Steroid ester
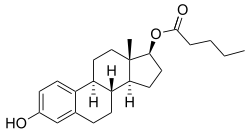
Estradiol valerate, an ester of estradiol and one of the most widely used estrogen esters. It has increased oral bioavailability and a longer duration with intramuscular injection relative to estradiol.
A steroid ester is an ester of a steroid.[1][2] They include androgen esters, estrogen esters, progestogen esters, and corticosteroid esters.[1] Steroid esters may be naturally occurring/endogenous like DHEA sulfate or synthetic like estradiol valerate.[1][2] Esterification is useful because it is often able to render the parent steroid into a prodrug of itself with altered chemical properties such as improved metabolic stability, water solubility, and/or lipophilicity.[2] This, in turn, can enhance pharmacokinetics, for instance by improving the steroid's bioavailability and/or conferring depot activity and hence an extended duration with intramuscular or subcutaneous injection.[1][3]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 Vermeulen A (1975). "Longacting steroid preparations". Acta Clin Belg. 30 (1): 48–55. PMID 1231448.
- 1 2 3 Valentino Stella; Ronald Borchardt; Michael Hageman; Reza Oliyai, Hans Maag, Jefferson Tilley (12 March 2007). Prodrugs: Challenges and Rewards. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 220–. ISBN 978-0-387-49782-2. CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
- ↑ William N. Taylor, M.D. (16 January 2002). Anabolic Steroids and the Athlete, 2d ed. McFarland. pp. 39–. ISBN 978-0-7864-1128-3.
Further reading
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.