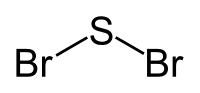
Sulfur dibromide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
bromo thiohypobromite | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Br2S | |
| Molar mass | 191.873 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | gas |
| Structure | |
| C2v | |
| Bent | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | ICSC 1661 |
| EU classification (DSD) (outdated) |
Corrosive (C) Irritant (Xi) Dangerous for the environment (N) |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R14, R34, R37, R50 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | (S1/2), S26, S45, S61 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related |
Disulfur dibromide Thionyl bromide Sulfuryl bromide |
| Related compounds |
Sulfur difluoride Sulfur tetrafluoride Sulfur hexafluoride Sulfur diiodide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Sulfur dibromide is the chemical compound with the formula Br2S. It is a toxic gas.
Sulfur dibromide readily decomposes into S2Br2 and elemental bromine. In analogy to sulfur dichloride, it hydrolyzes in water to give hydrogen bromide, sulfur dioxide and elemental sulfur.
SBr2 can be prepared by reacting SCl2 with HBr, but due to its rapid decomposition it cannot be isolated at standard conditions. Instead the more stable S2Br2 is obtained.[1]
References
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.