneath Fire Sprinklers". Retrieved November 14, 2014.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dropped ceilings. |